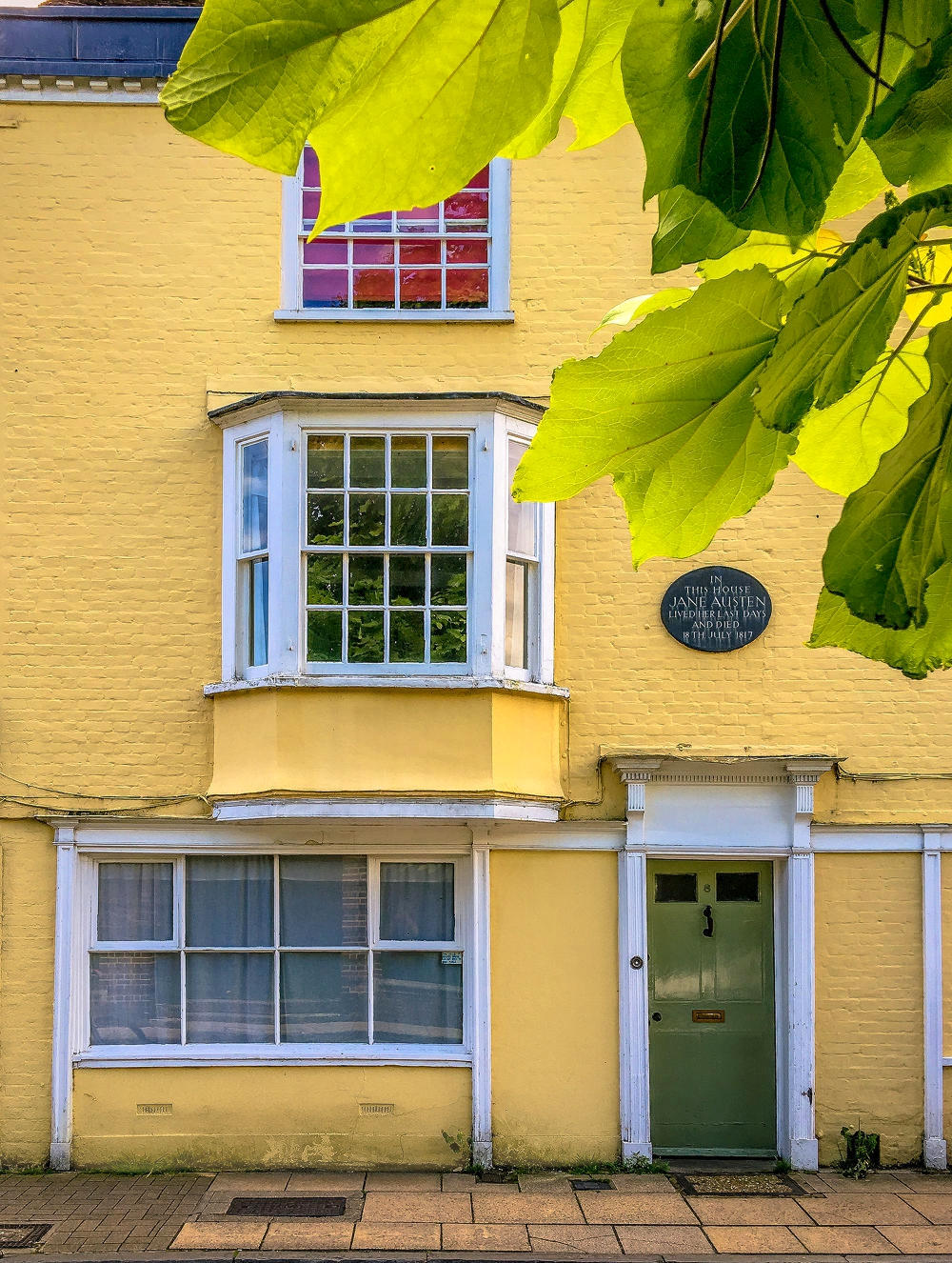
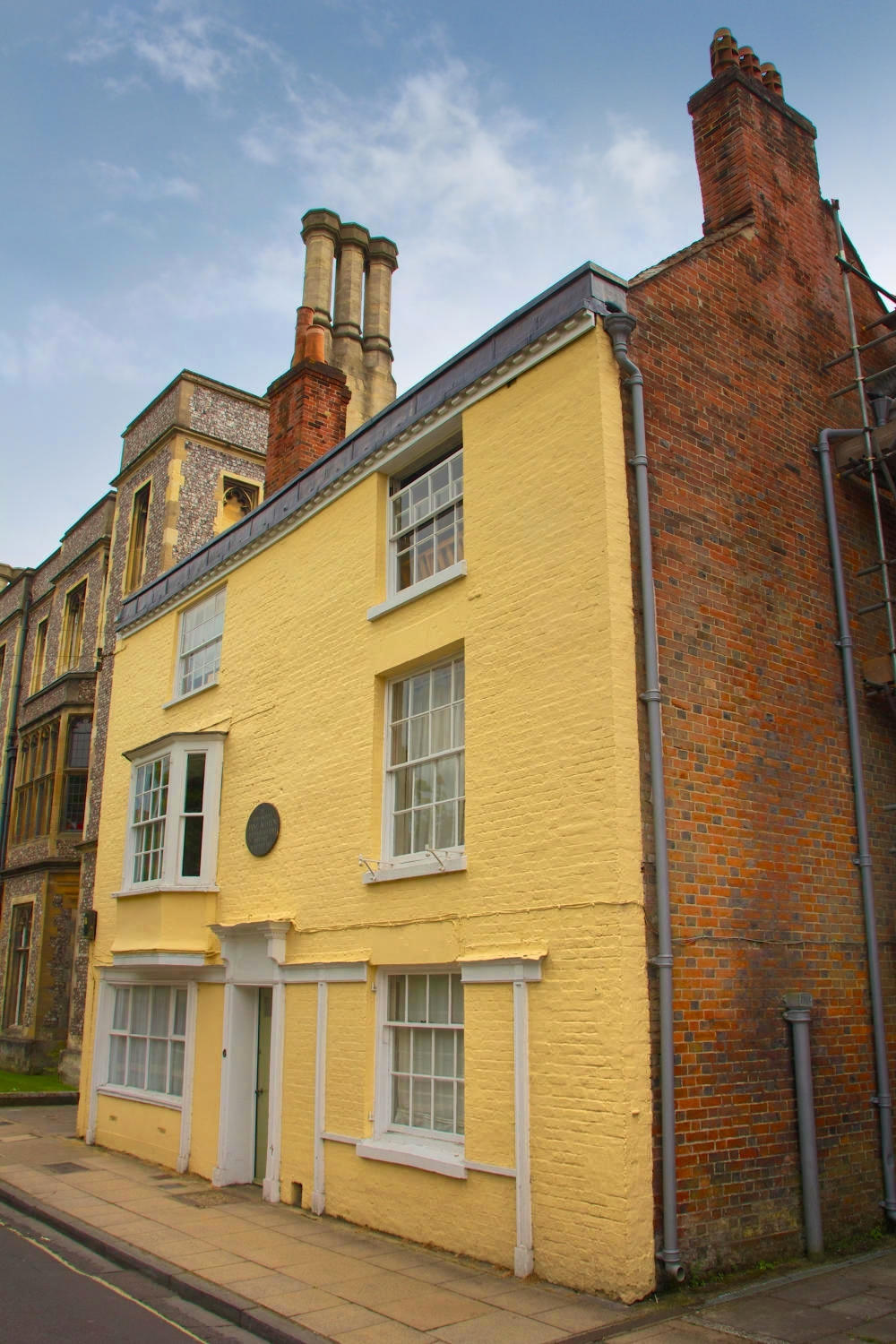
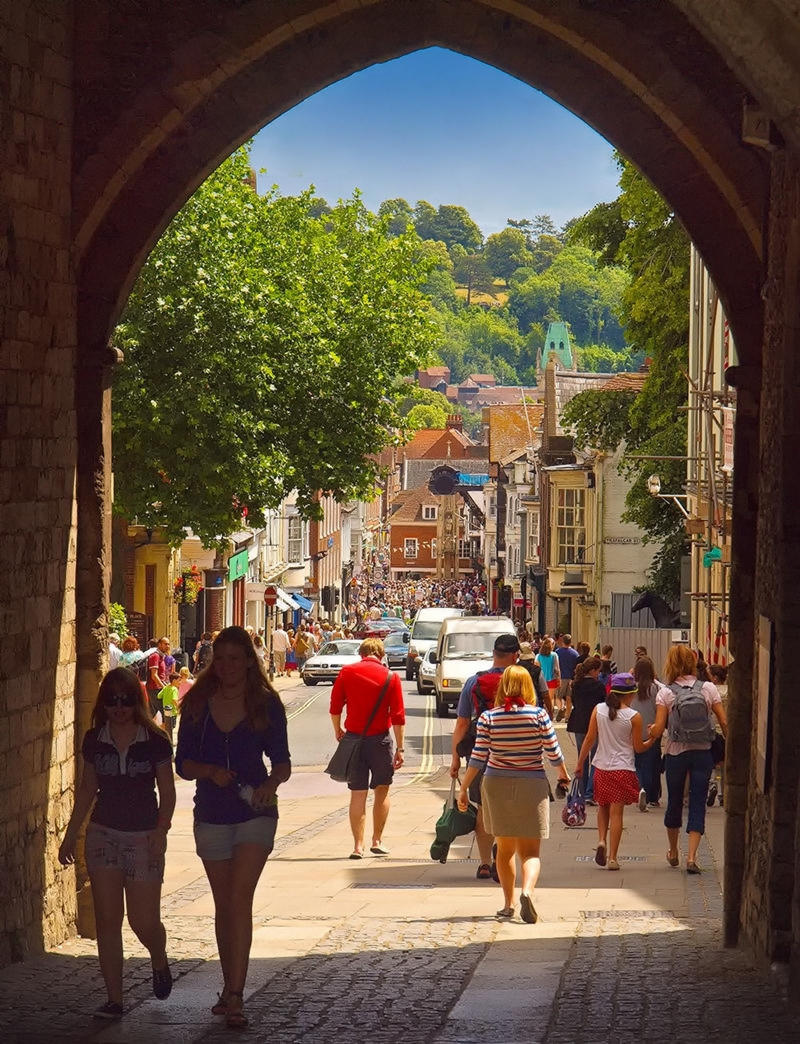
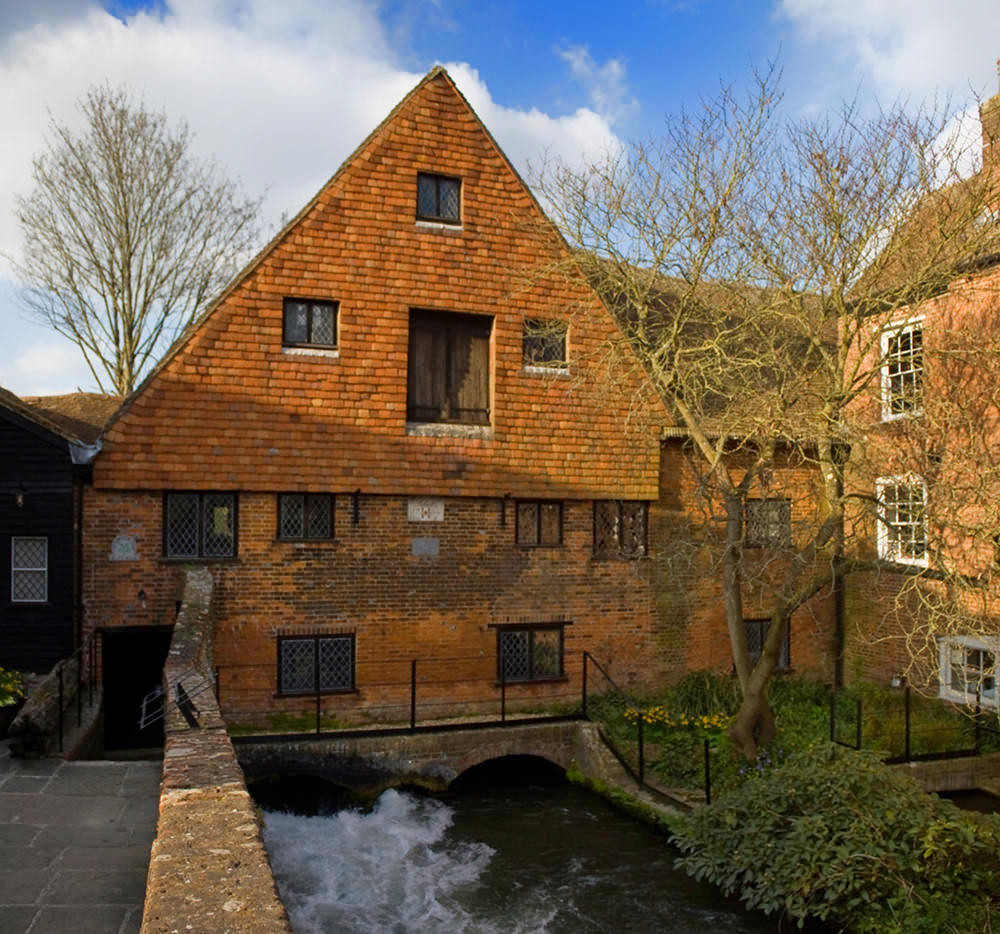
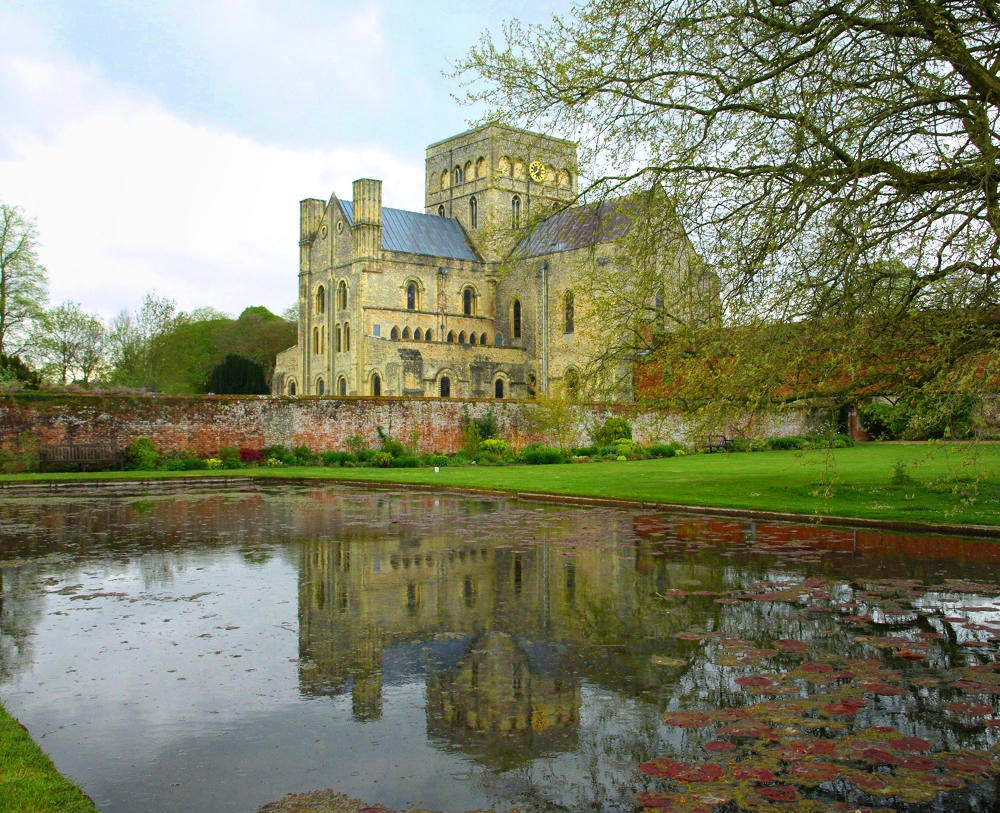
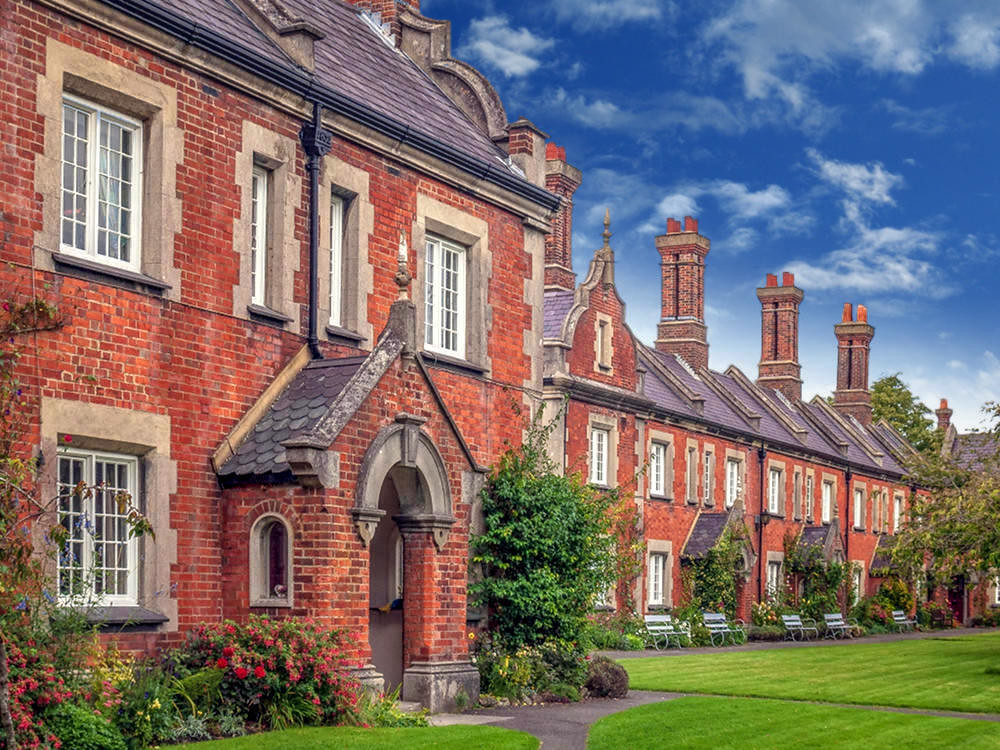
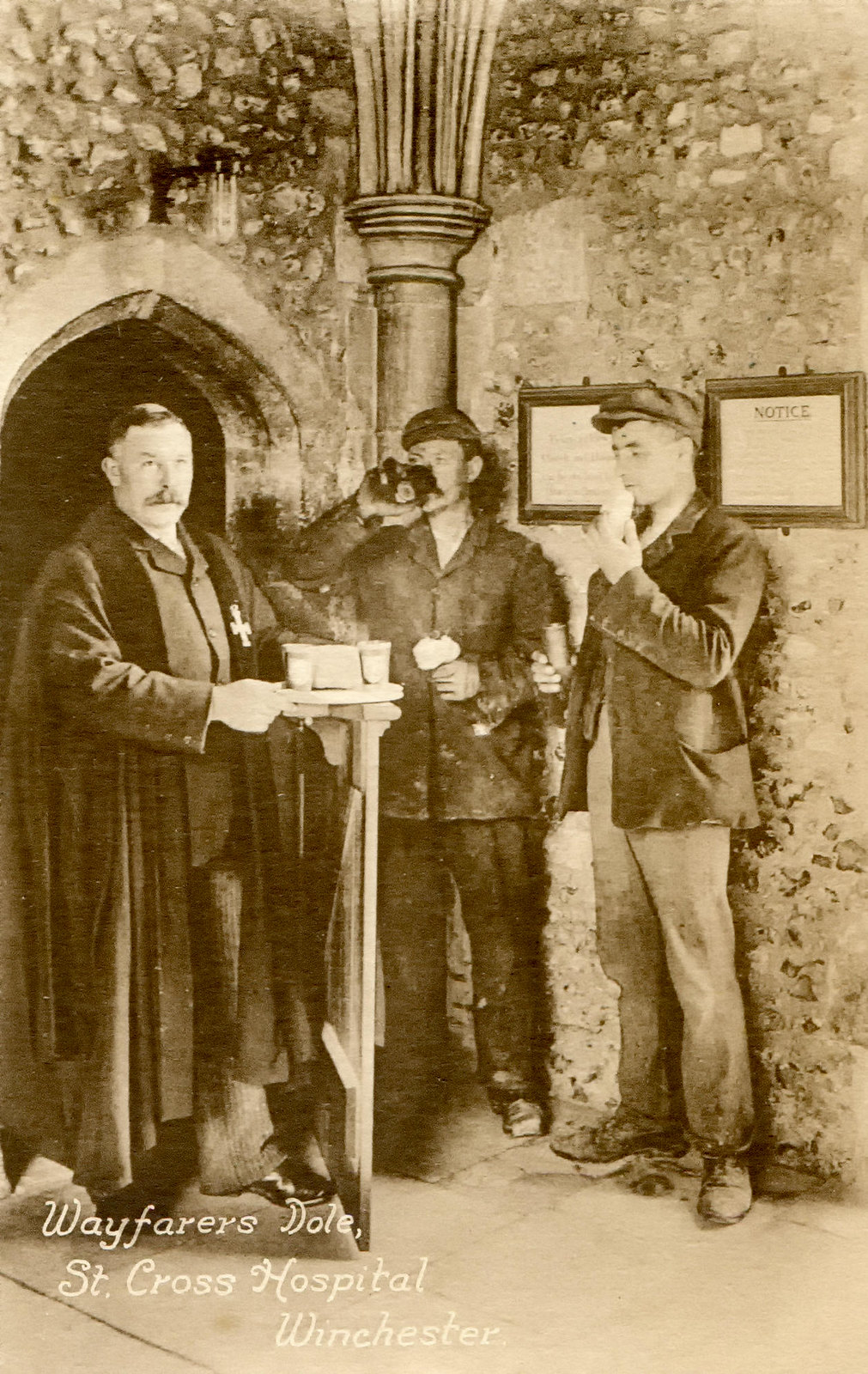
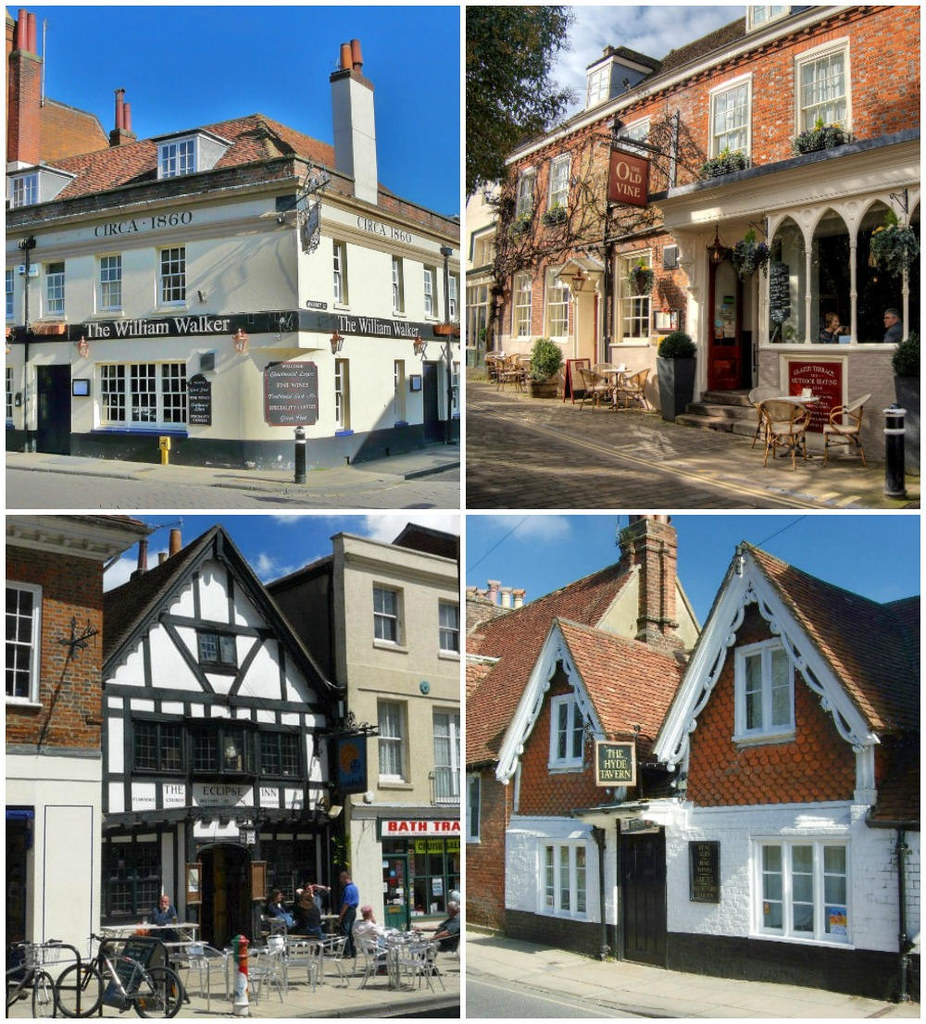
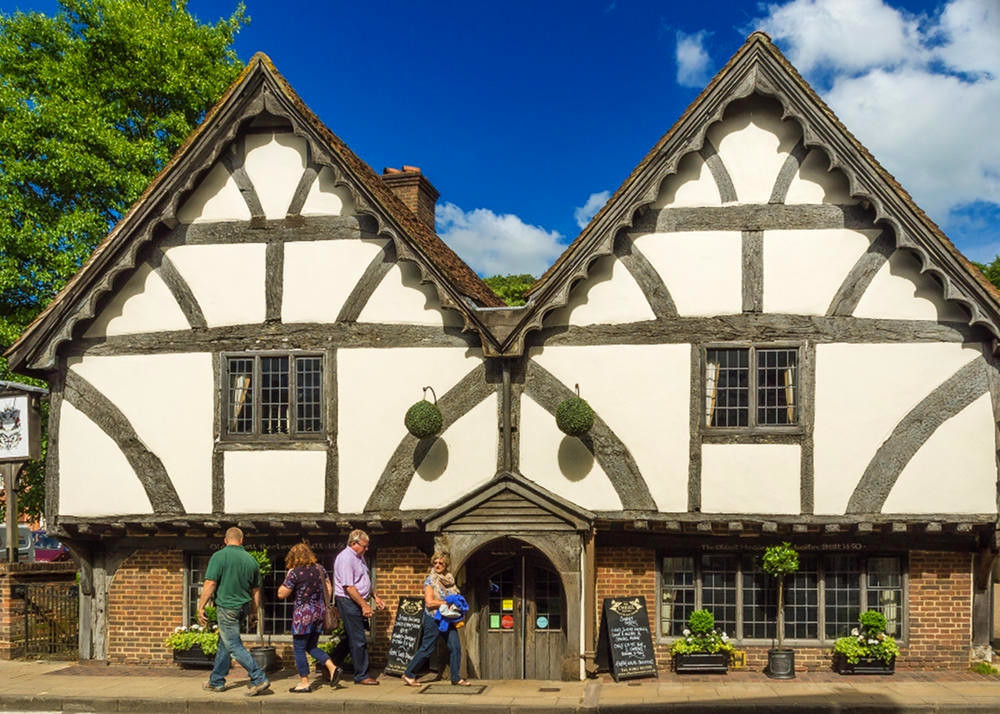
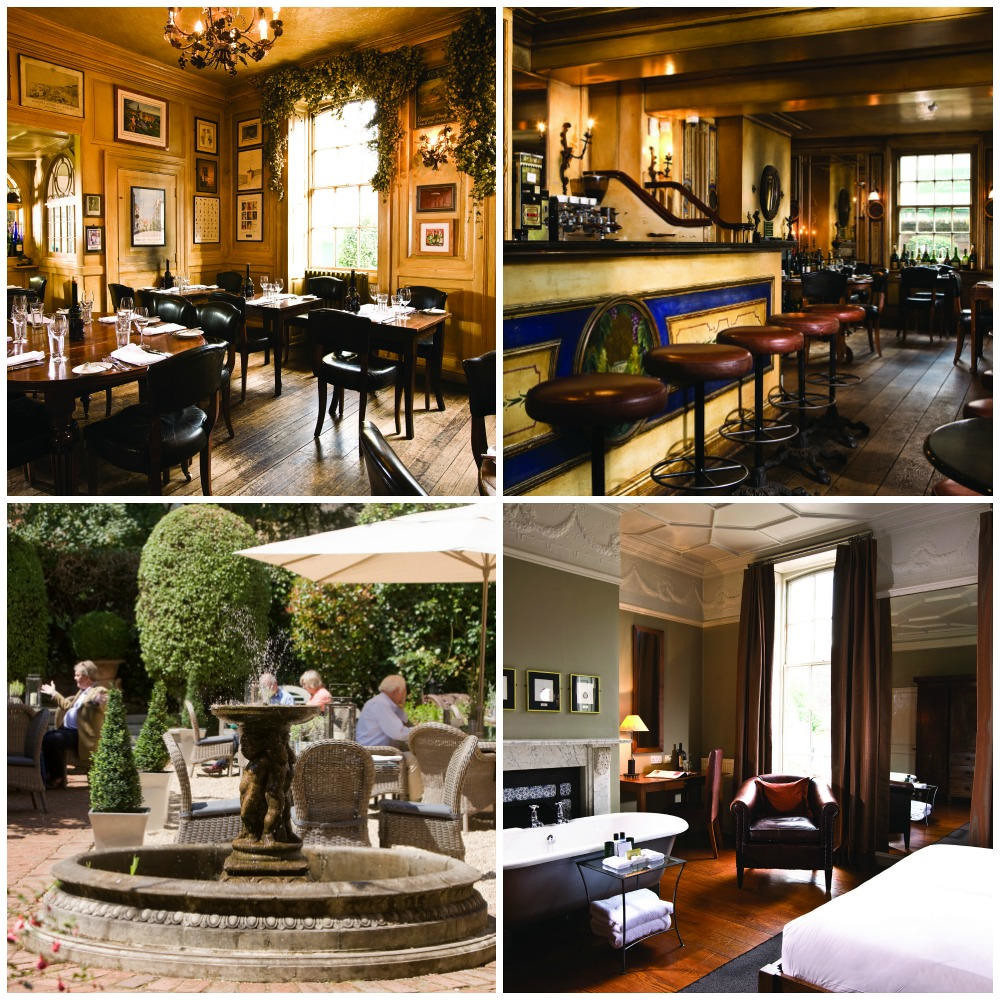
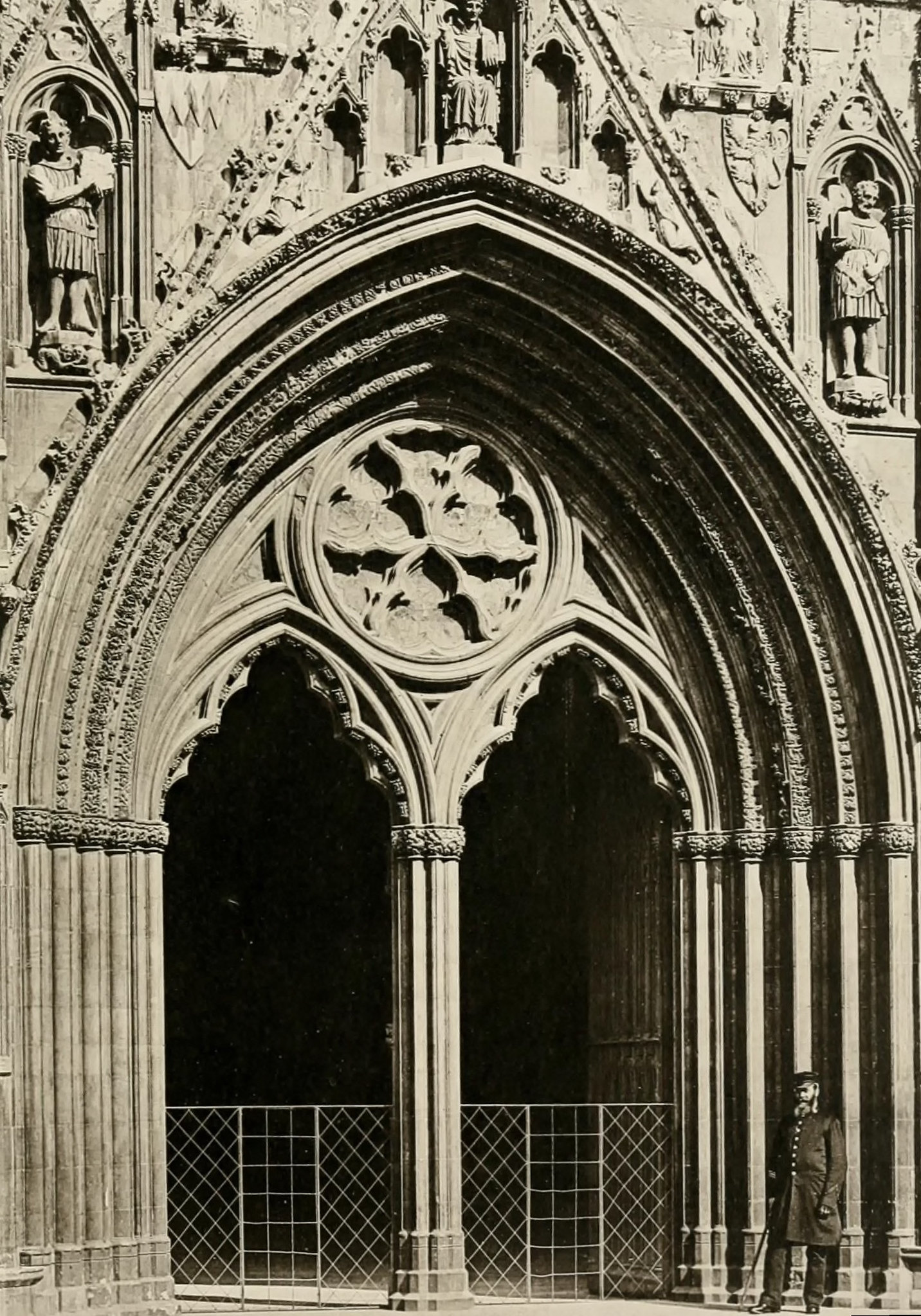
