Tea’s rise in popularity in Britain coincided with a flowering of intellectual and creative thought that we call the Enlightenment.
By the middle of the 18th century, tea had replaced ale & gin as the people’s favorite beverage.
Is tea a magical elixir?
You decide as we look at 10 fascinating facts about the history of tea in Britain.
1. Tea was first offered in London coffeehouses in 1657
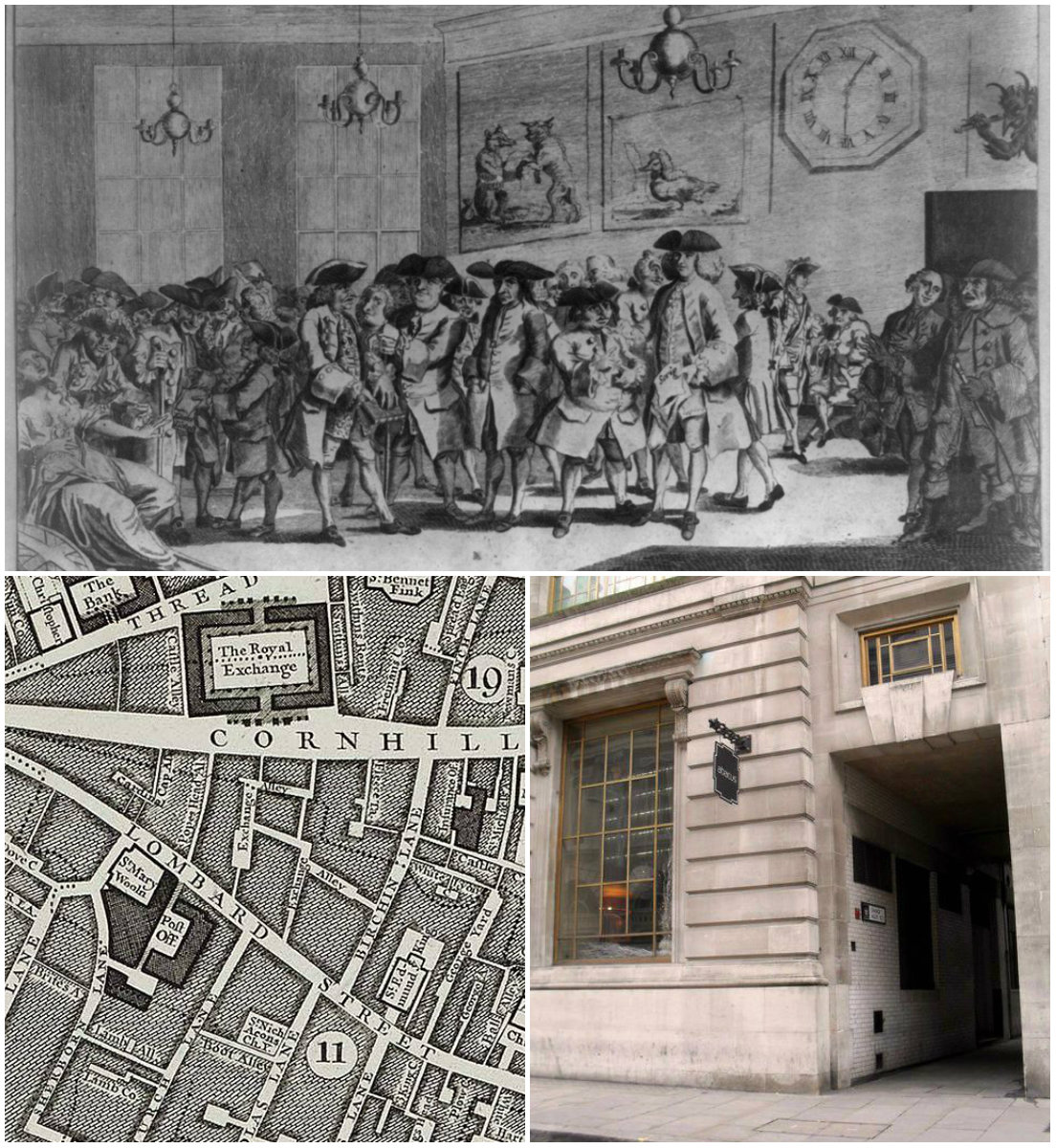


Chinese green tea was first introduced into the London coffeehouse scene in around 1657.