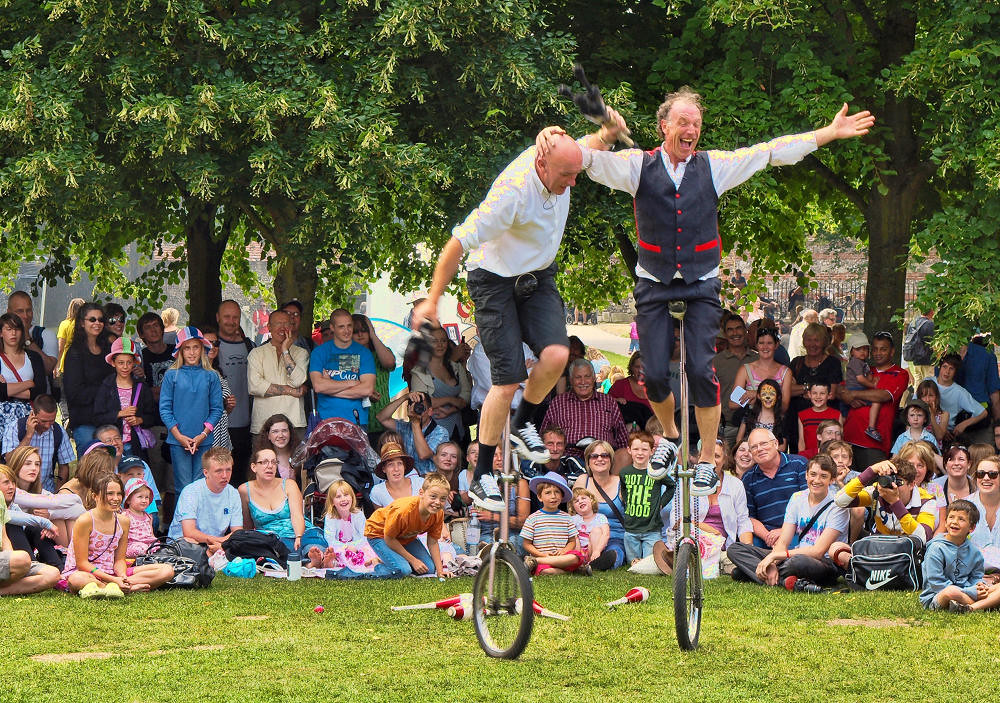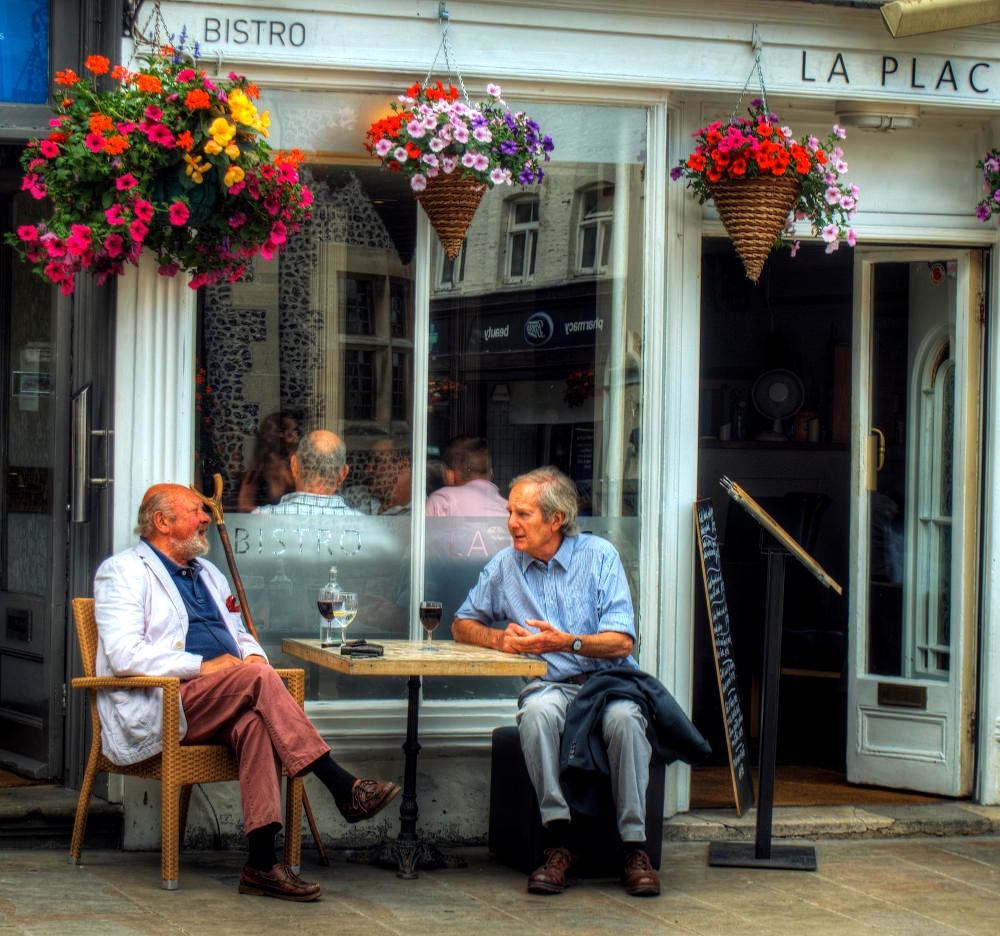Beautiful villages, a Regency spa town, an ancient city, historic docklands, and some of England’s most picturesque open countryside are yours to discover and explore when you visit Gloucestershire.
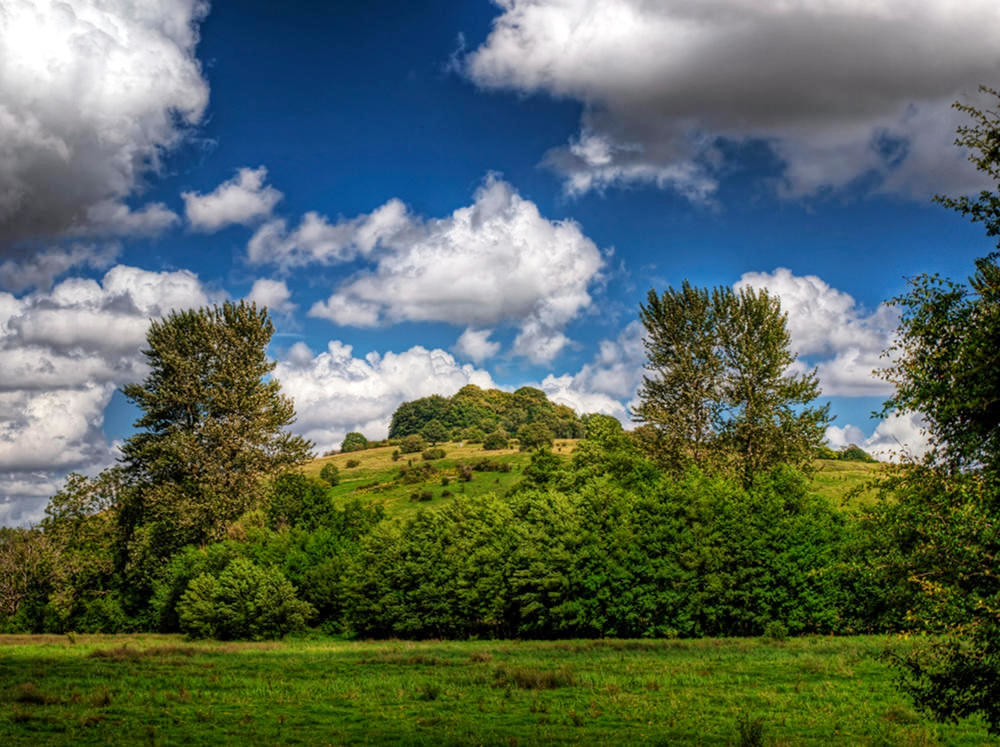
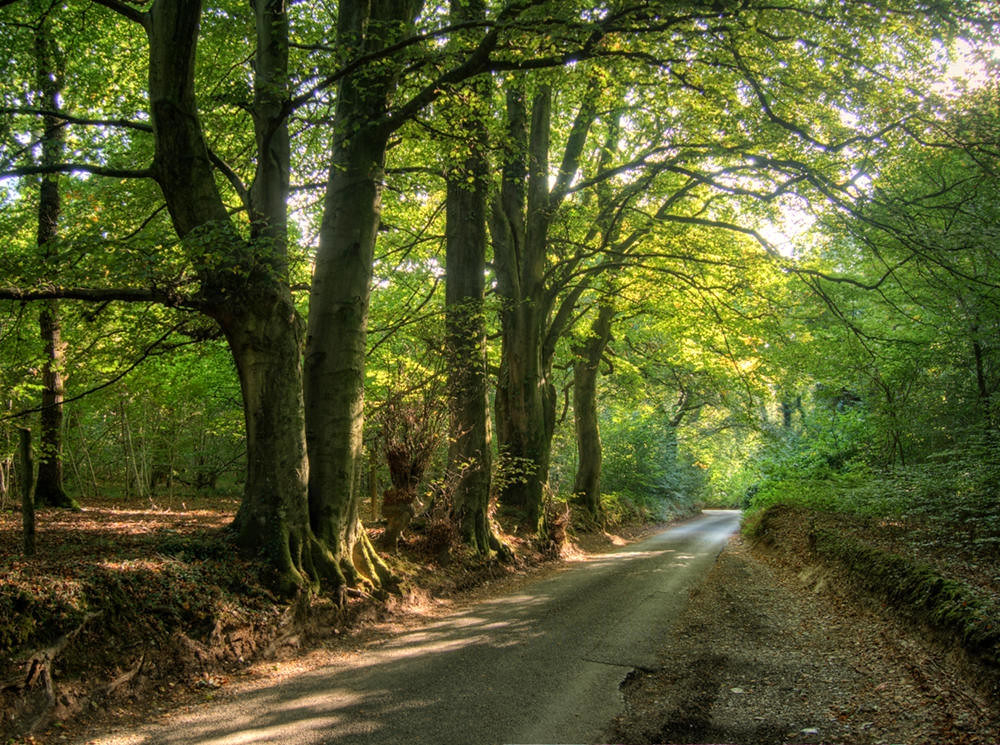
Comprising part of the Cotswold Hills, the River Severn fertile valley, and the Forest of Dean, Gloucestershire offers some of the most outstanding scenery anywhere in Britain.
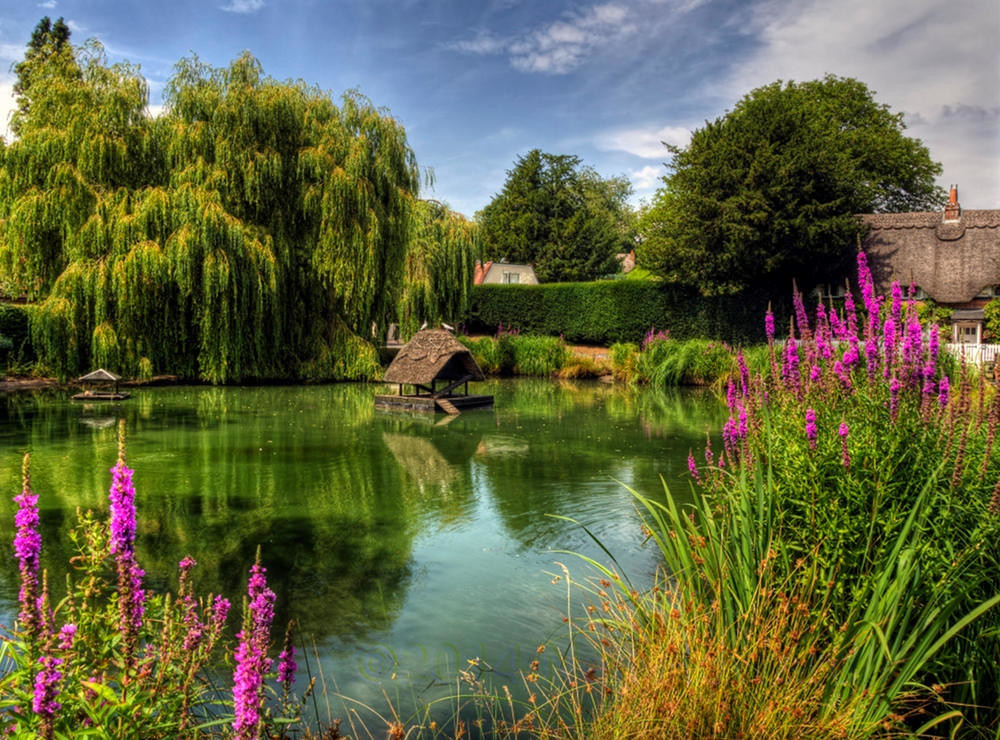
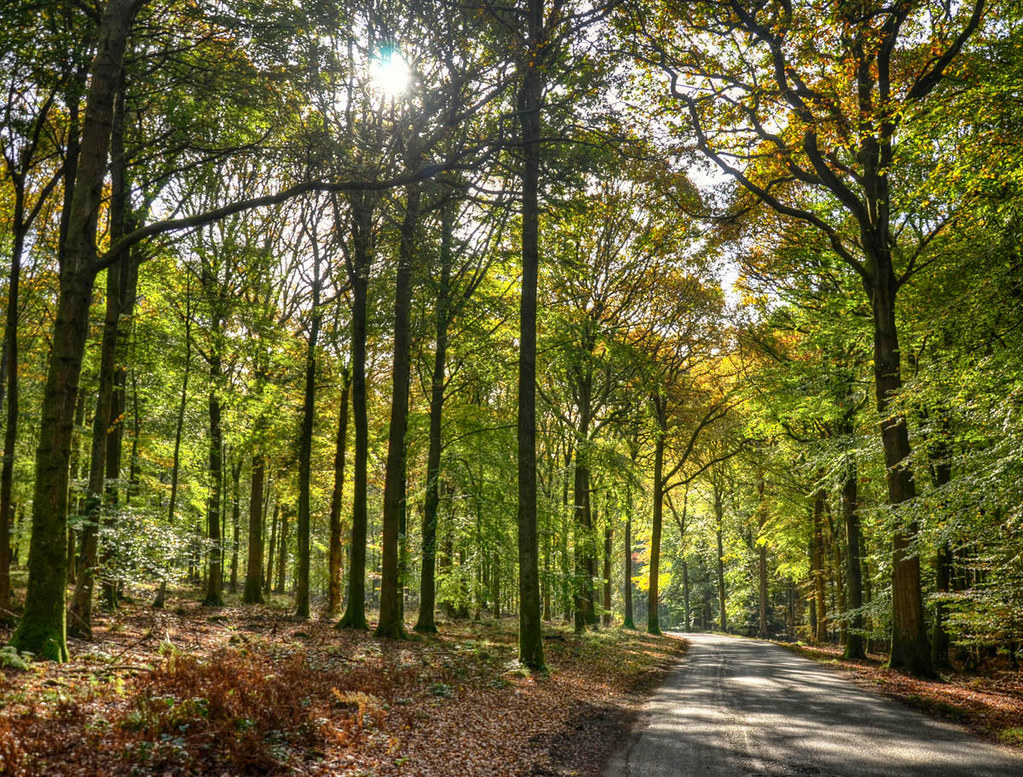
Gloucestershire’s Countryside
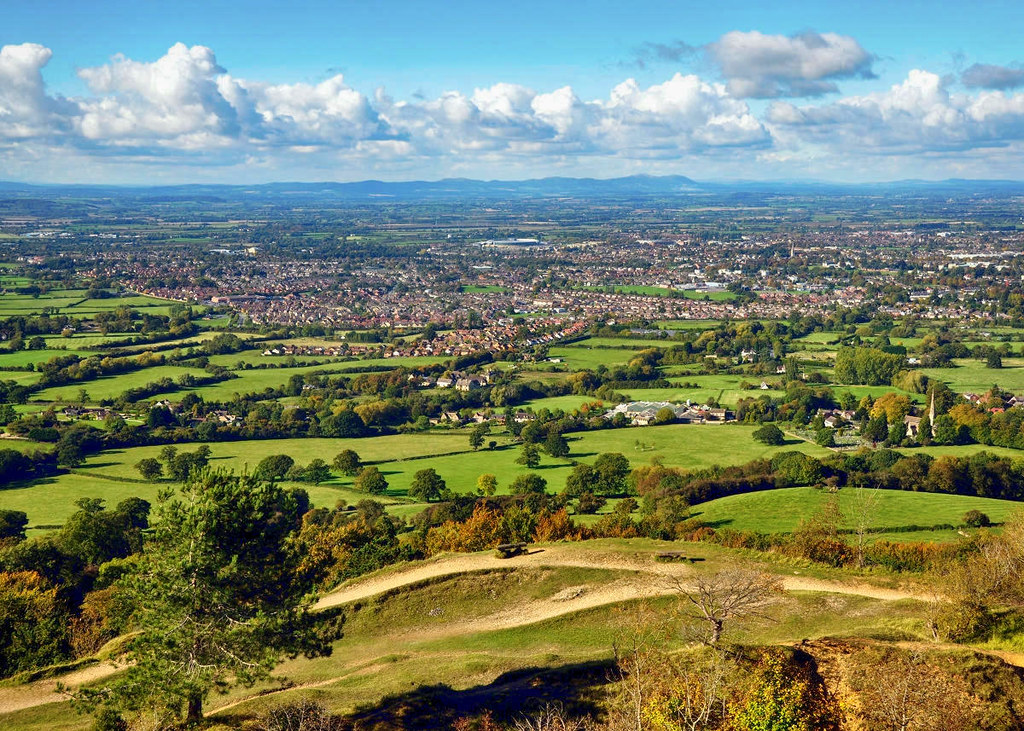
On a clear day, one of the finest views across the spa town of Cheltenham and out toward the Malvern Hills beyond can be enjoyed from the top of Leckhampton Hill.
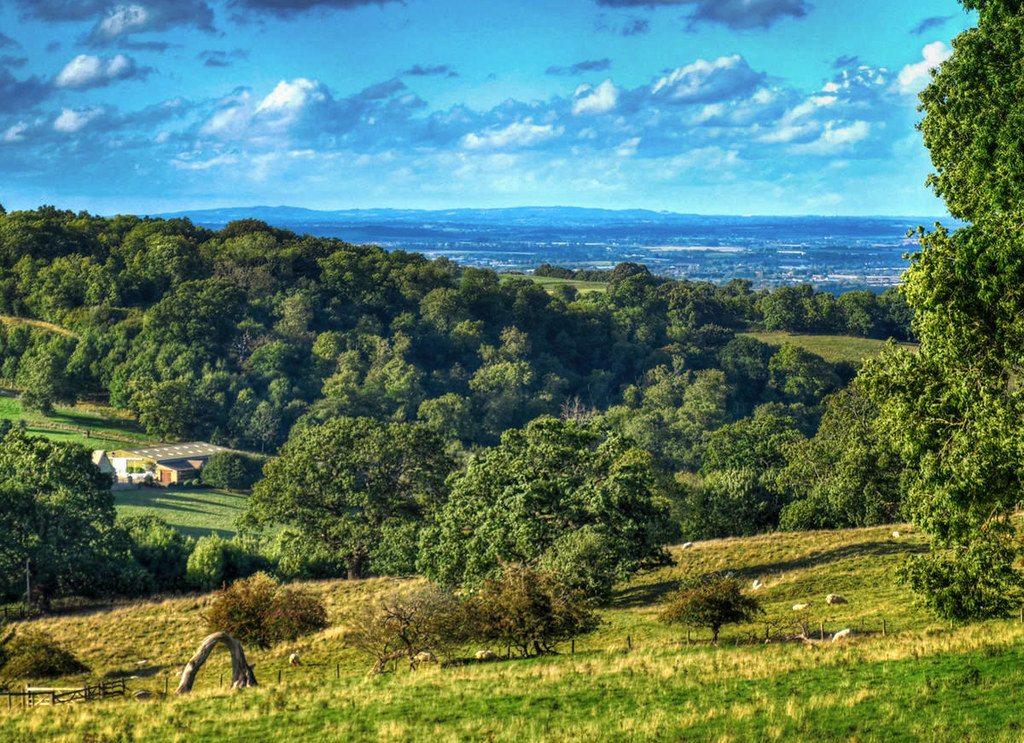
Gloucestershire’s countryside is gorgeous.


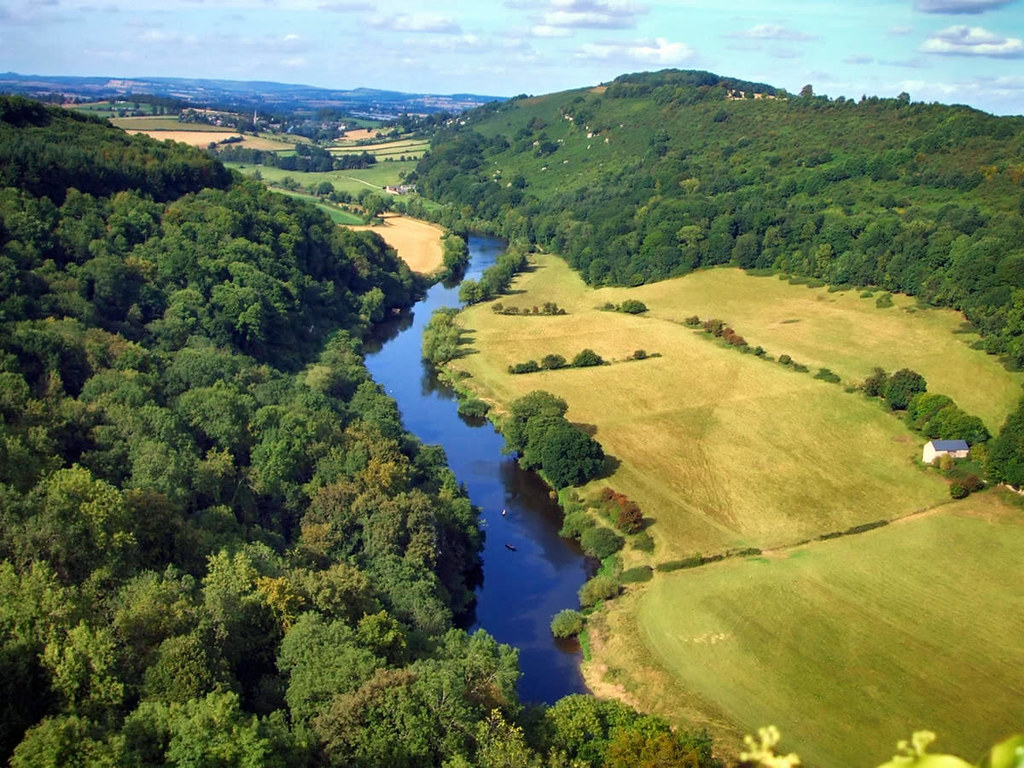
Winding through the Wye Valley Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONB), the River Wye is the fifth-longest river in the United Kingdom and forms part of the border between England and Wales.

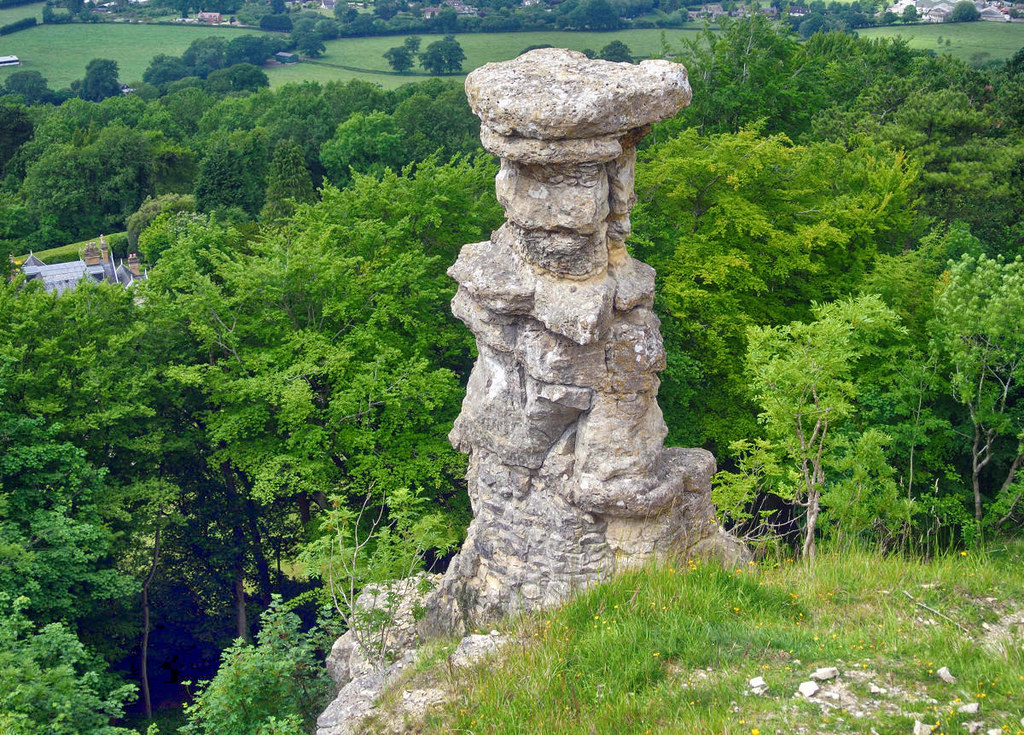
Above a disused quarry in Leckhampton, a peculiar-shaped limestone rock formation known as “the Devil’s Chimney” rises from the ground.
Legend has it that the Devil would sit atop Leckhampton Hill and hurl stones at Sunday churchgoers, but that God turned the stones back, driving the Devil underground and trapping him there forever.

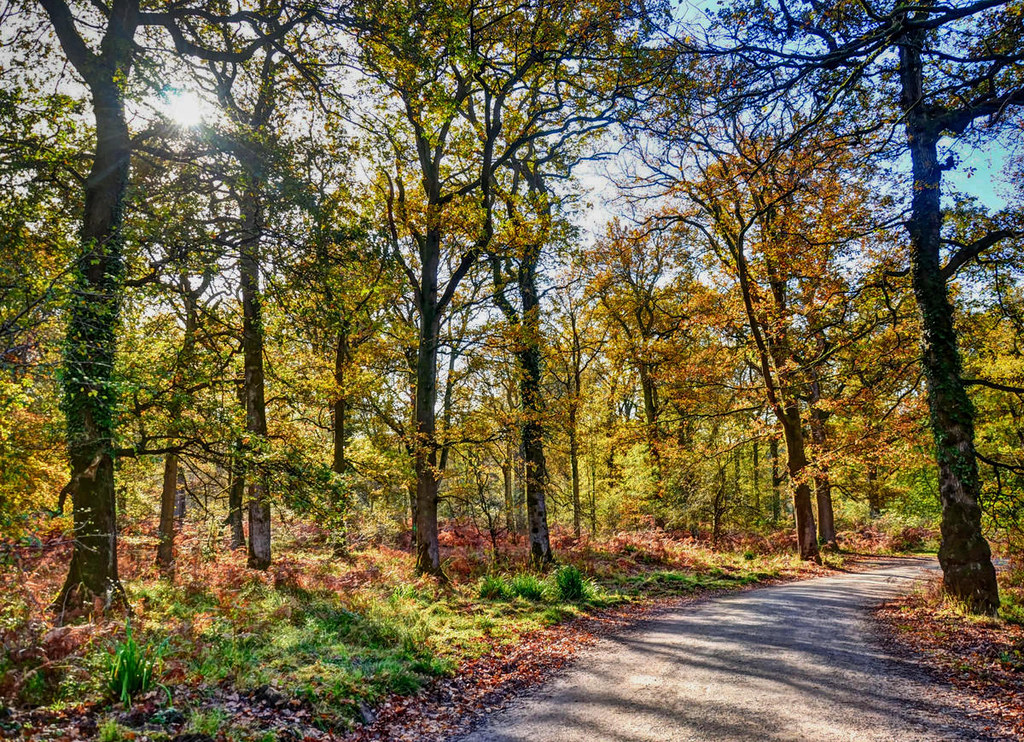
Reserved for royal hunting by Anglo-Saxon kings, the Forest of Dean is one of the last surviving ancient woodlands in England.
Covering almost 43 square miles, the name is thought to originate from the Viking settlements, referring to the region as “Danubia” meaning “land of Danes”.


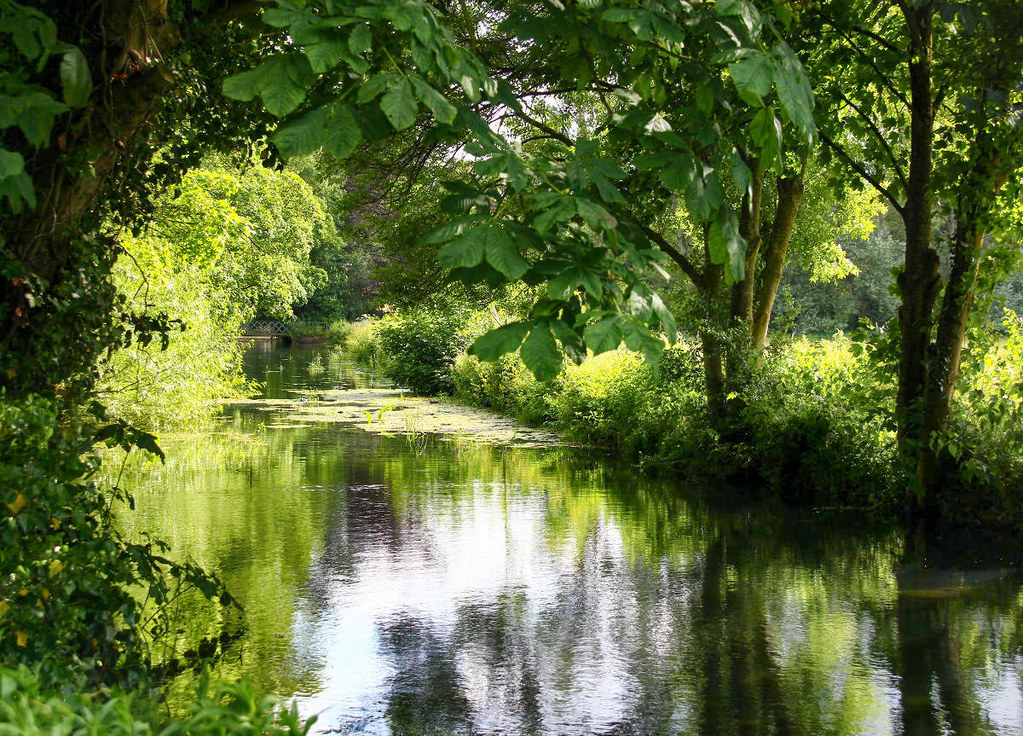
Rising in the Cotswold Hills of Gloucestershire, the River Churn is the first tributary of the famous River Thames.
Much of the catchment basin of the River Churn is known to have been an important area of Roman settlement in the second to fourth centuries AD.