It was down these narrow alleys that the mercantile class of London would meet to discuss business in coffeehouses.
Opposite the Royal Exchange on Cornhill, there is an entrance to a network of alleyways called Change Alley (formerly known as Exchange Alley).
Nestled beside makers of fine wands, there was something else magical for sale: tea.

The owner of one establishment created a pamphlet and advertisement to explain the new beverage as an early form of health drink:
“That Excellent, and by all Physicians approved, China drink, called by the Chinese, Tcha, by other nations Tay alias Tee, …sold at the Sultaness-head, ye Cophee-house in Sweetings-Rents, by the Royal Exchange, London.”
How did the introduction of tea impact the city of London? It became the most powerful city in the world for 200 years.
Today, London vies with New York as the world’s most influential city.
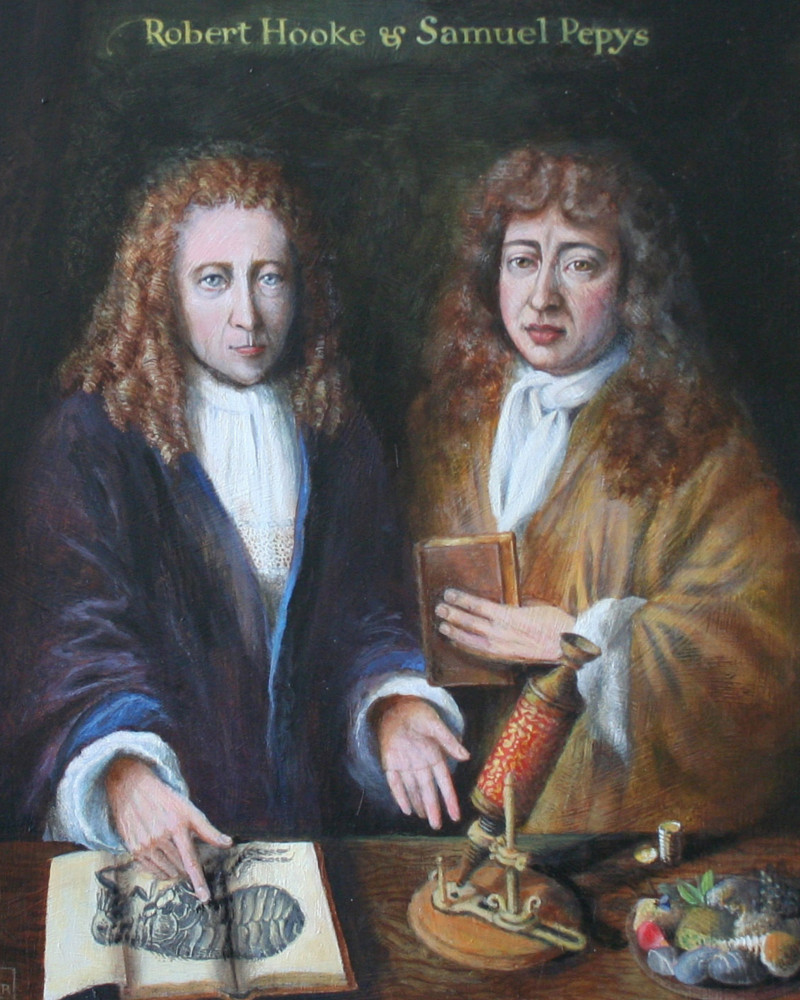
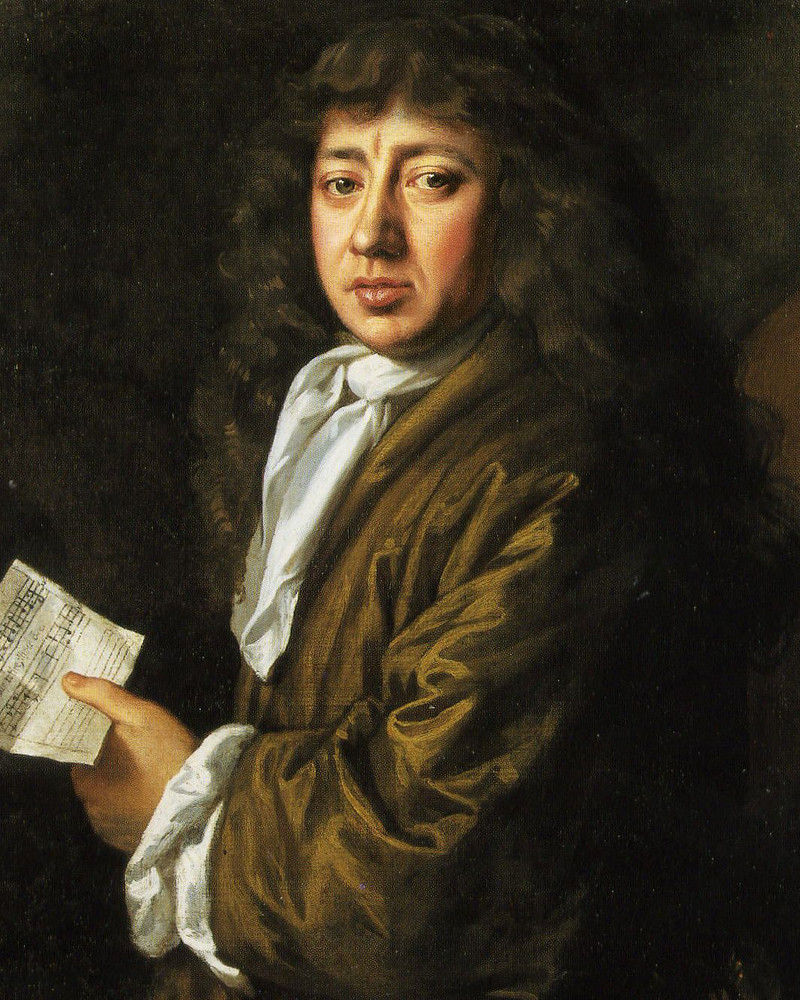
2. Samuel Pepys wrote about drinking tea in 1660
“I did send for a cup of tee, (a China drink) of which I had never had drunk before.”