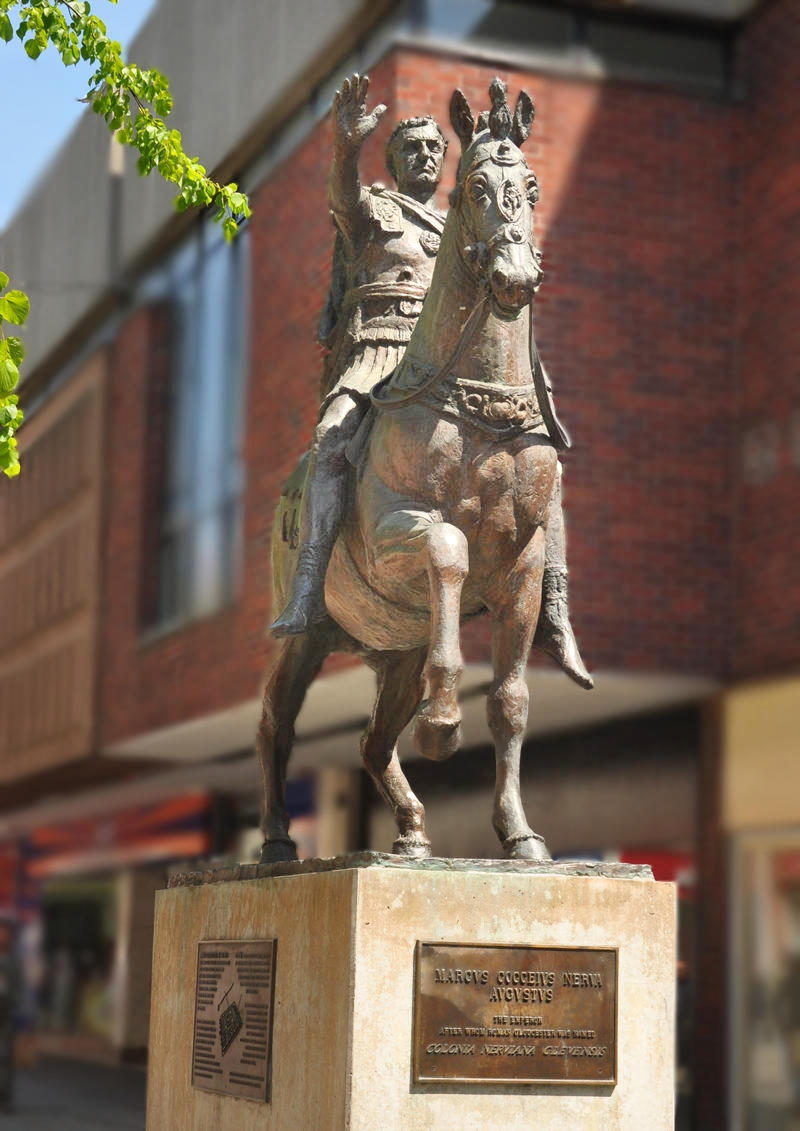
Gloucestershire’s Roman Beginnings
Founded in AD 97 by the Romans under Emperor Nerva, Gloucester is the county city of Gloucestershire.
Derived from the Roman name “Glevum” or “Glouvia” and the Anglo-Saxon word “ceaster” meaning fort, Gloucester was once a Roman colony for retired legionaries.

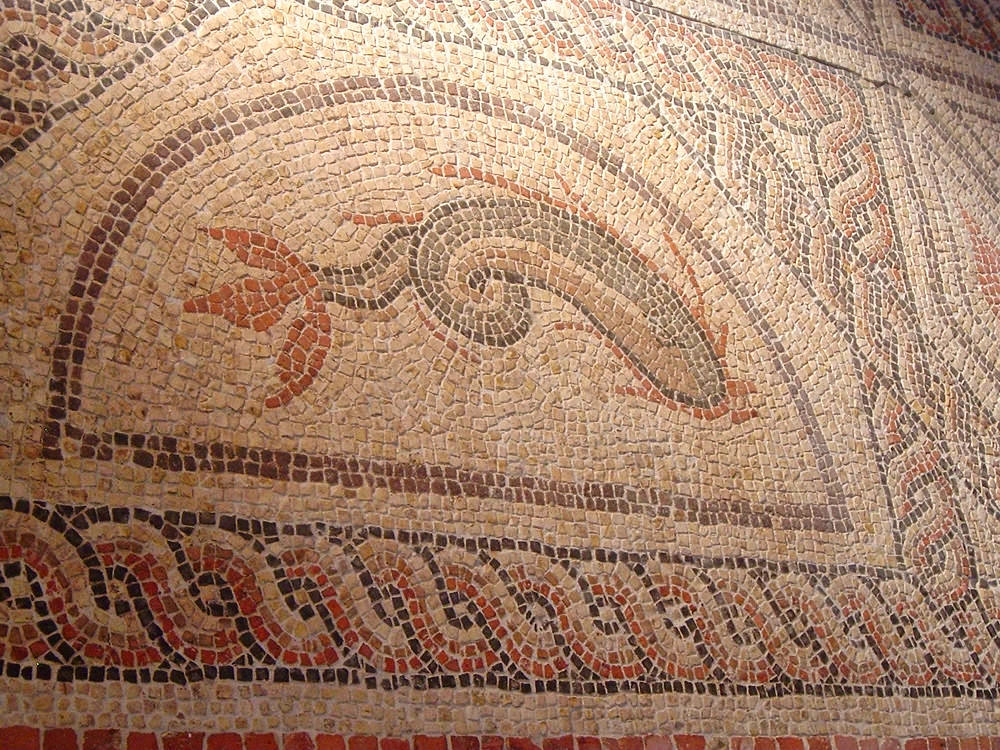
Granted farmland and called upon as Roman auxiliaries, legionaries built luxurious villas with exquisite mosaic floors.
Gloucestershire has some of the best Roman villas in Britain.
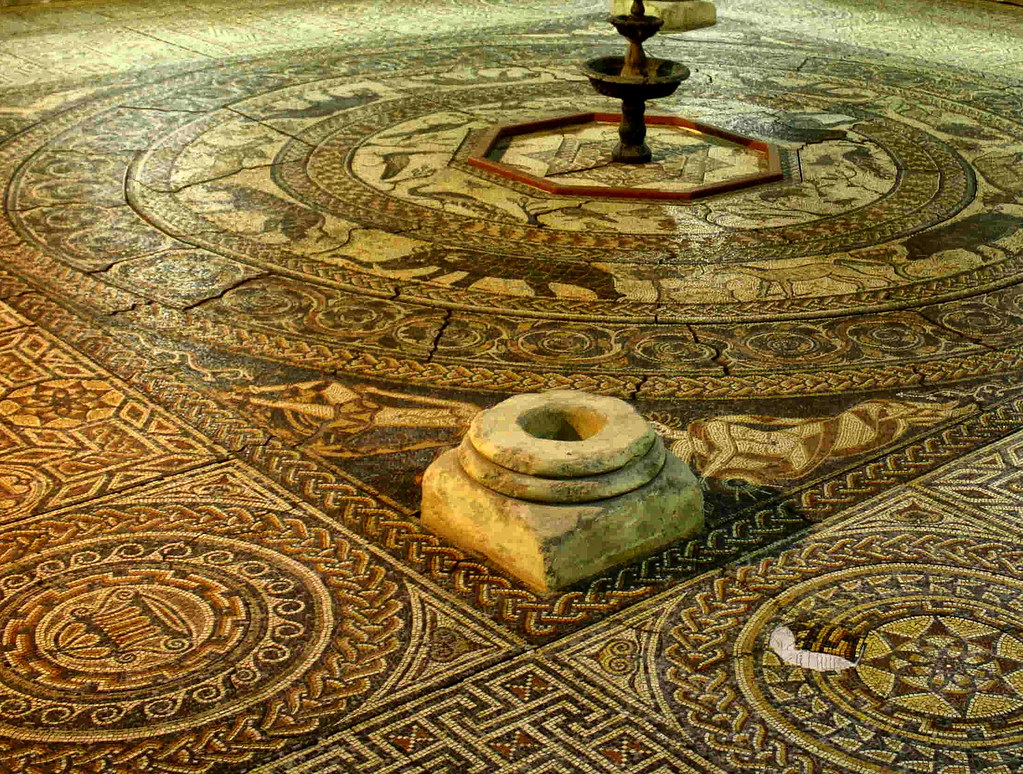

Including a heated and furnished west wing containing a dining-room (triclinium) with a fine mosaic floor, as well as two separate bathing suites—one for damp-heat and one for dry-heat—Chedworth Villa was an elite dwelling and one of the largest Roman villas in Britain.
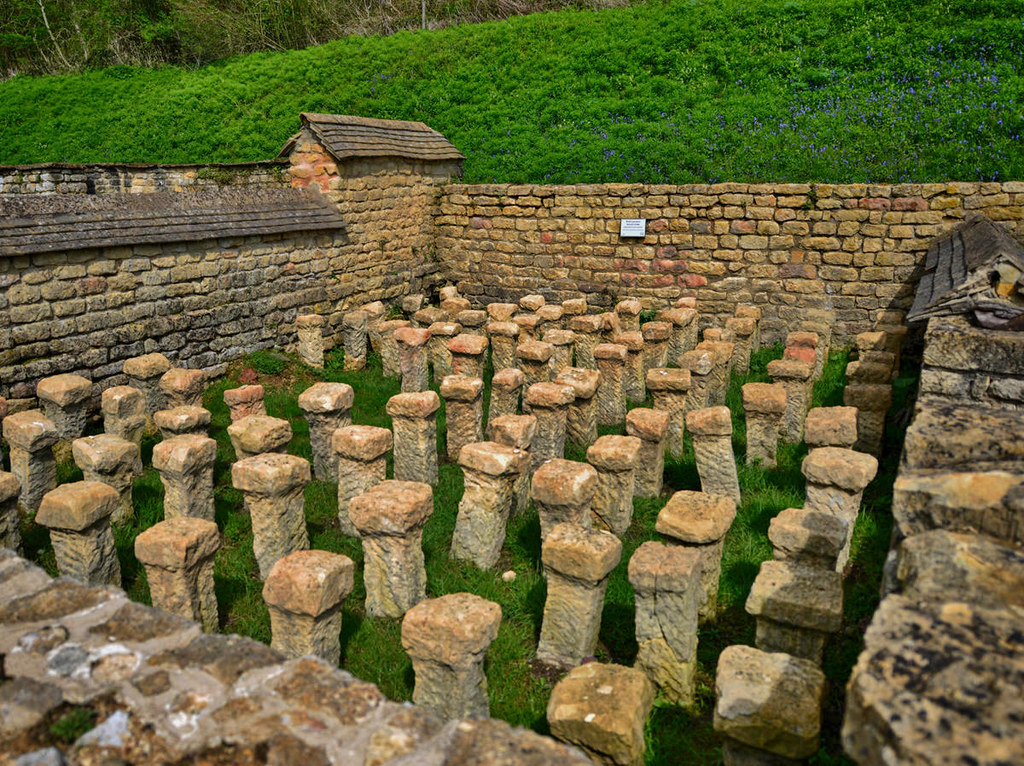

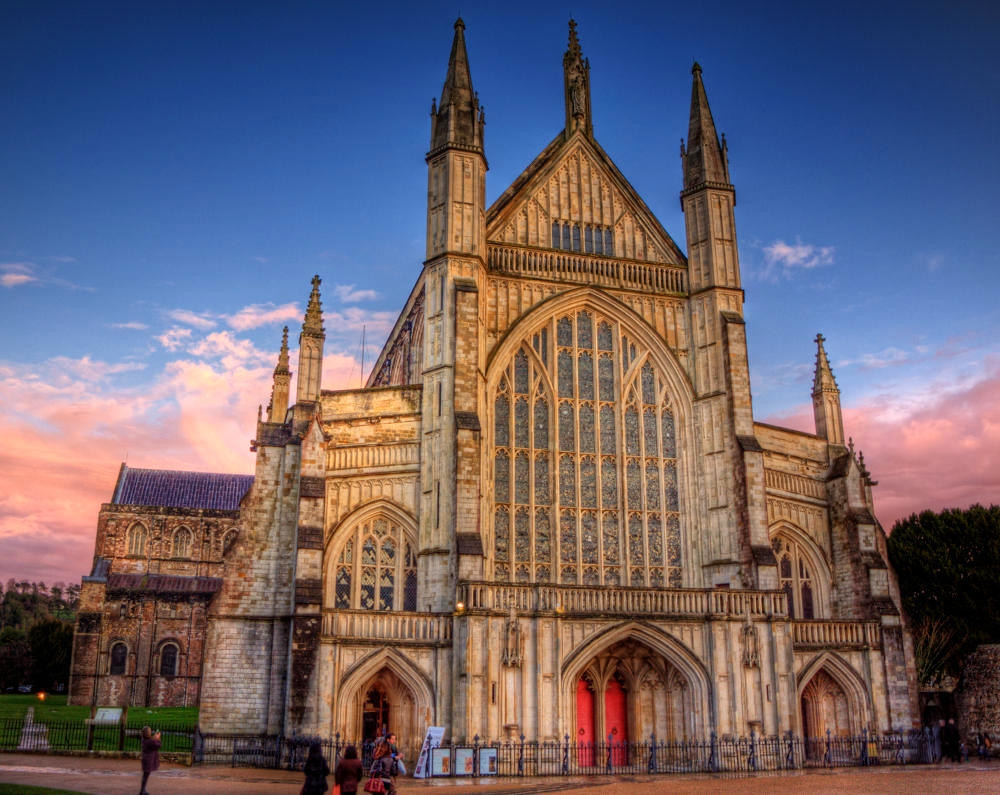
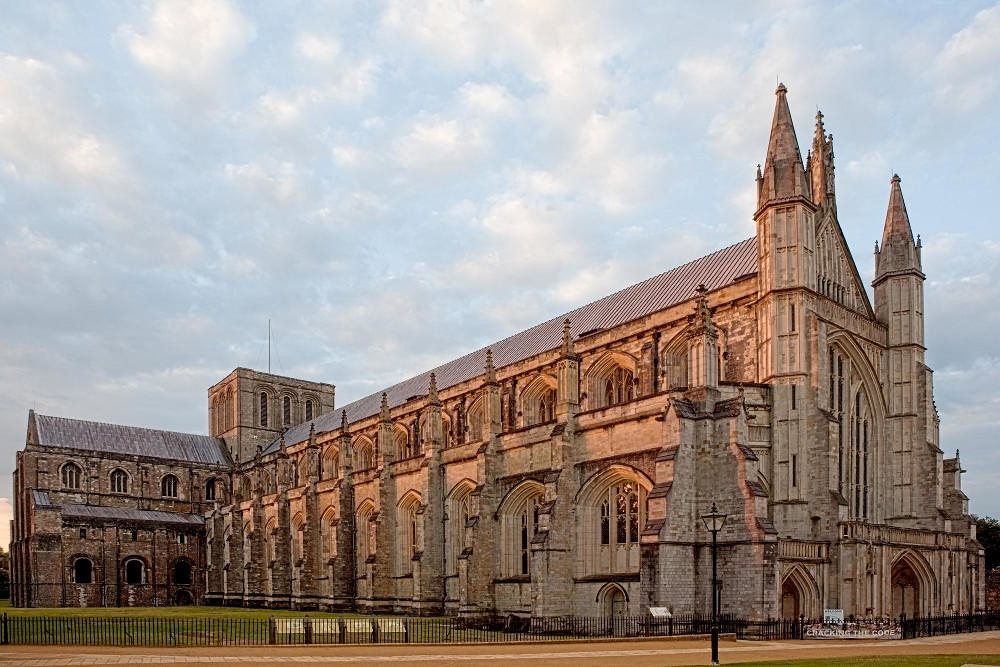
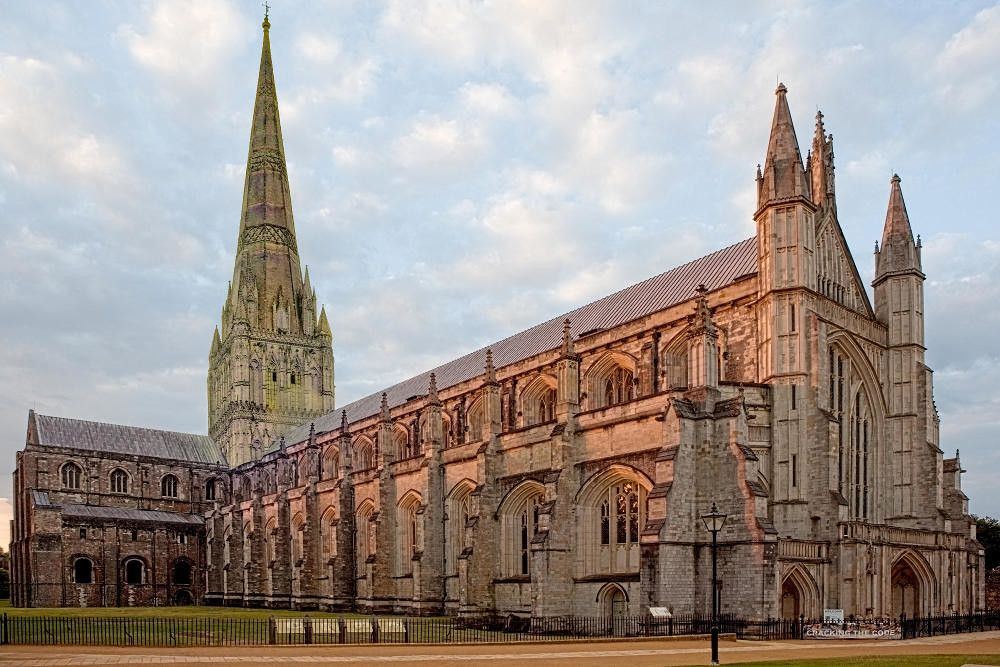
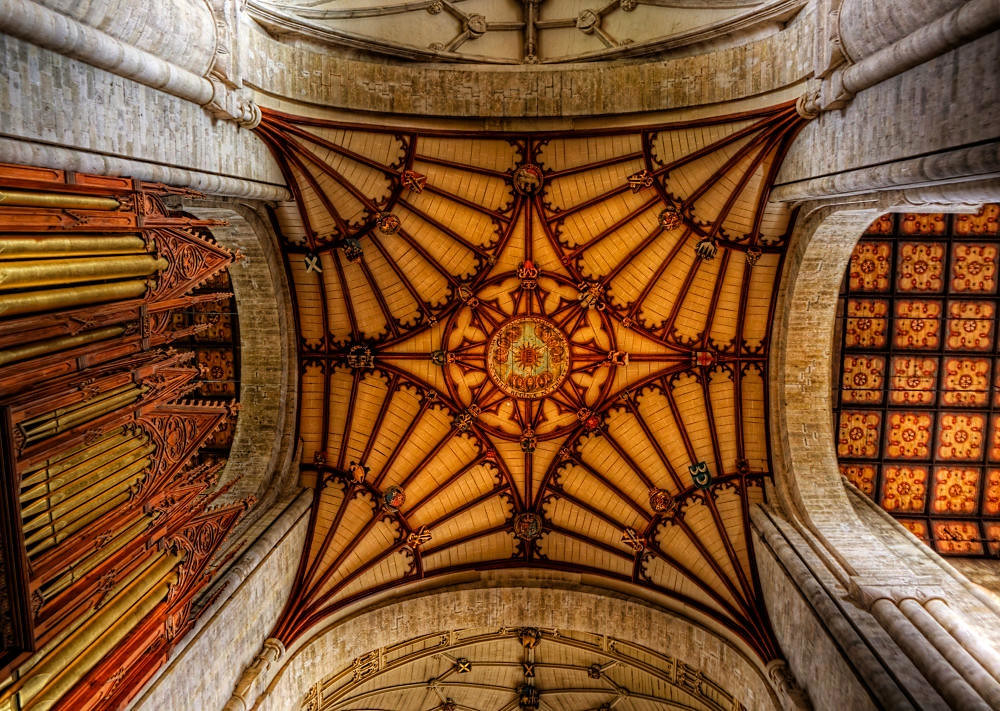
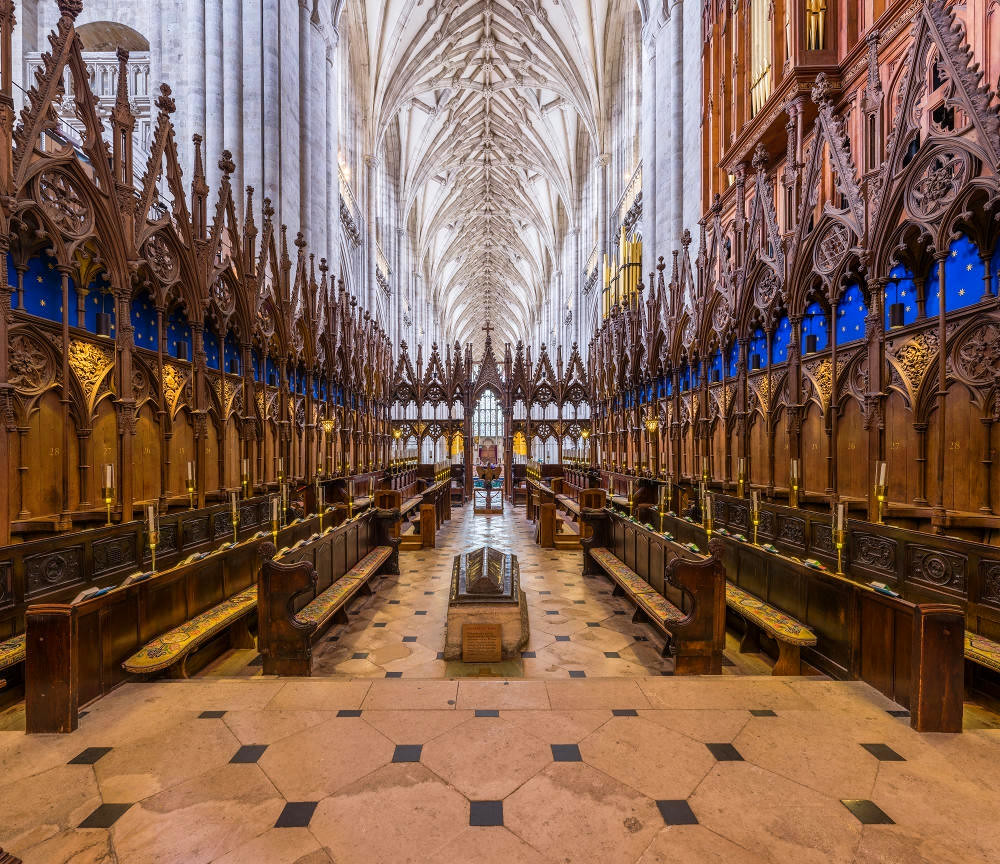