Samuel Pepys (1633 – 1703) was an English Member of Parliament and naval administrator who is famous for keeping a detailed diary for a decade as a young man.
Trivia: his work as Chief Secretary to the Admiralty would help position Britain’s Royal Navy as the world’s most powerful in years to come.
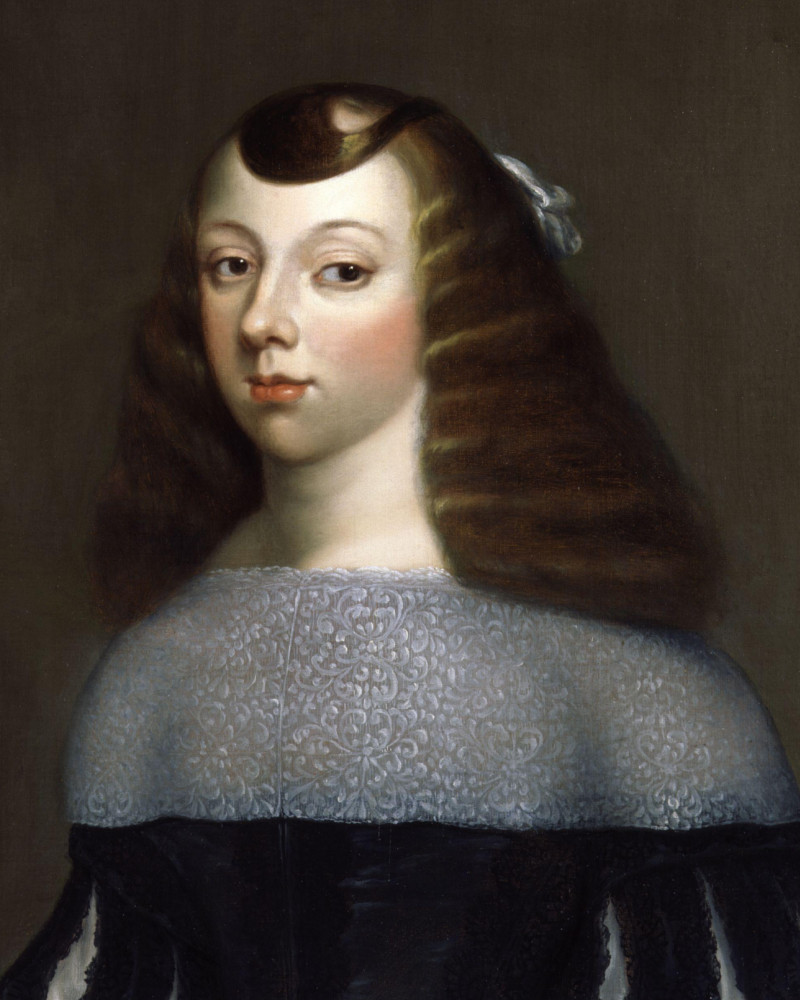
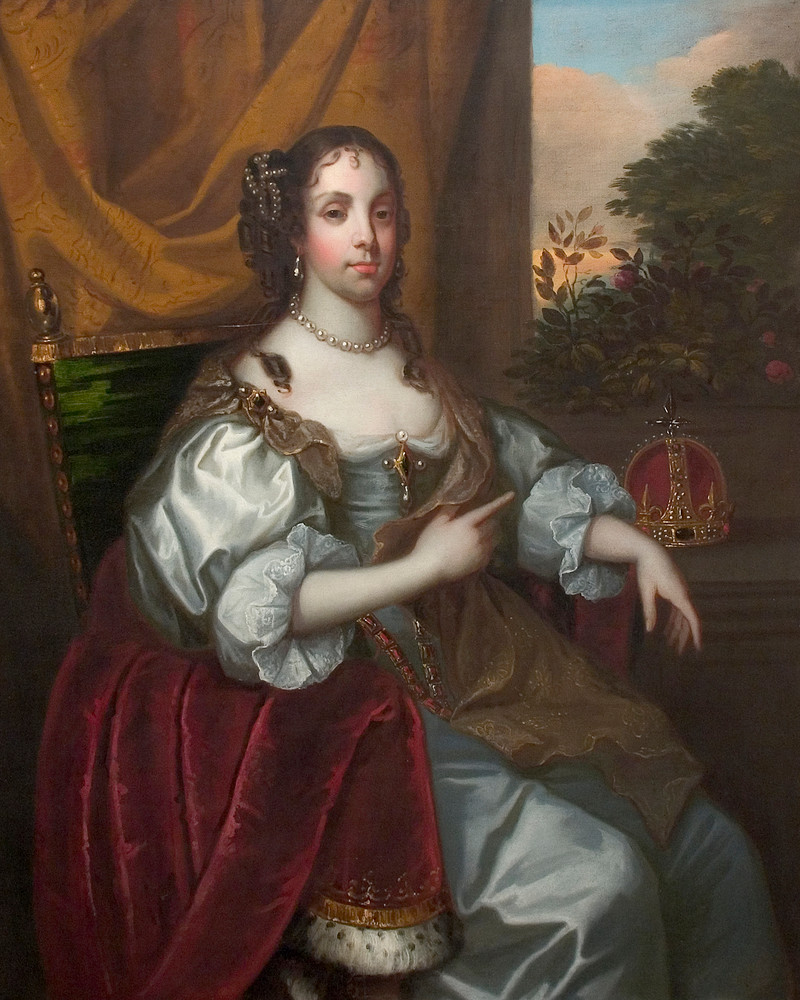
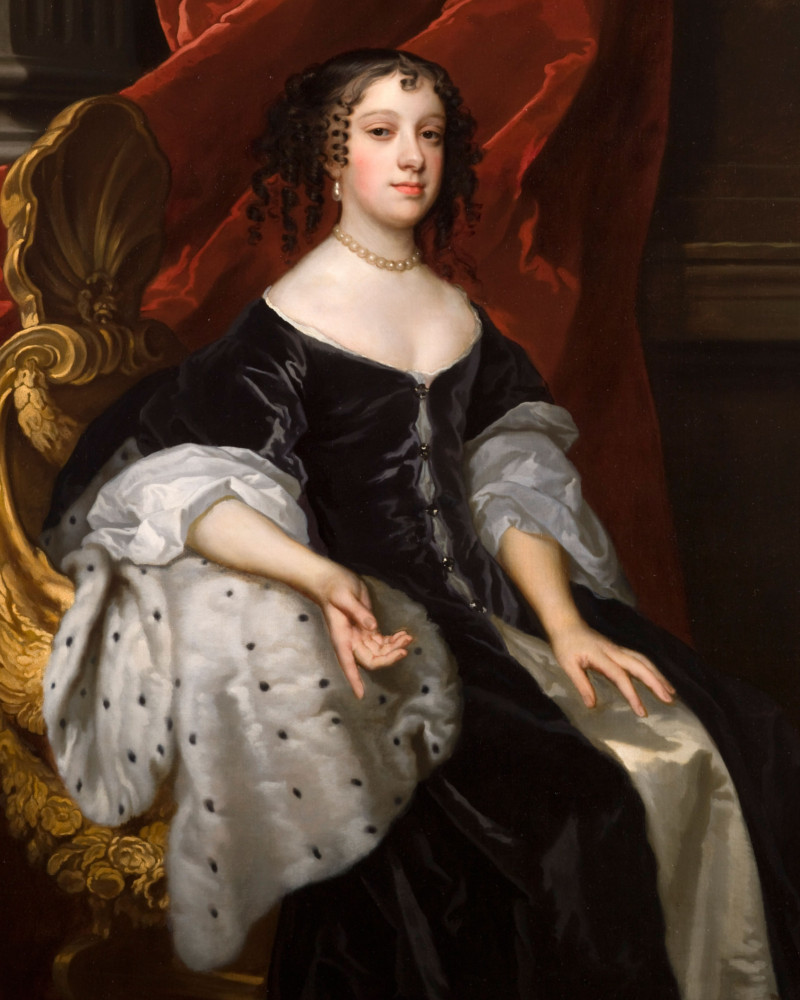
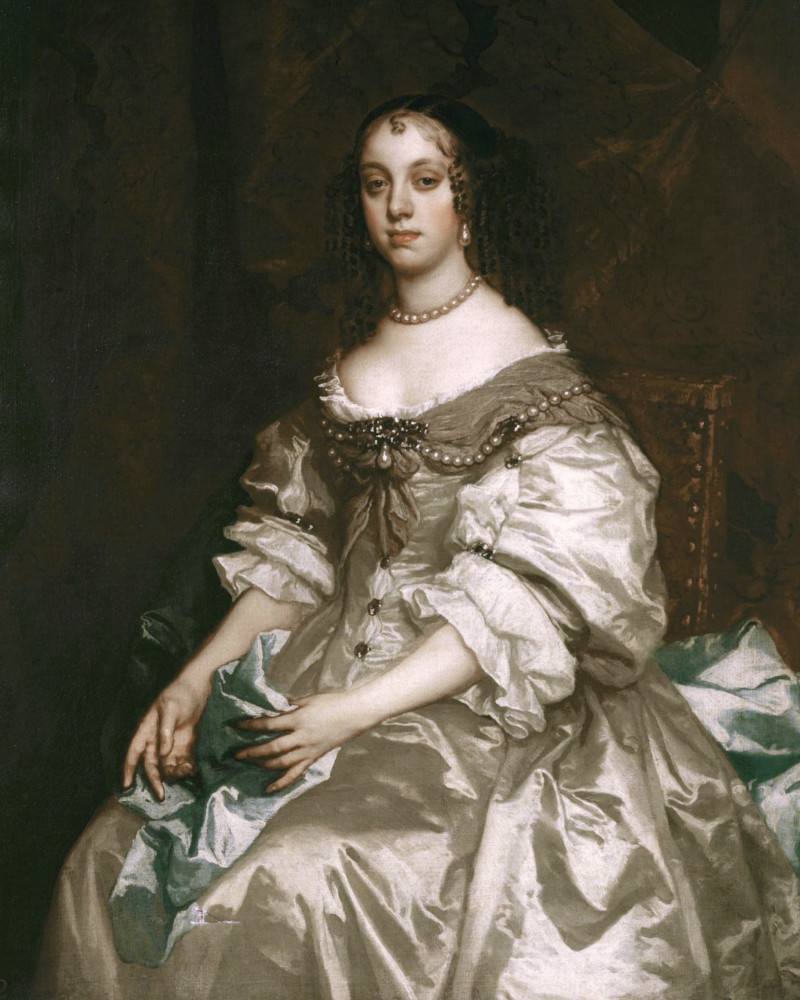
3. A Portuguese Princess made tea popular in Britain
Catherine of Braganza (1638 – 1705) was Queen Consort of England, Scotland and Ireland from 1662 to 1685, as the wife of King Charles II.
Although Catherine didn’t actually introduce tea into Britain, she was instrumental in making it fashionable. Her use of tea as a court beverage, rather than a medicinal drink, influenced its popularity in literary circles.
Trivia: Queens, a borough of New York City, is thought to be named after Catherine of Braganza since she was queen when Queens County was established in 1683.
4. These could be the earliest British directions for how to make tea
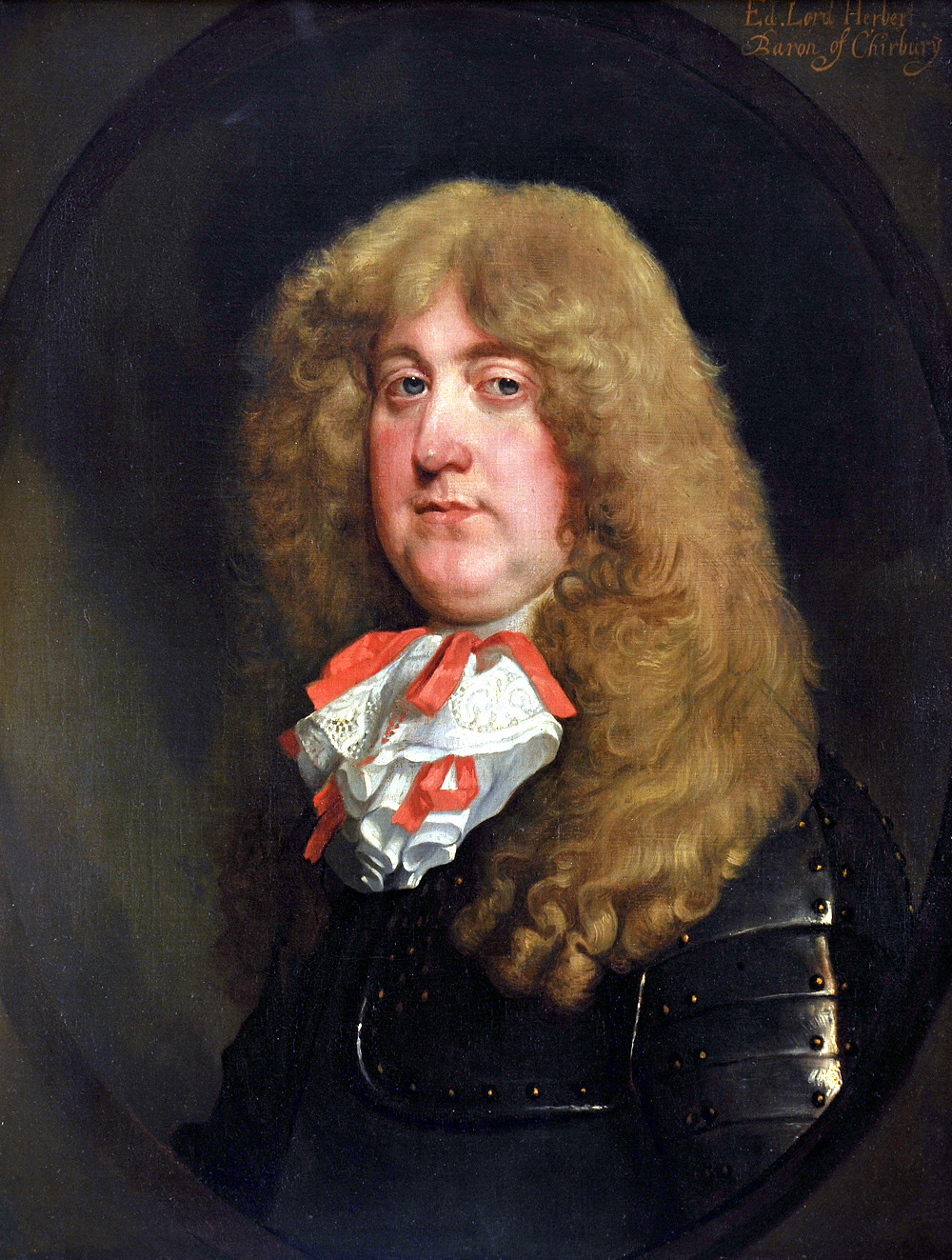

In 1672, Edward Herbert, 3rd Baron Herbert of Chirbury sent directions for tea making, and warming the delicate cups, to Shropshire;
“The directions for the tea are: a quart of spring water just boiled, to which put a spoonful of tea, and sweeten to the palate with candy sugar. As soon as the tea and sugar are in, the steam must be kept in as much as may be, and let it lie half or quarter of an hour in the heat of the fire but not boil. The little cups must be held over the steam before the liquid be put in.”