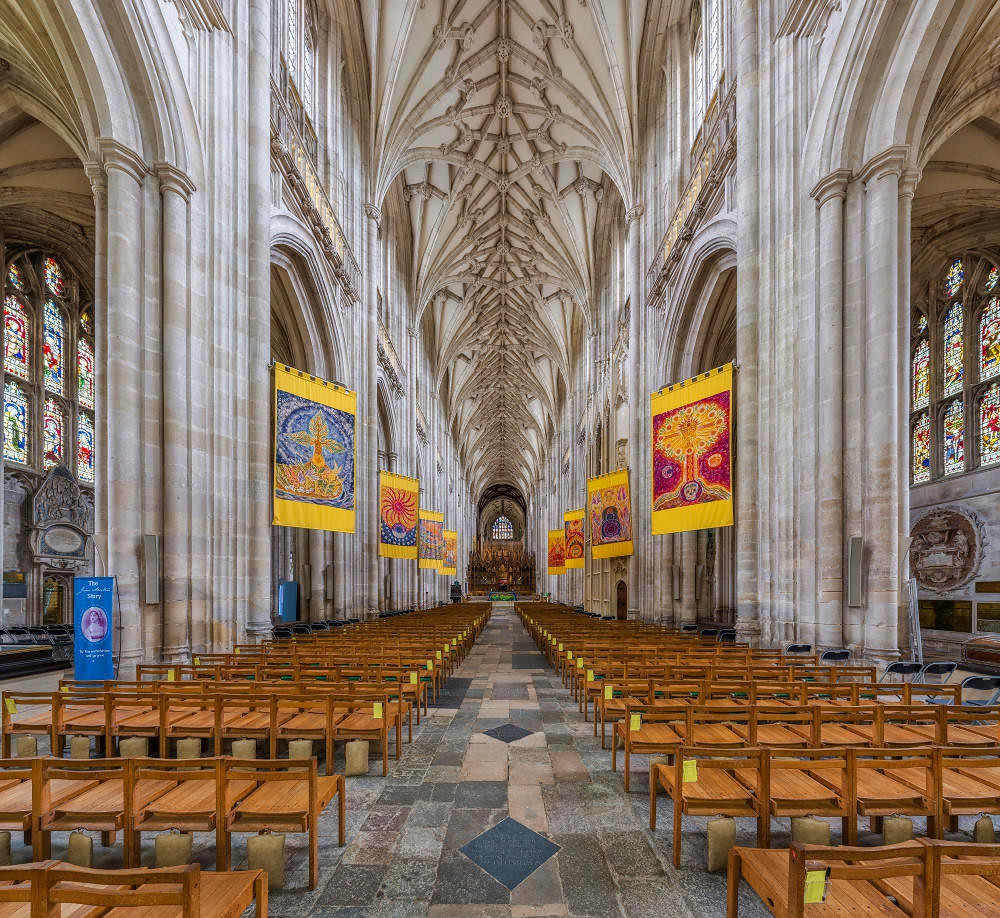
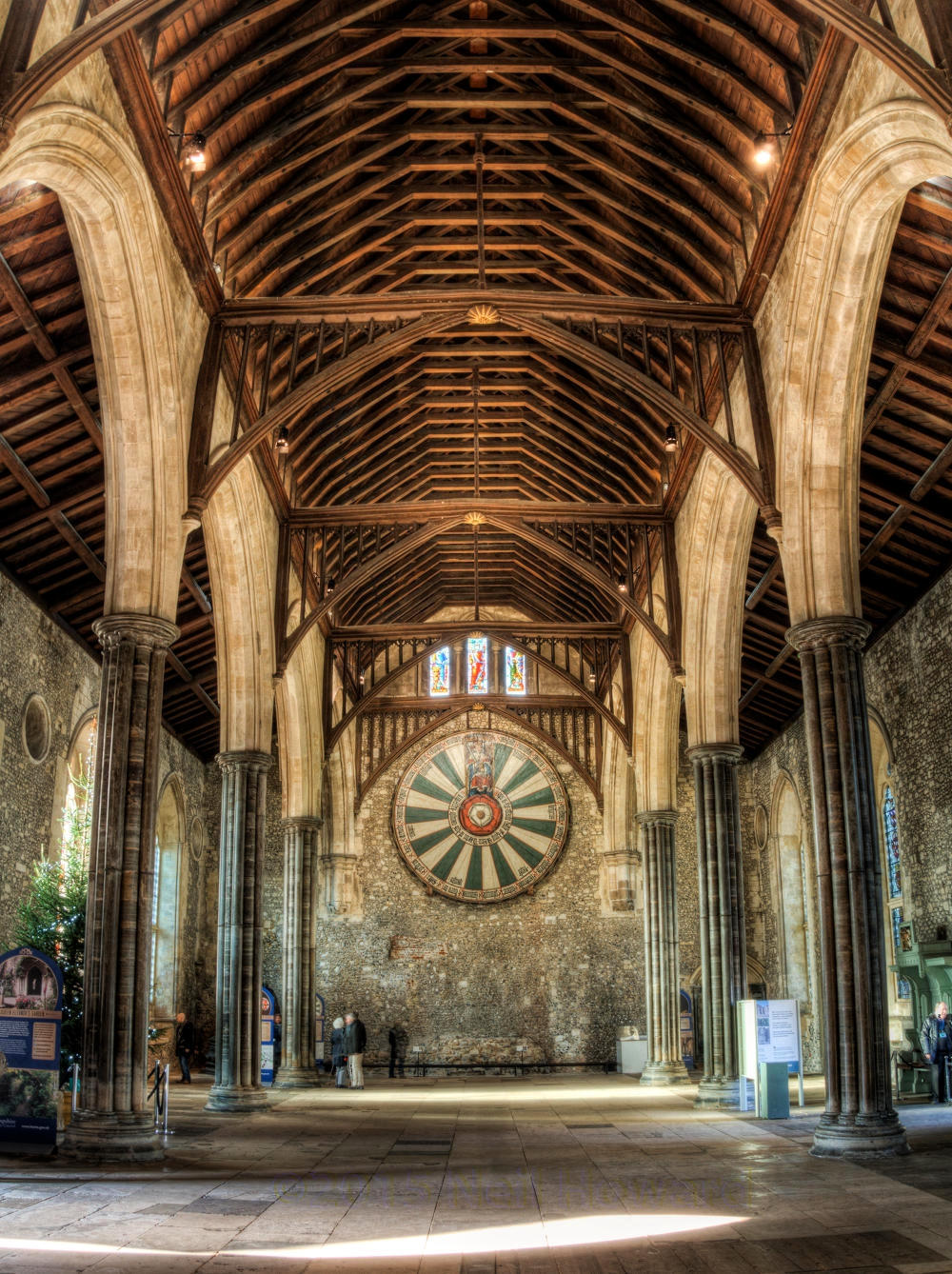
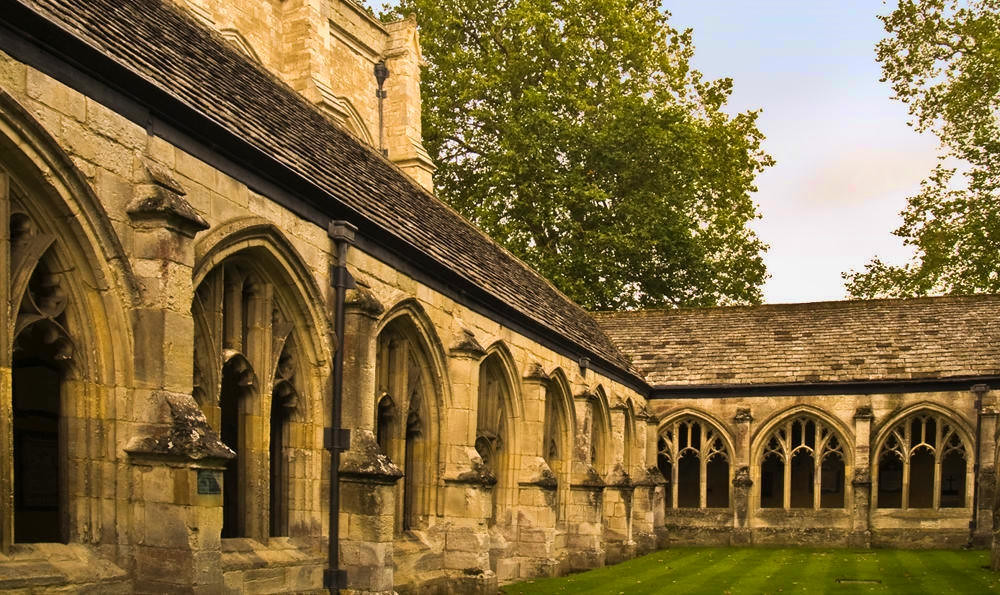
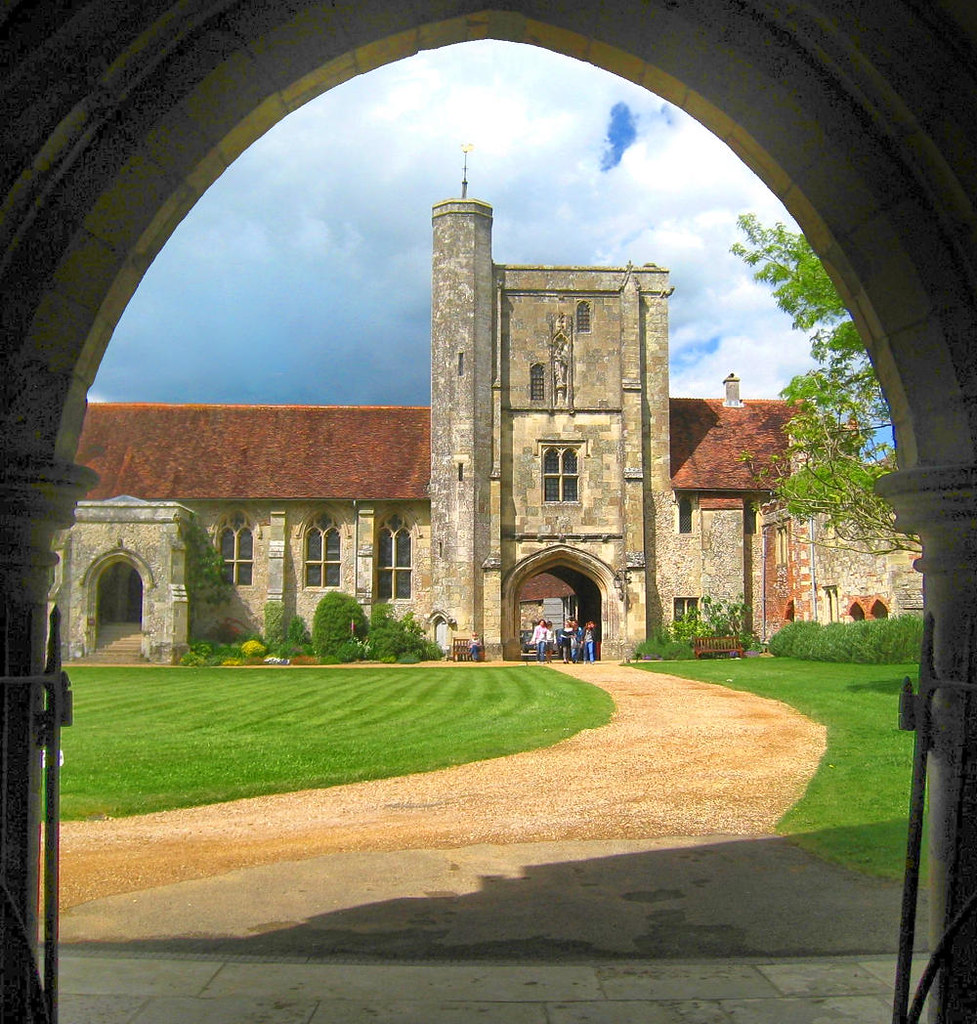
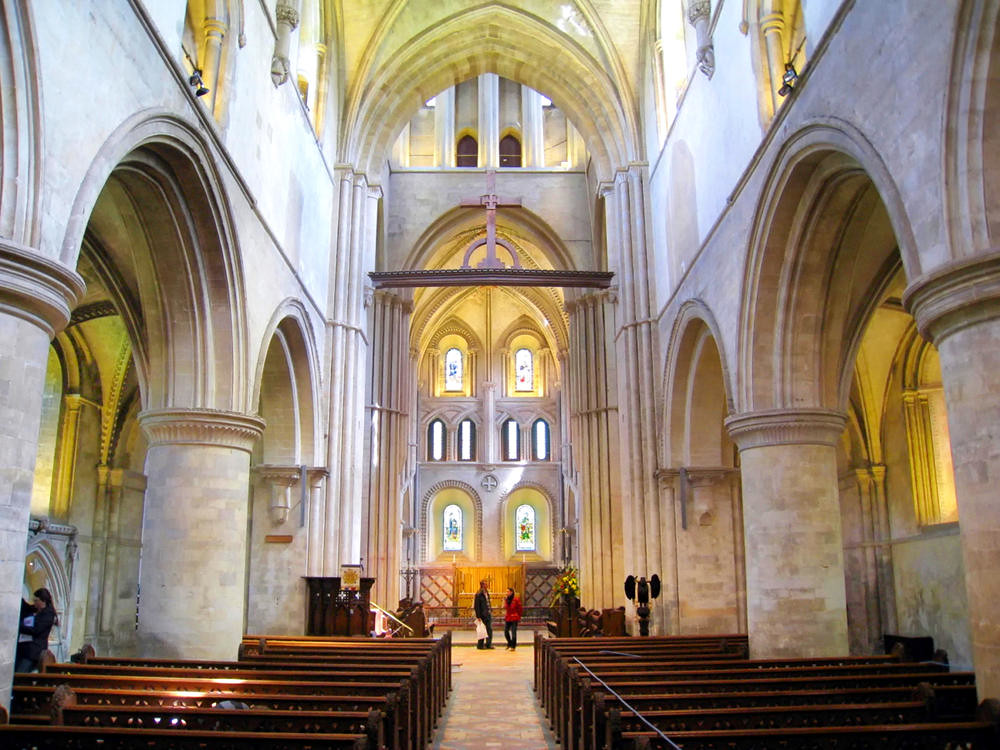
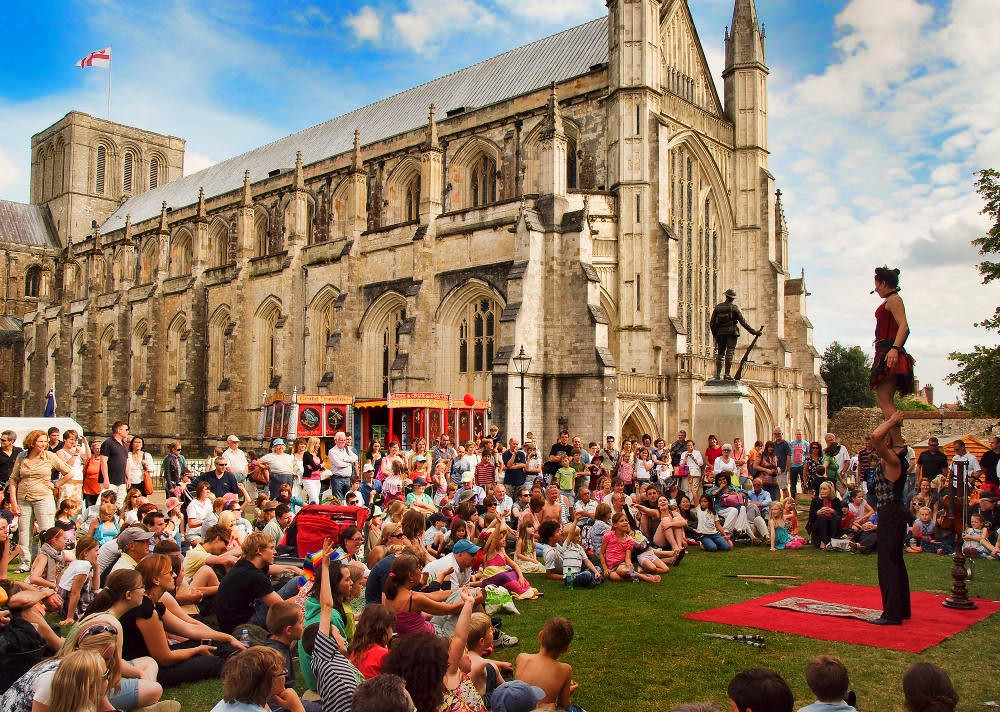
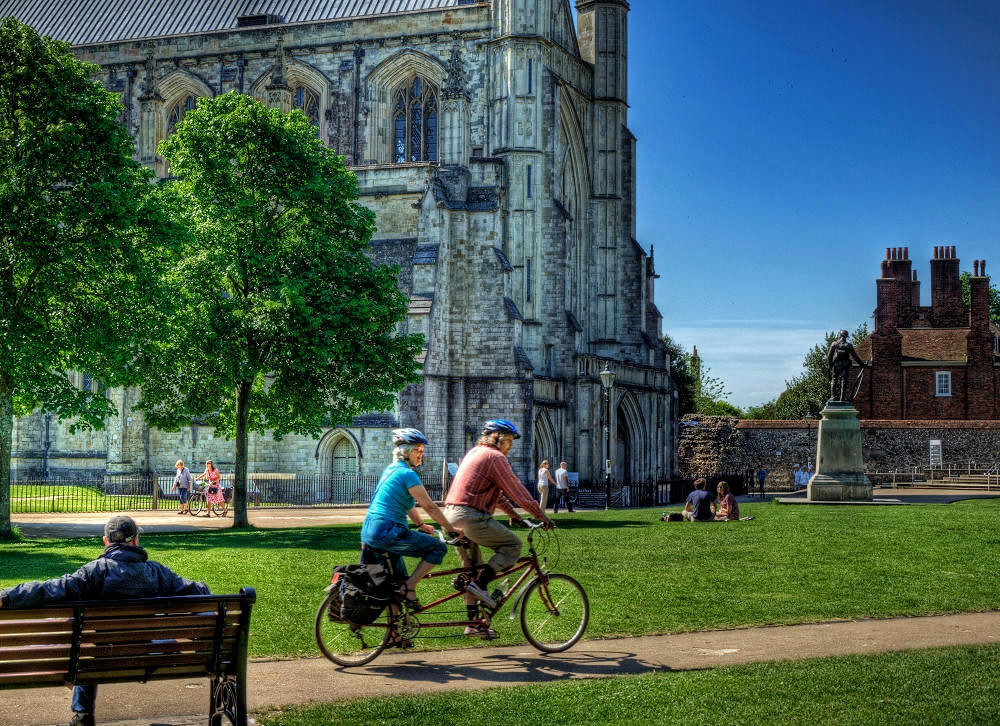
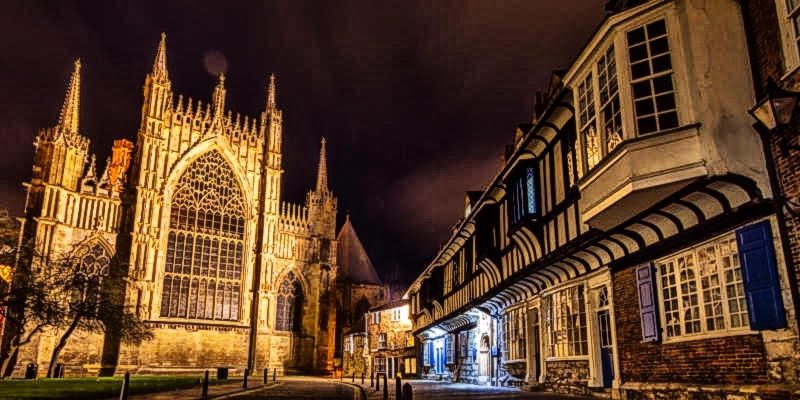
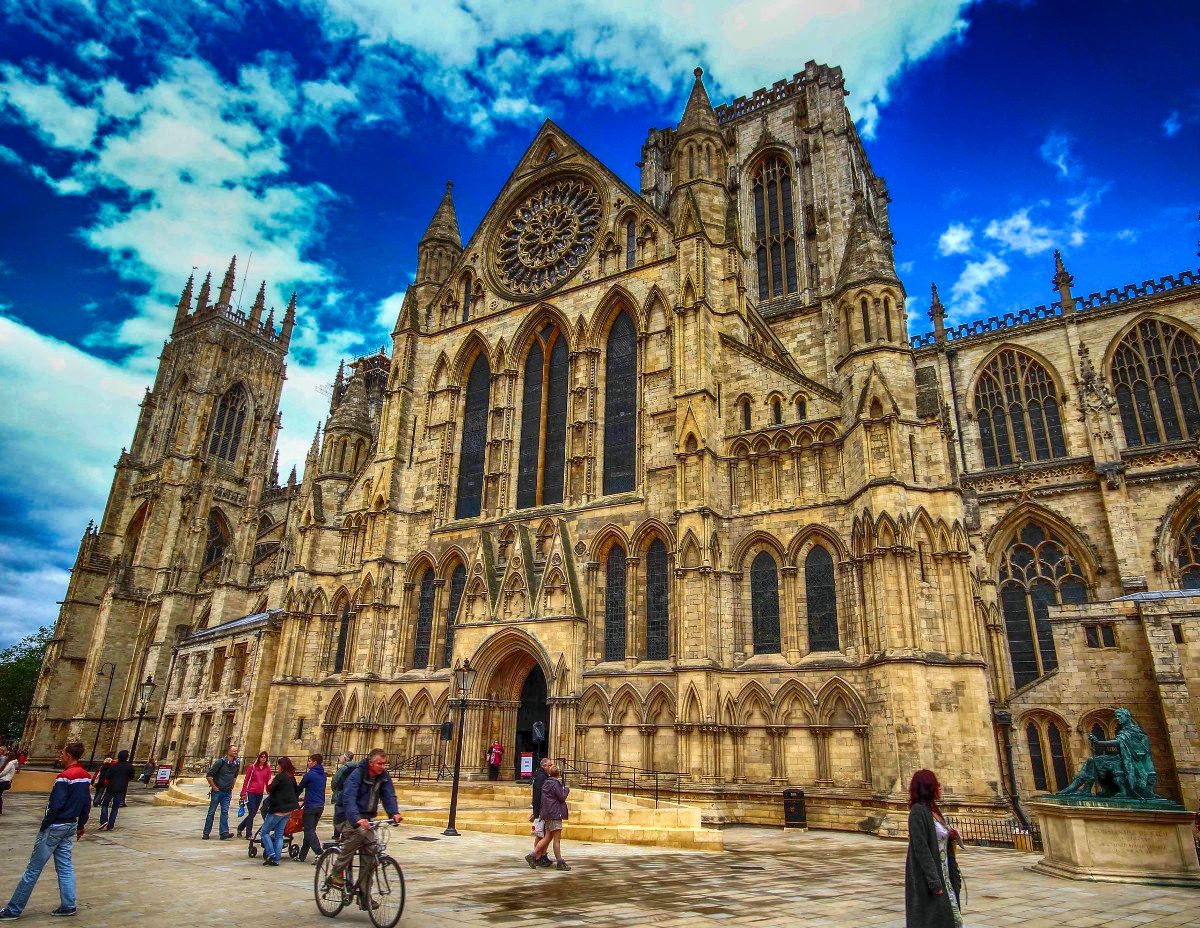
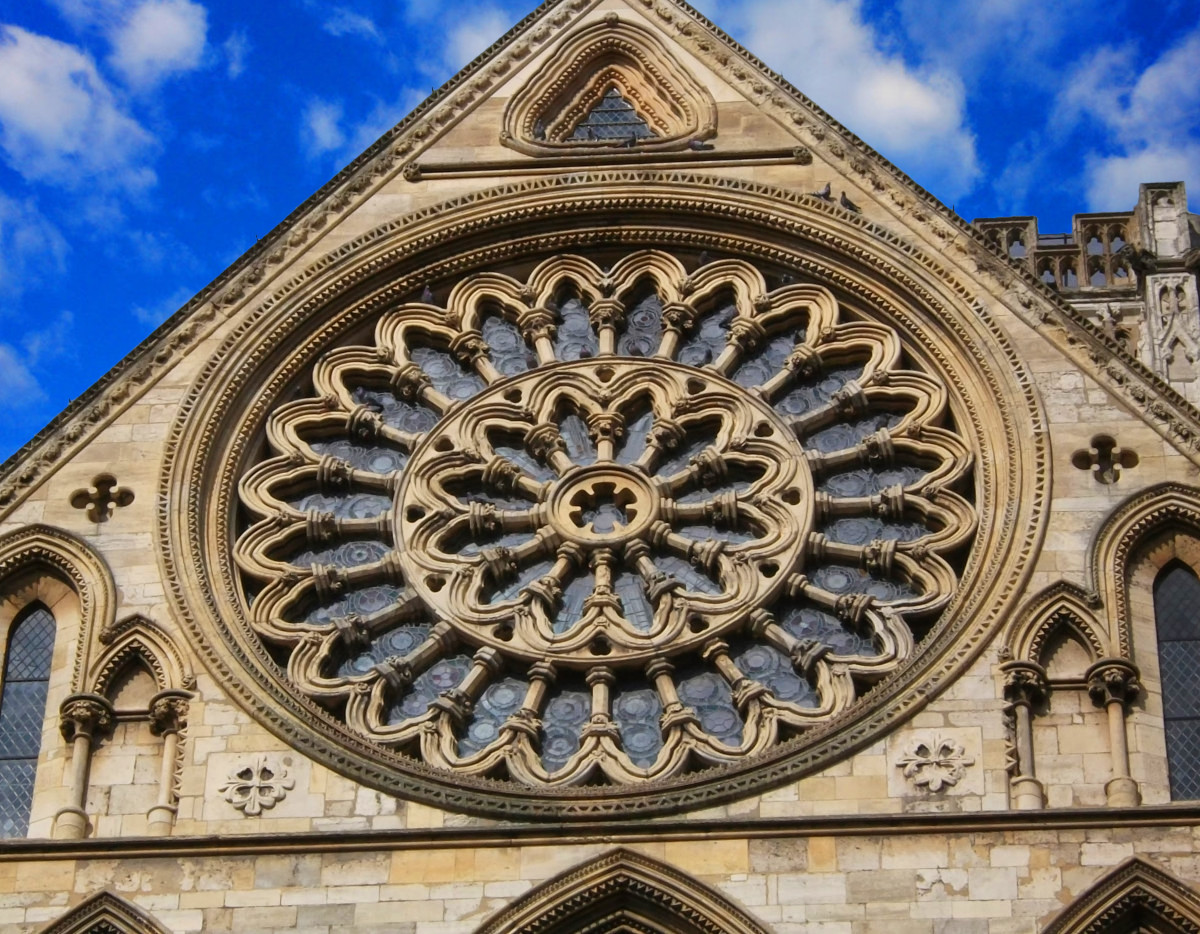
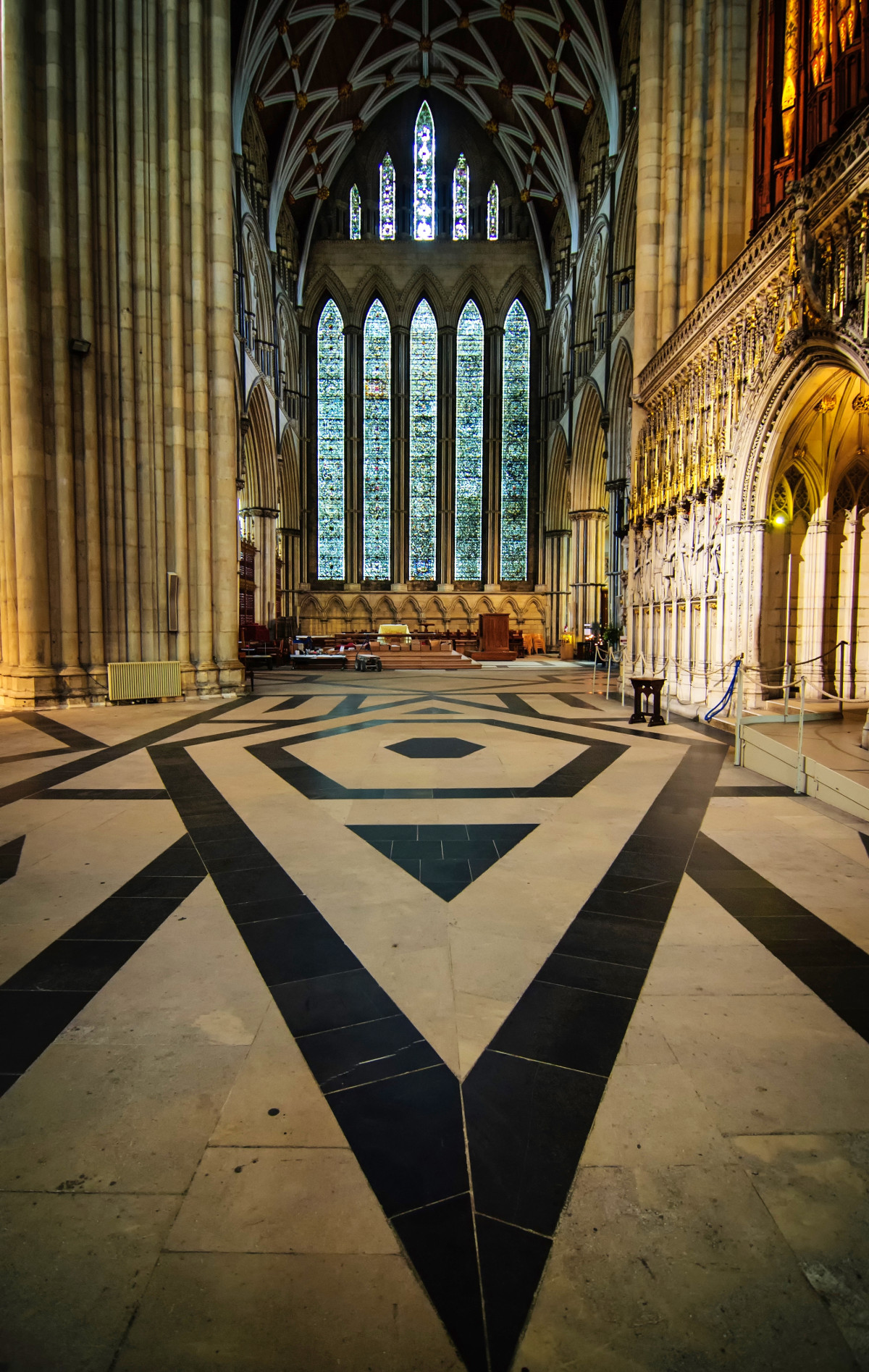
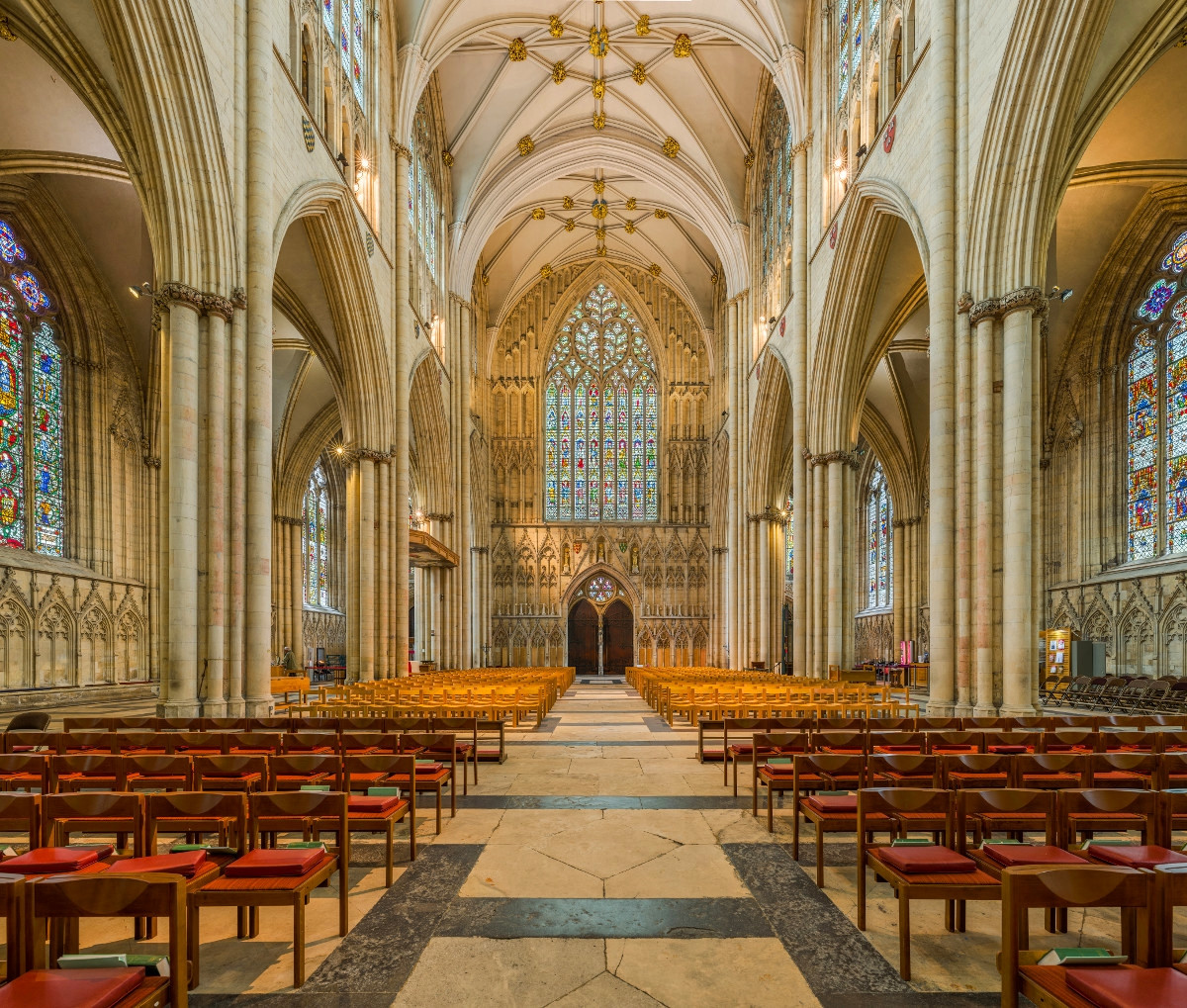
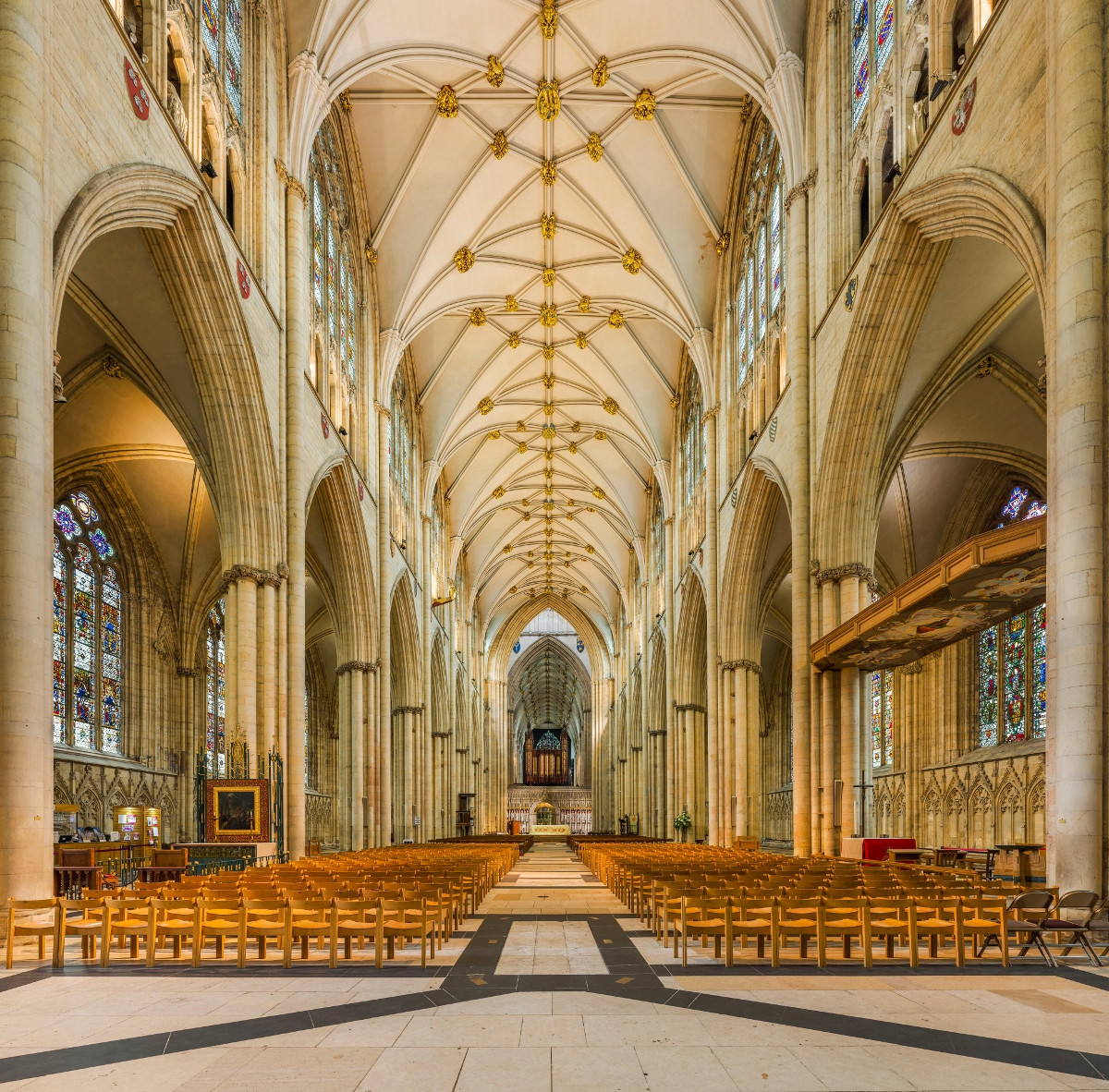