5. Tea may have been instrumental to the English Enlightenment

It was a summer afternoon in 1665 and Sir Isaac Newton was taking tea under the apple trees in the family gardens at Woolsthorpe Manor in Lincolnshire, England.
By chance, an apple fell from an overhanging branch, hitting him on the head and sparking the “a-ha” moment for his law of gravitation.
Whether precisely true or not, is it a coincidence that a flowering of intellectual thinking in Britain occurred at around the same time that tea was fast becoming the nation’s favorite drink?
By 1720, black tea had overtaken green tea in popularity and was generally taken with milk and sugar.
Could this magical potion be the brain stimulant of Newton, Locke, and Hobbes?
6. Did tea power the British Industrial Revolution?
Not only was tea powering the massive minds of some of history’s greatest thinkers, but some scholars suggest that tea played a key role in the British Industrial Revolution.
The stimulants in the tea, coupled with the extra energy from sugar and milk would act like today’s energy drinks and give workers a boost—helping them work longer hours.
Even today, “builder’s tea” is a favorite for anyone doing physically strenuous work as part of their job. A colloquial term for strong tea, builder’s tea is typically brewed in a mug, always has milk, and two (or more) teaspoons of sugar.
Furthermore, because water has to be boiled for tea, water-borne diseases like dysentery, cholera, and typhoid were killed.
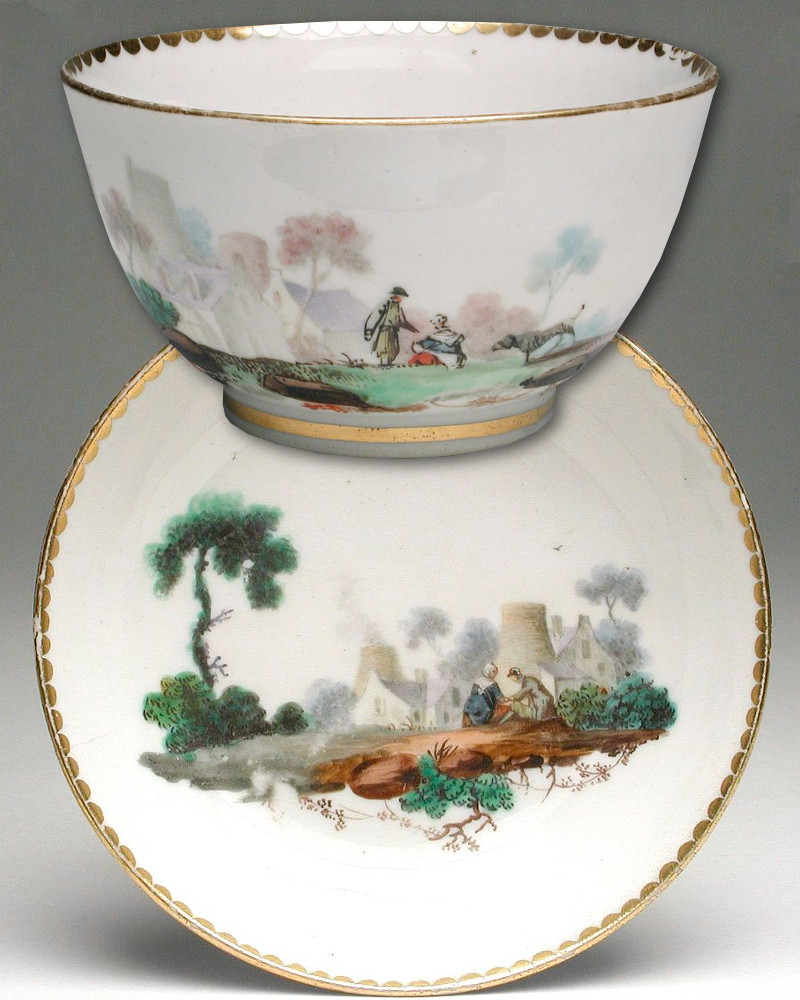
7. Chelsea porcelain manufactory produced the first British teaware
Fashionable 17th-century tea drinkers used small porcelain tea bowls that were sometimes shipped with the tea itself.
Established in 1743, the Chelsea porcelain manufactory produced the first successful porcelain equipages and were quickly imitated.