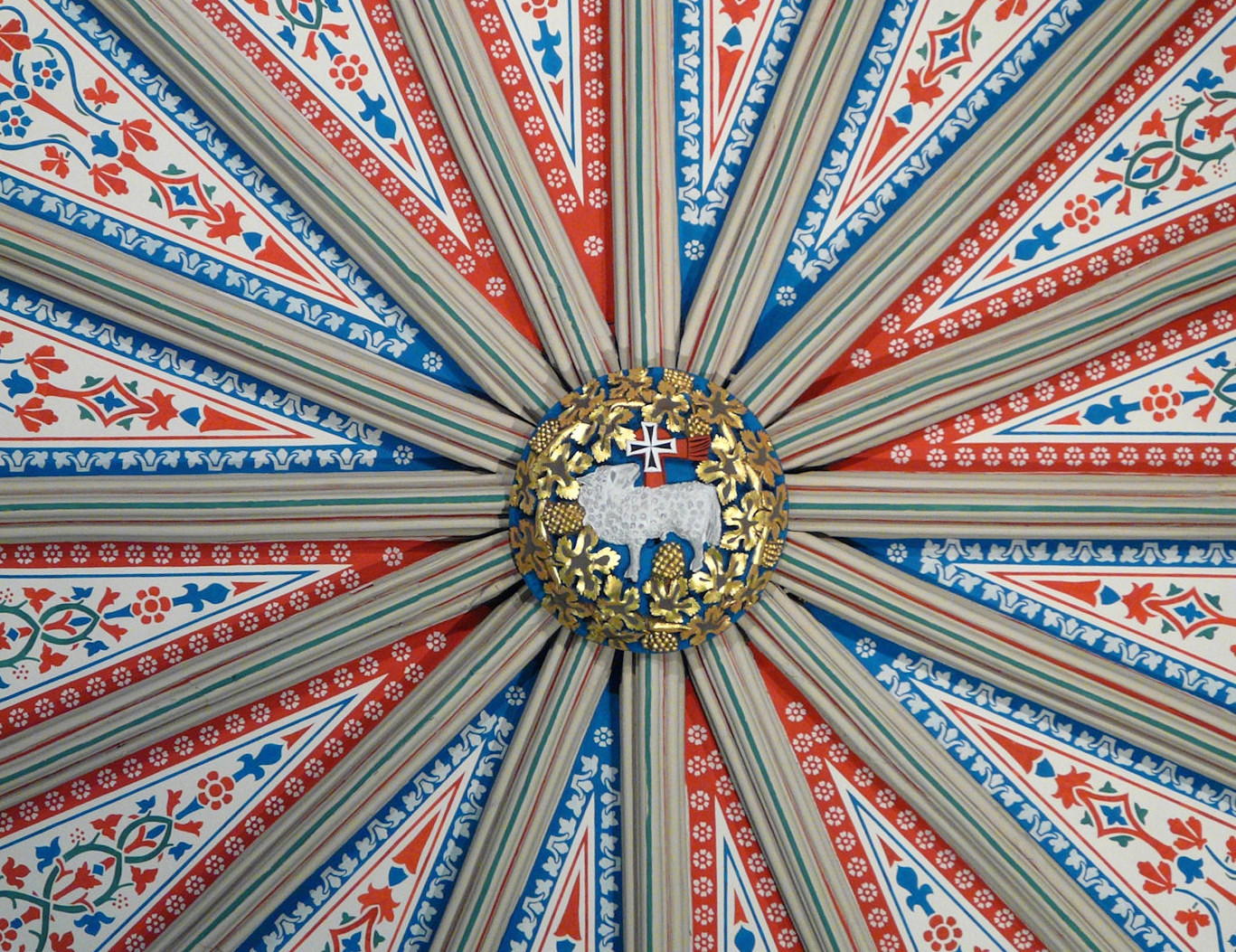
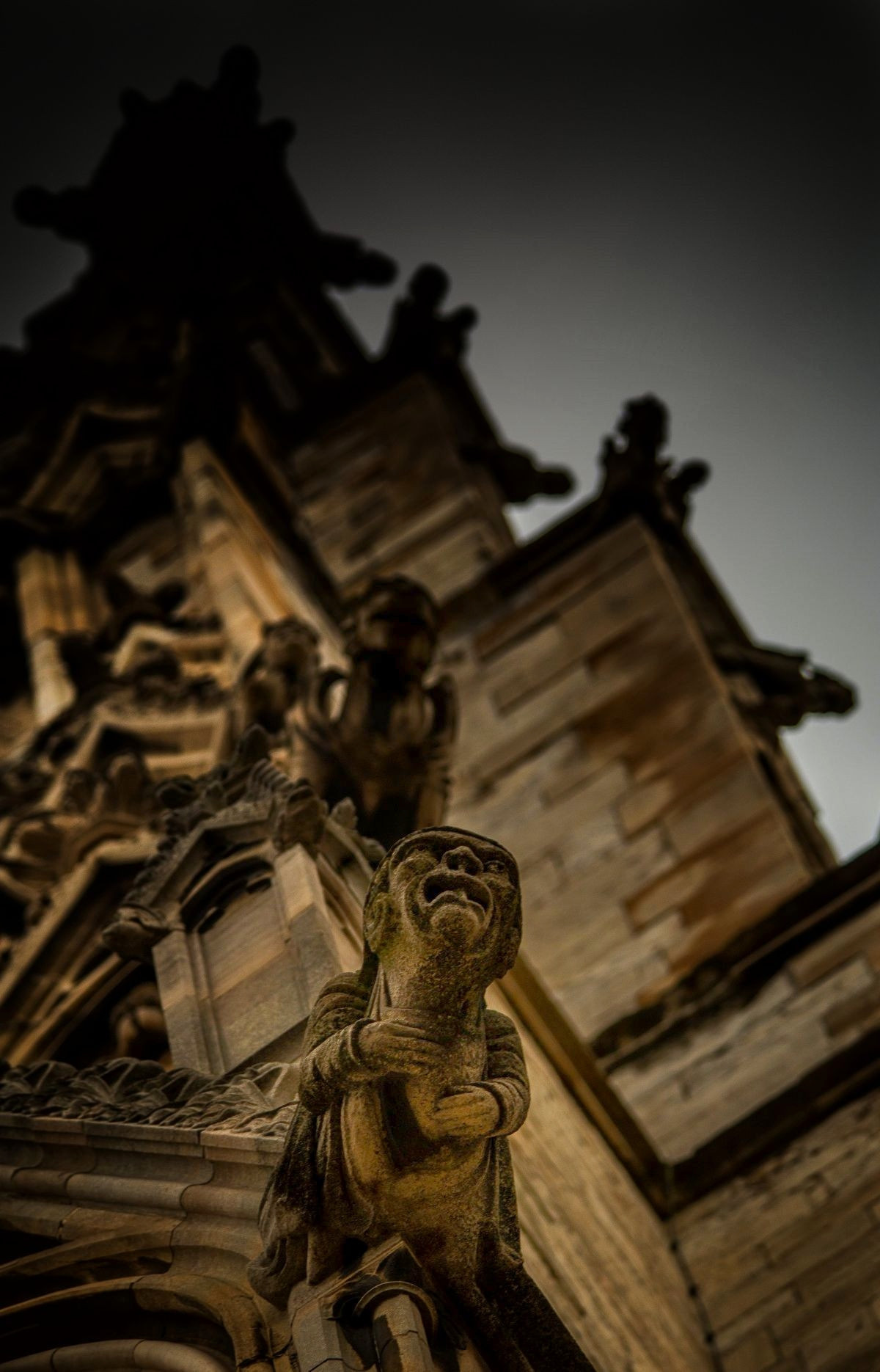
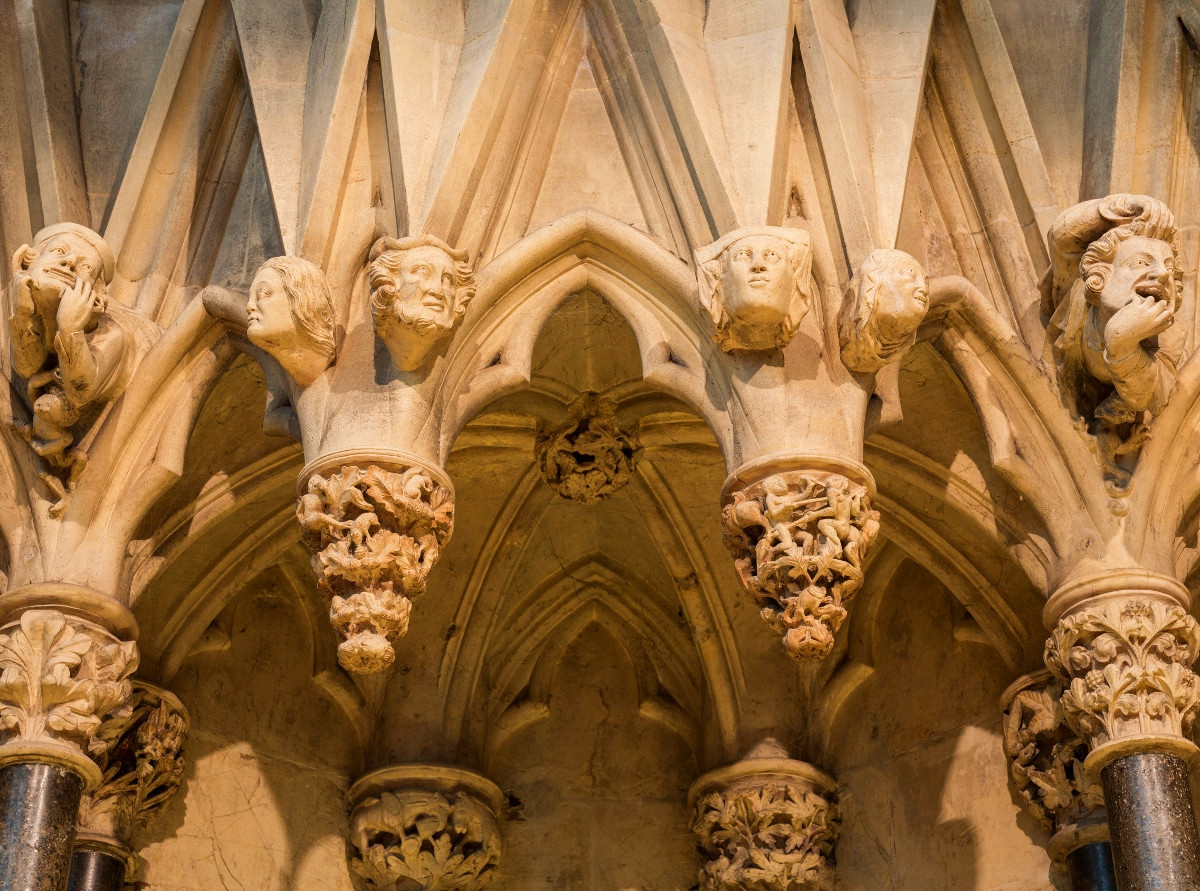
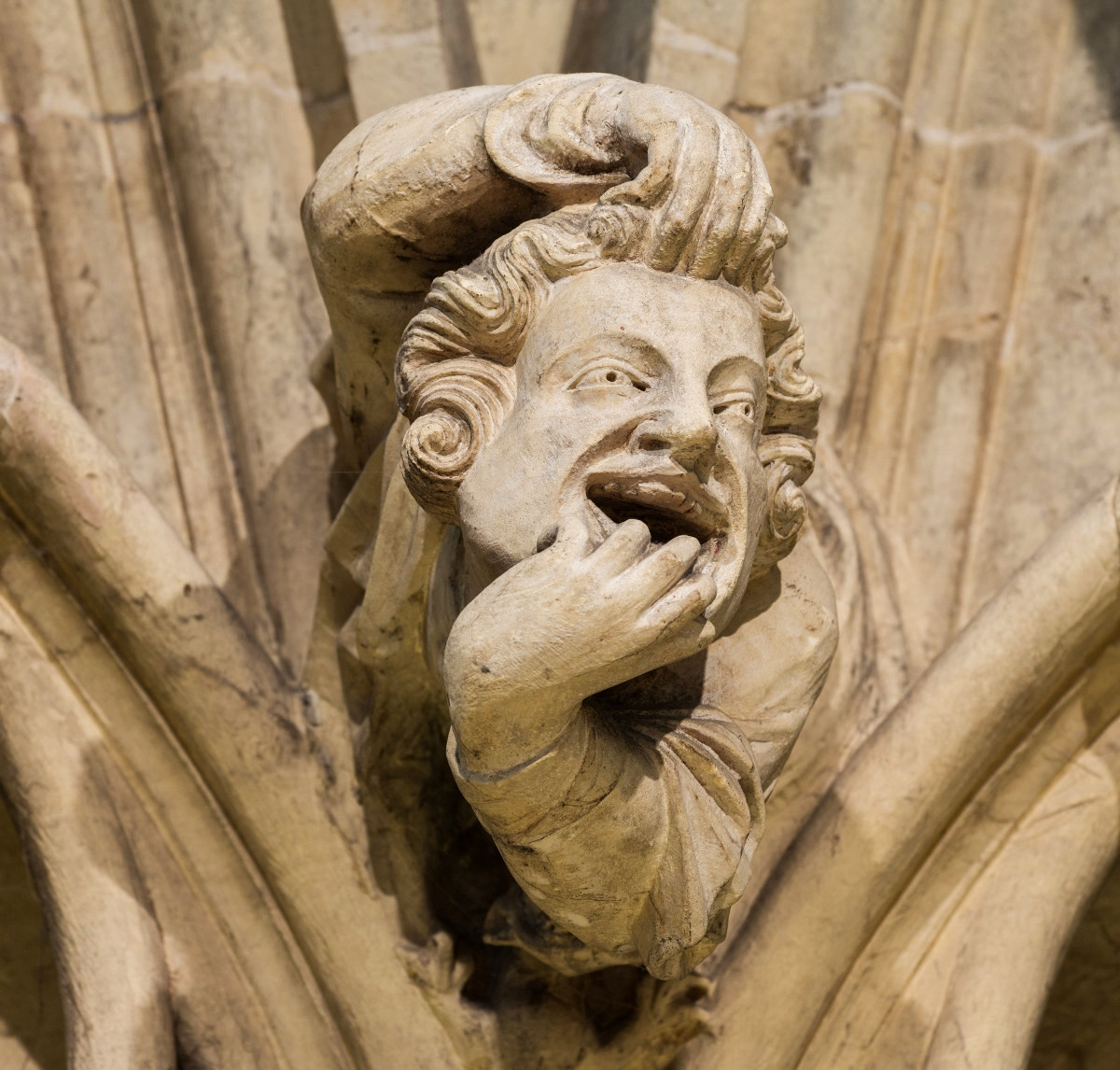
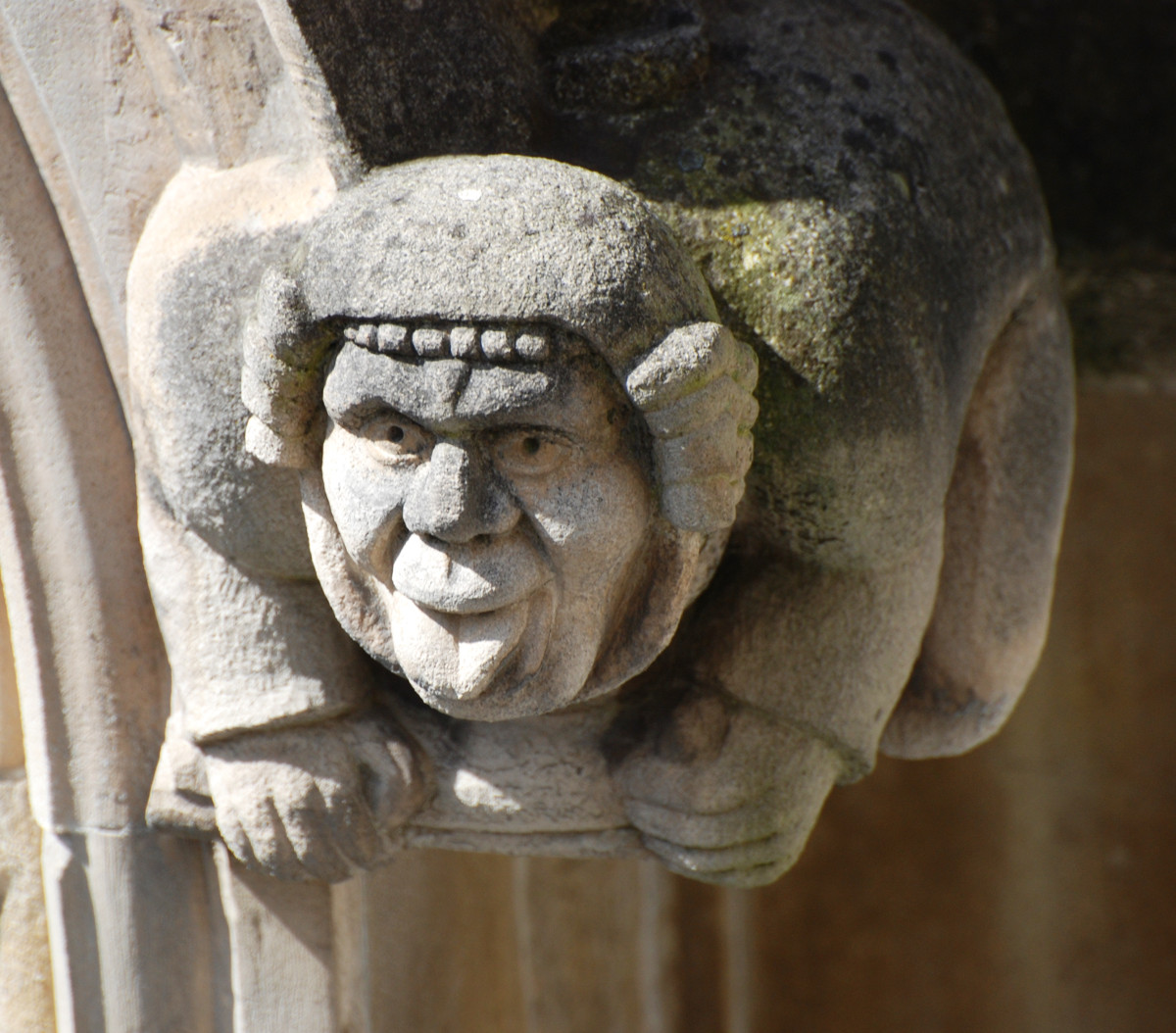
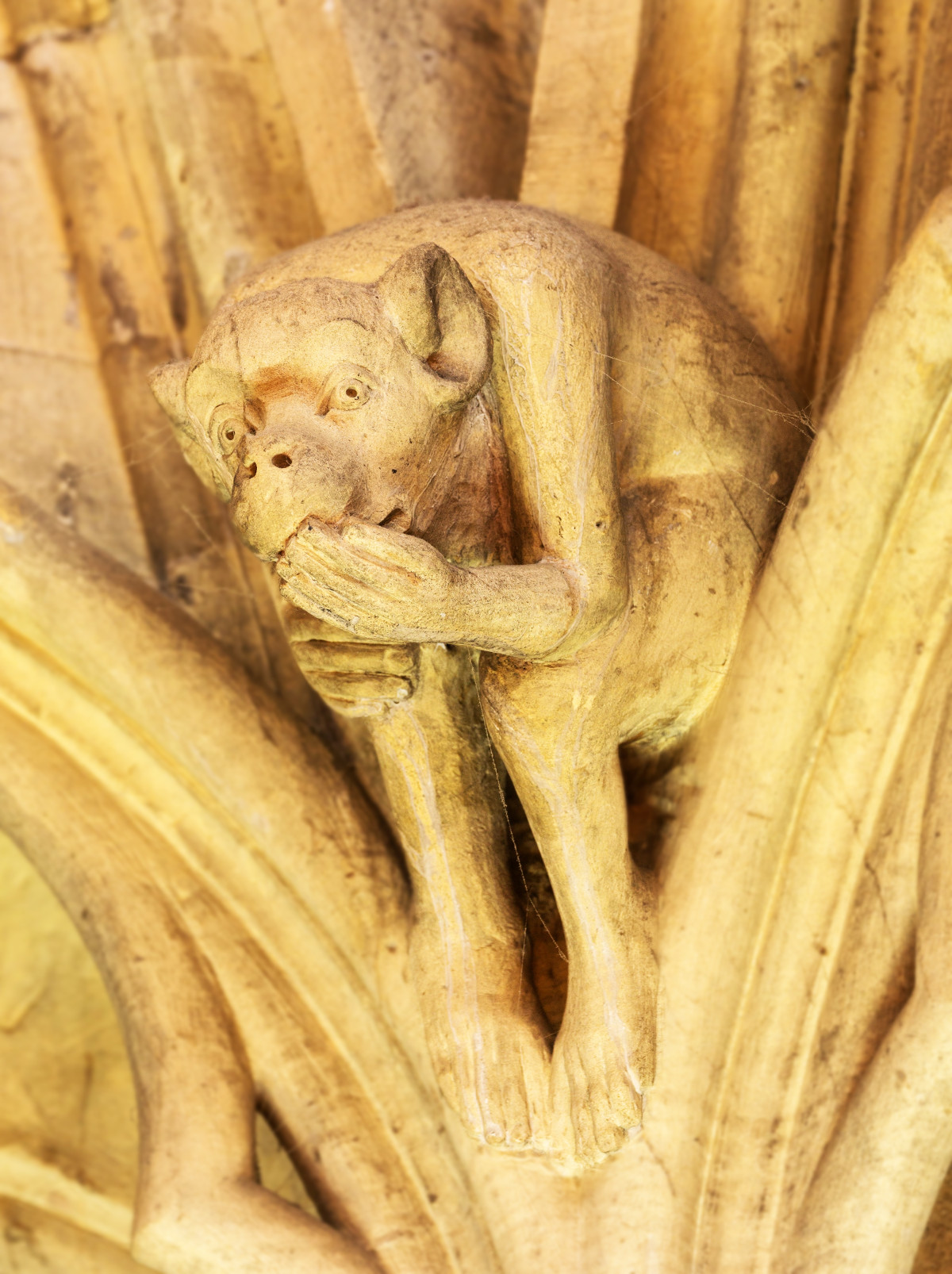
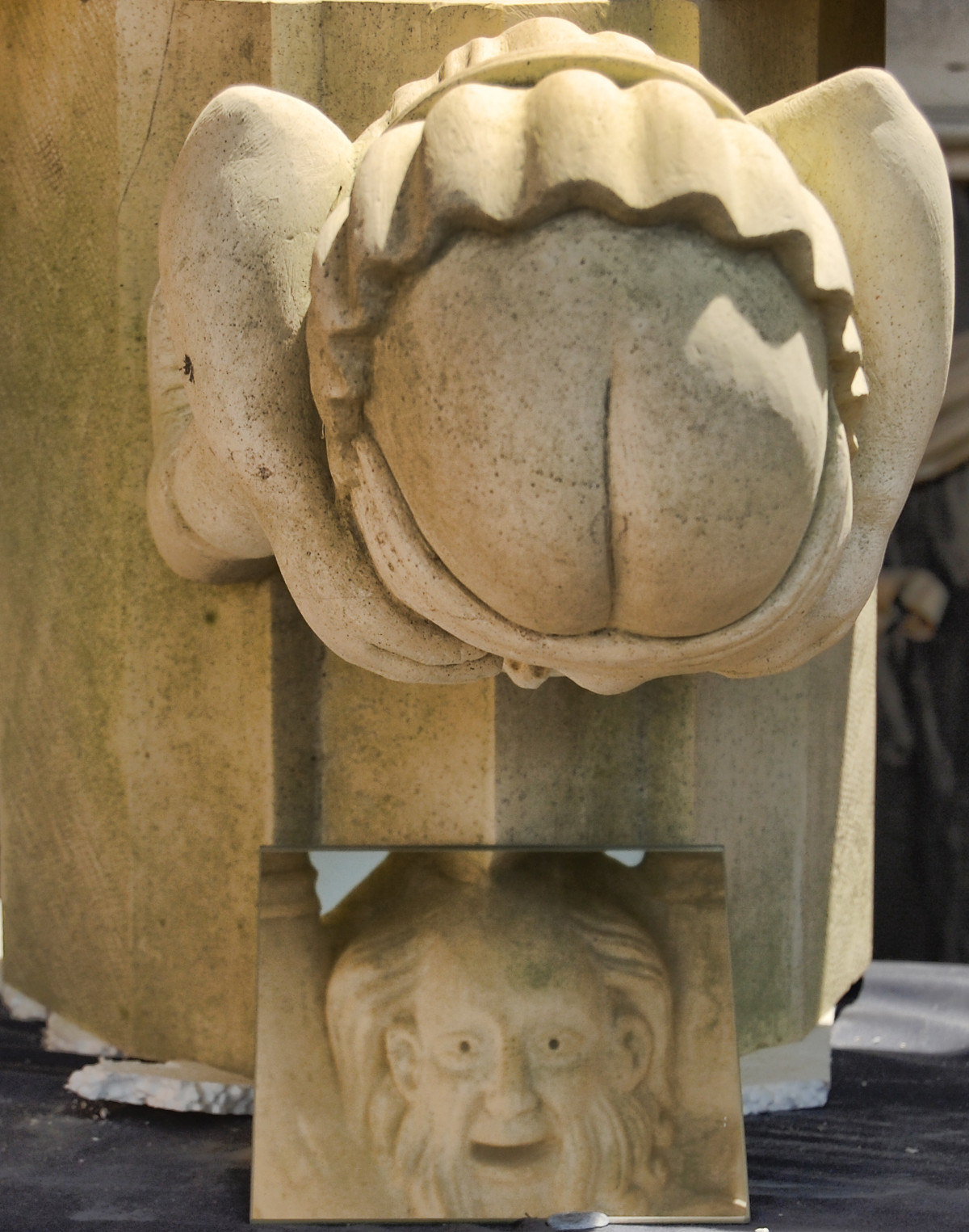
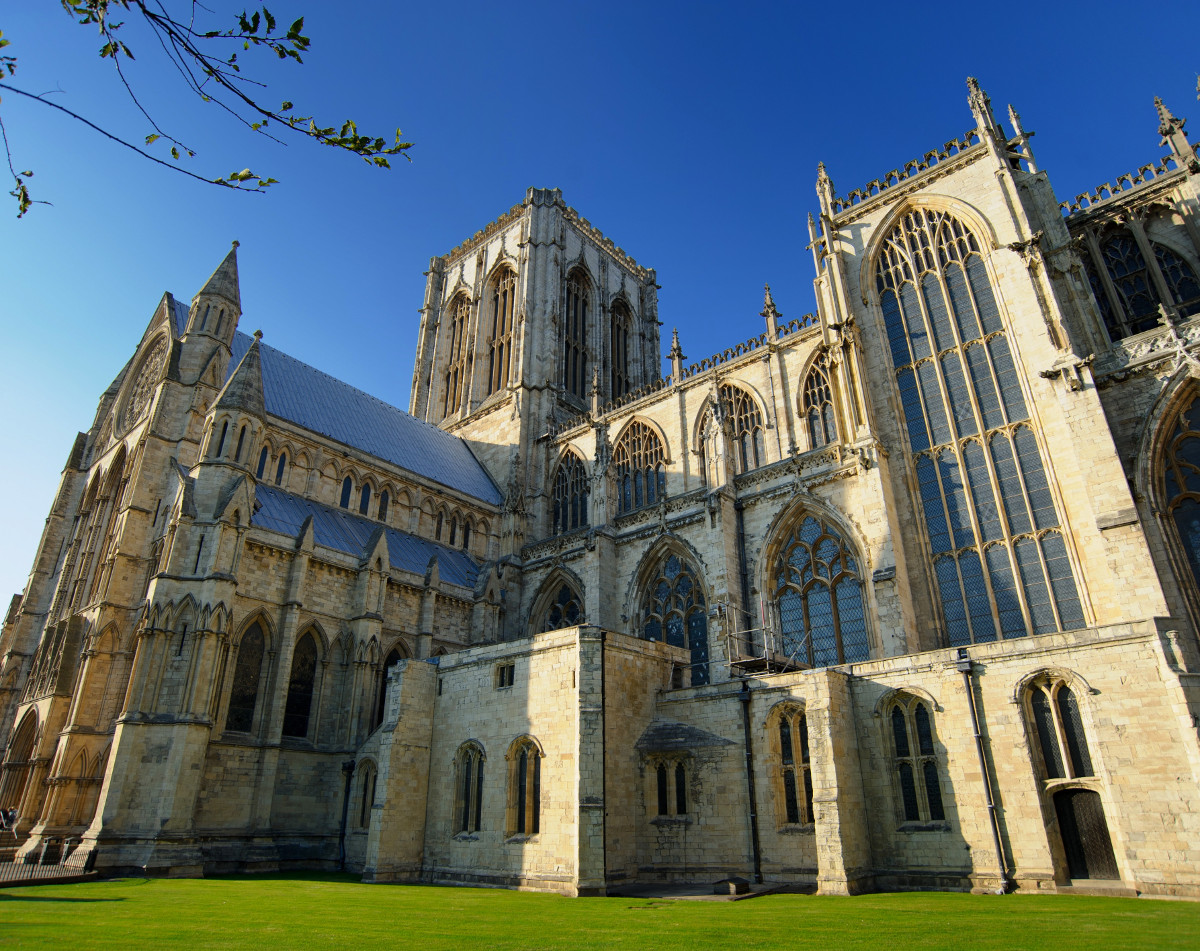
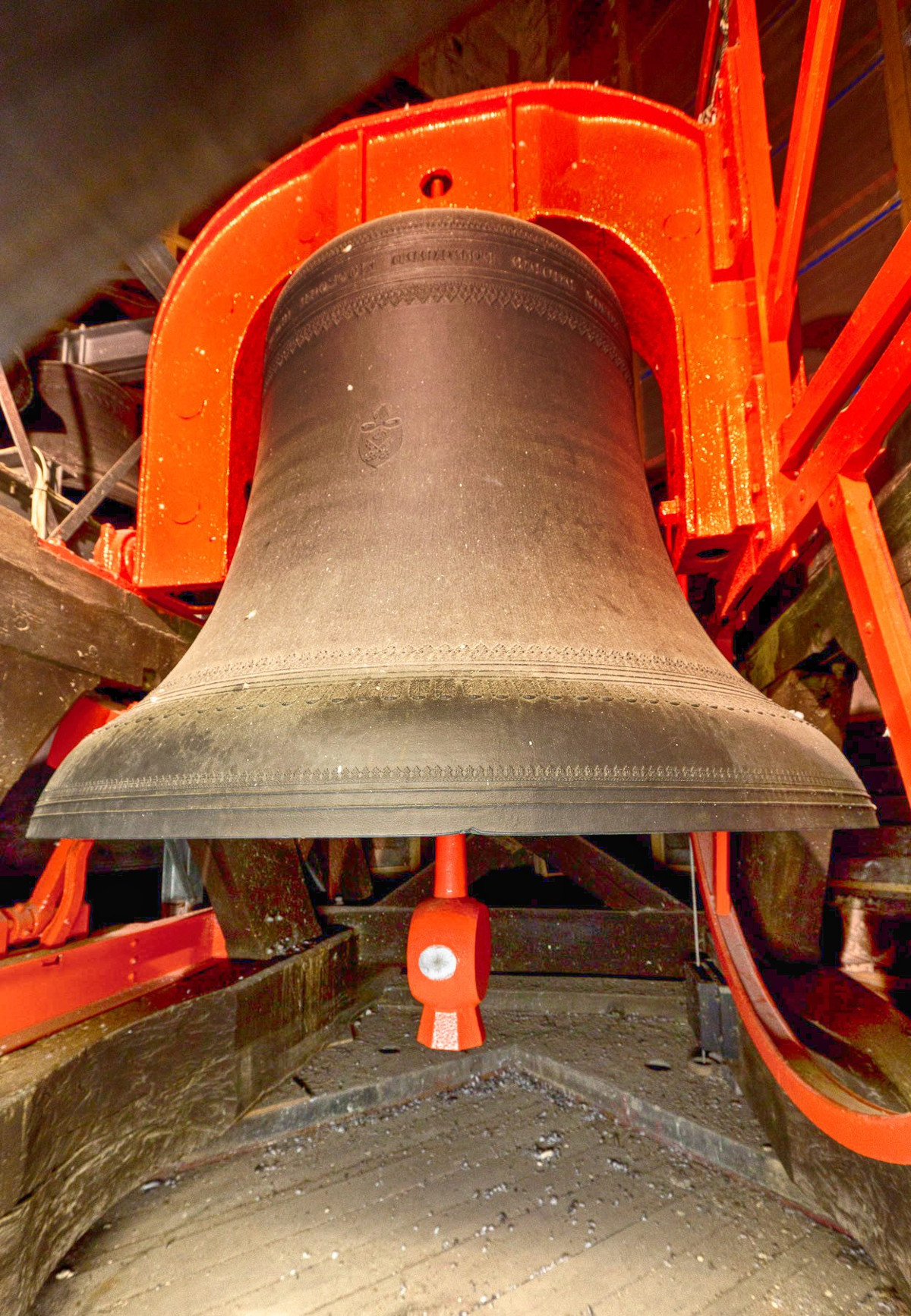
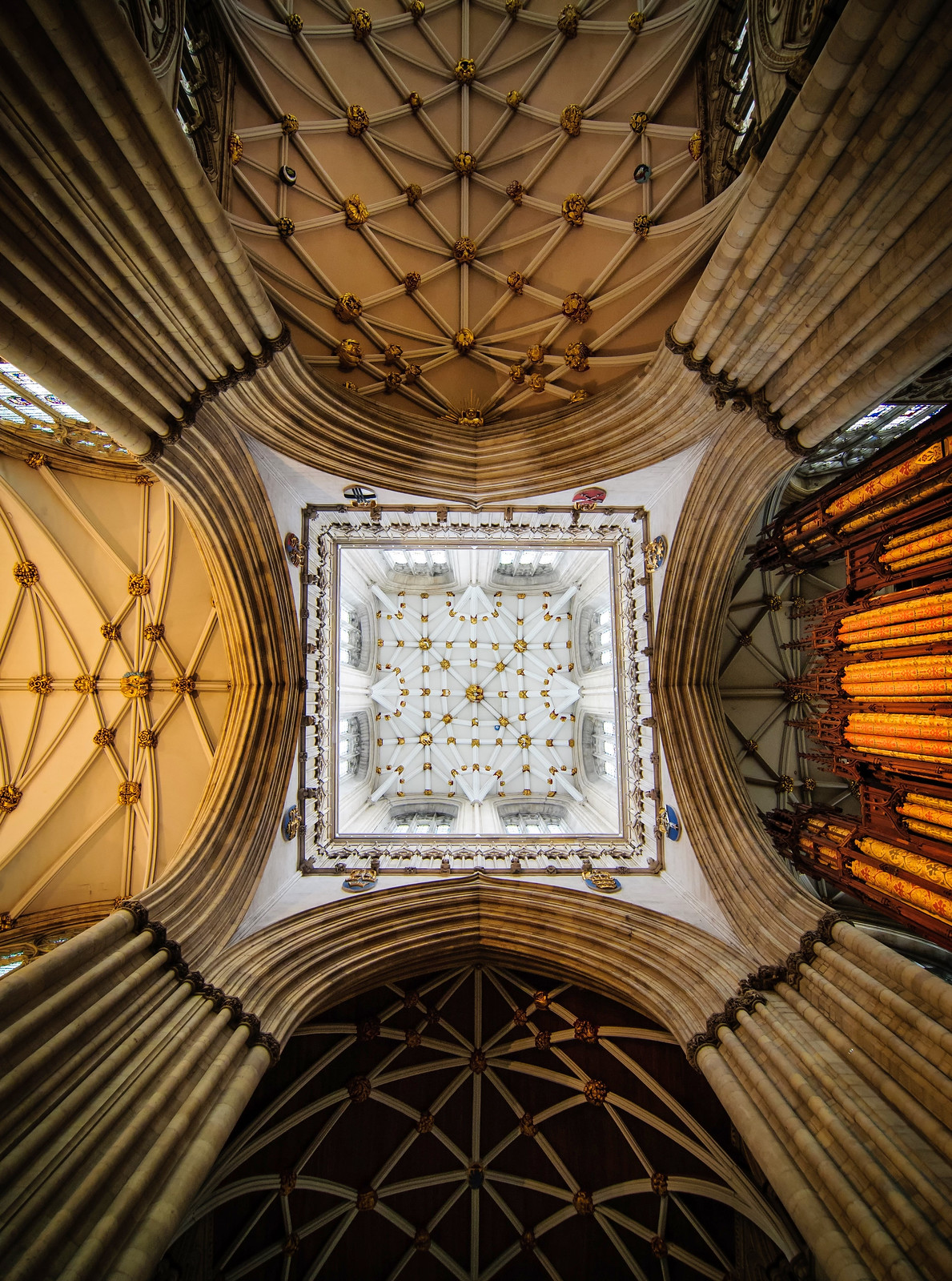
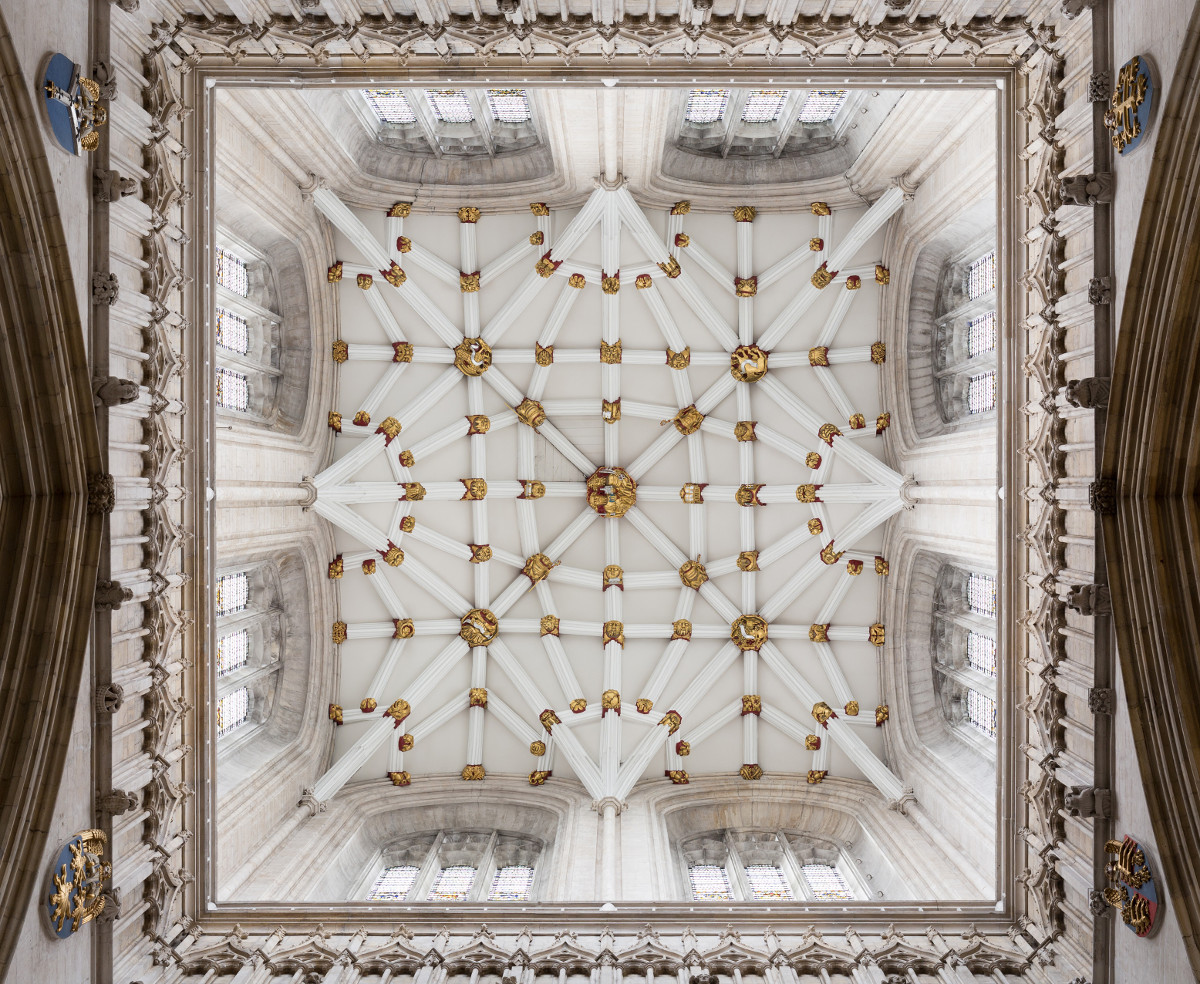
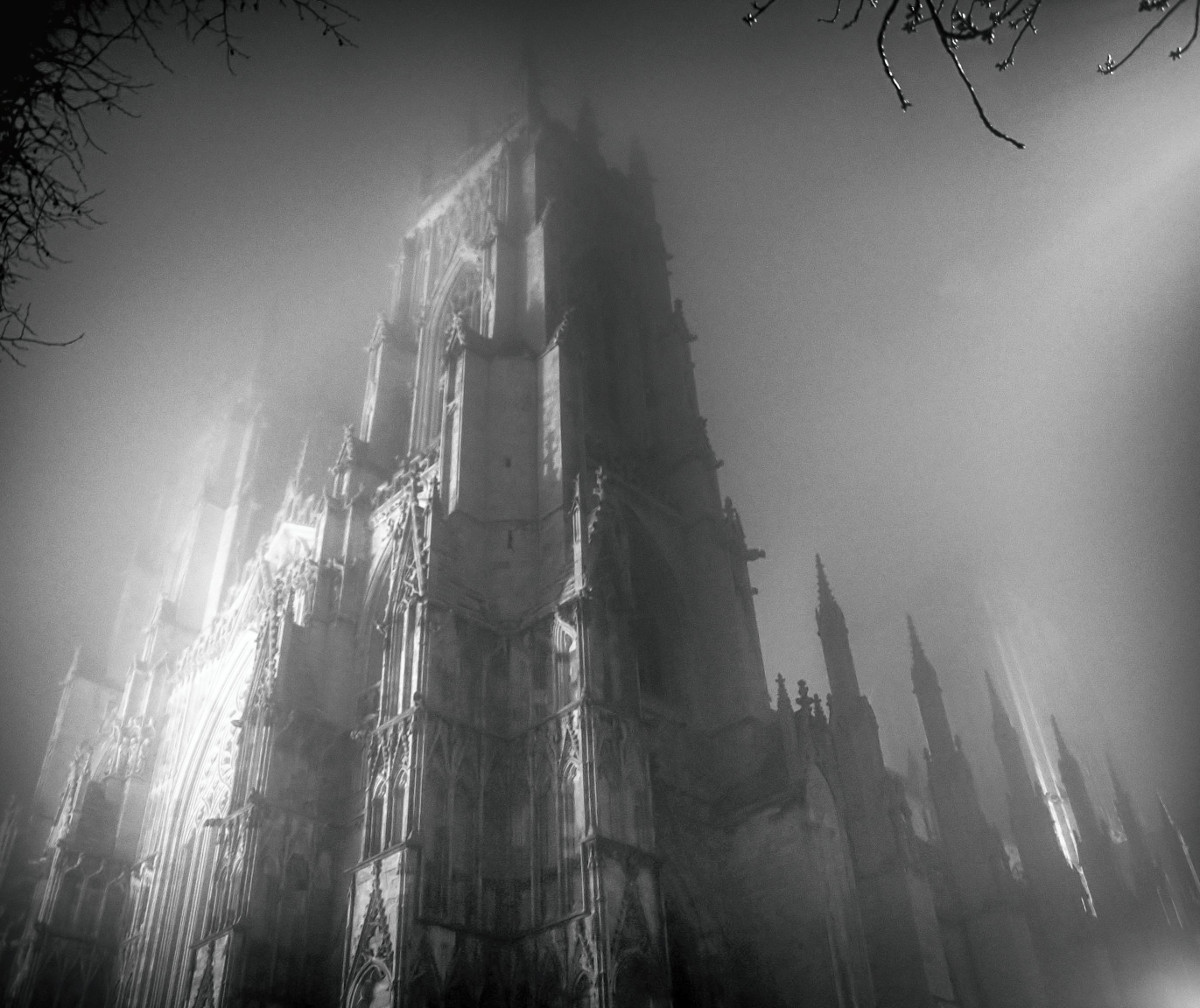
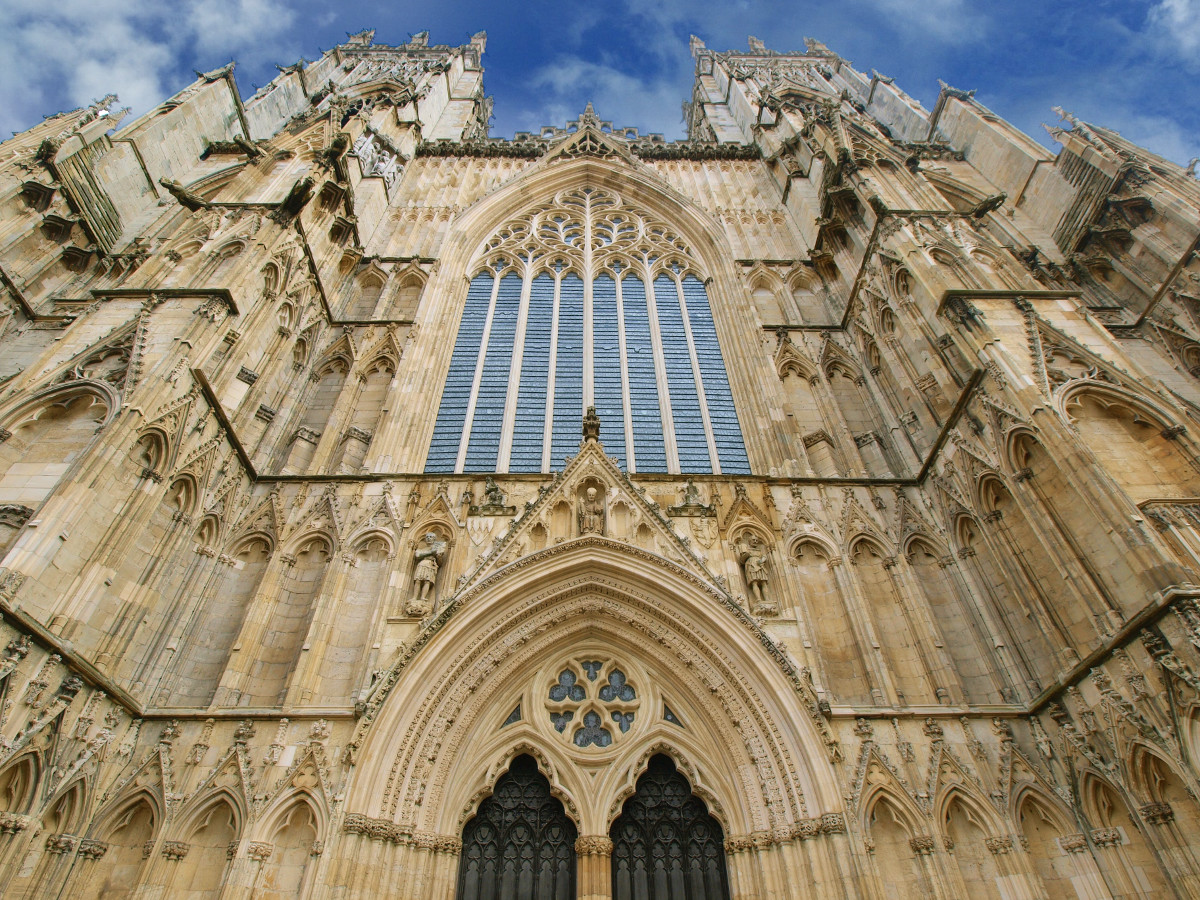
Gloucester’s Medieval Gothic Cathedral