During the 1770s and 1780s, tea was sometimes drunk from saucers. Deeper than today’s, they were similar to the Chinese bowls of the 17th century. It is thought the practice came from Russia, where samovars kept tea very hot and strong. Pouring from cup into saucer was a quick way to cool the tea.
8. Victorian tea rooms helped women win the right to vote
During the Victorian era, tea rooms may have helped the women’s suffrage movement.
Tea rooms were popular and fashionable social gathering places, especially for women.
British historian Sir Roger Fulford argued that tea rooms provided neutral public spaces to help women strategize political campaigns.
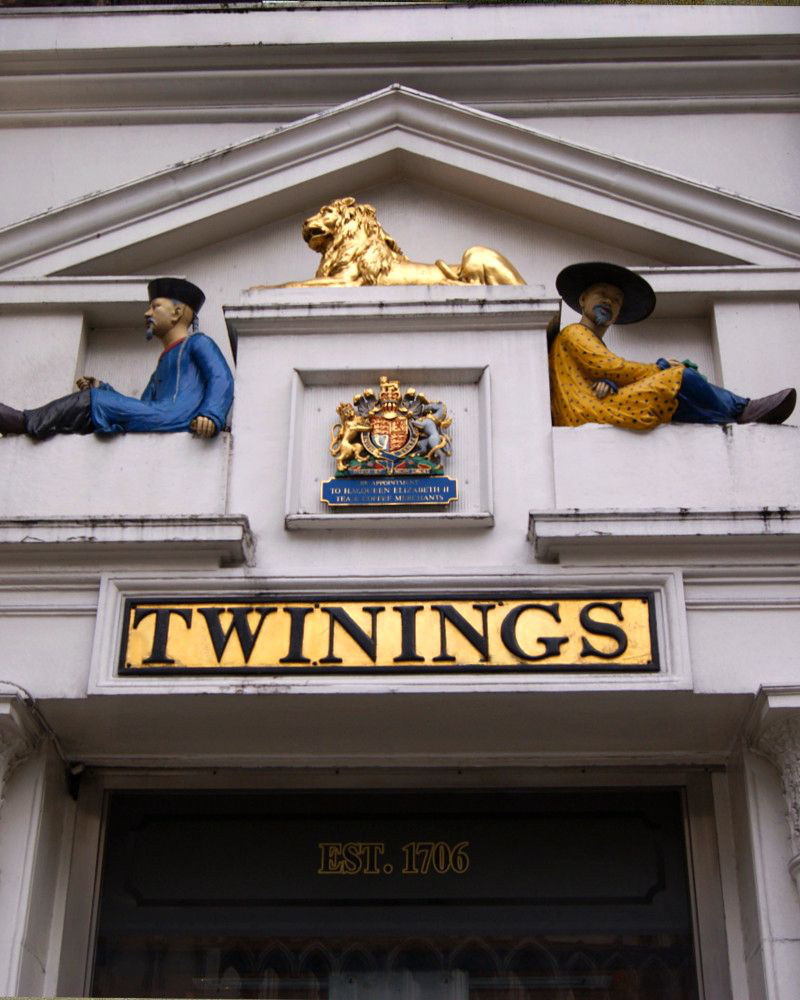
9. Thomas Twining opened the first known tea shop in London
Thomas Twining opened the first known tea shop in 1706.
Twinings holds the world’s oldest continually-used company logo and has occupied the same premises at 216 Strand, London, since inception.
A division of Associated British Foods since 1964, Stephen Twining now represents the company’s tenth generation.
Celebrating its 300th anniversary in 2006, Twinings launched a special tea and associated tea caddies.
Appointed by HM The Queen, Twining’s is a Royal Warrant holder.
10. Take a tea break—it’s the law!
In a working shift of six hours, British workers have the right in law to a minimum of a 20-minute break.
Described in government guidelines as “a tea or lunch break”, it is sometimes called “elevenses”, because 11 am is a good time to take a break, leaving two hours before the traditional lunchtime of 1 pm.
In Britain, where there is tea, there are usually biscuits too—it’s really hard to have one without the other.
Dunking biscuits in a “cuppa” (cup of tea) is a custom that Brits have exported around the globe.
McVitie’s biscuits are the most popular biscuits in the UK to “dunk” in tea, with McVitie’s chocolate digestives, Rich tea and Hobnobs ranked the nation’s top three favorites.
References
Wikipedia.org
Victoria & Albert Museum
Metropolitan Museum of Art
Los Angeles County Museum of Art
The Telegraph