Originating in the 7th century as a church for the abbey dedicated to Saint Peter, Gloucester Cathedral has a Norman core with a 15th-century tower rising 225ft and topped by four delicate pinnacles—a local landmark visible for miles.
The cathedral cloisters were used for corridor scenes in several Harry Potter films, whilst the crypt featured in Sherlock’s Christmas special.
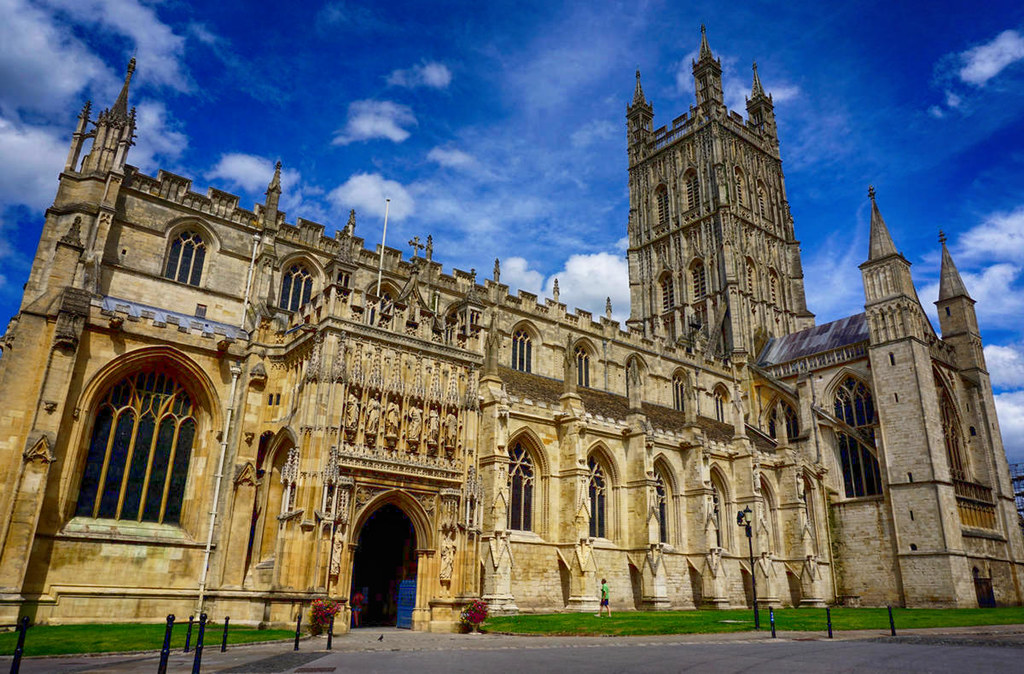

At over 1000 years old, Gloucester Cathedral is the oldest building in the world to have a solar array installed to reduce energy costs.
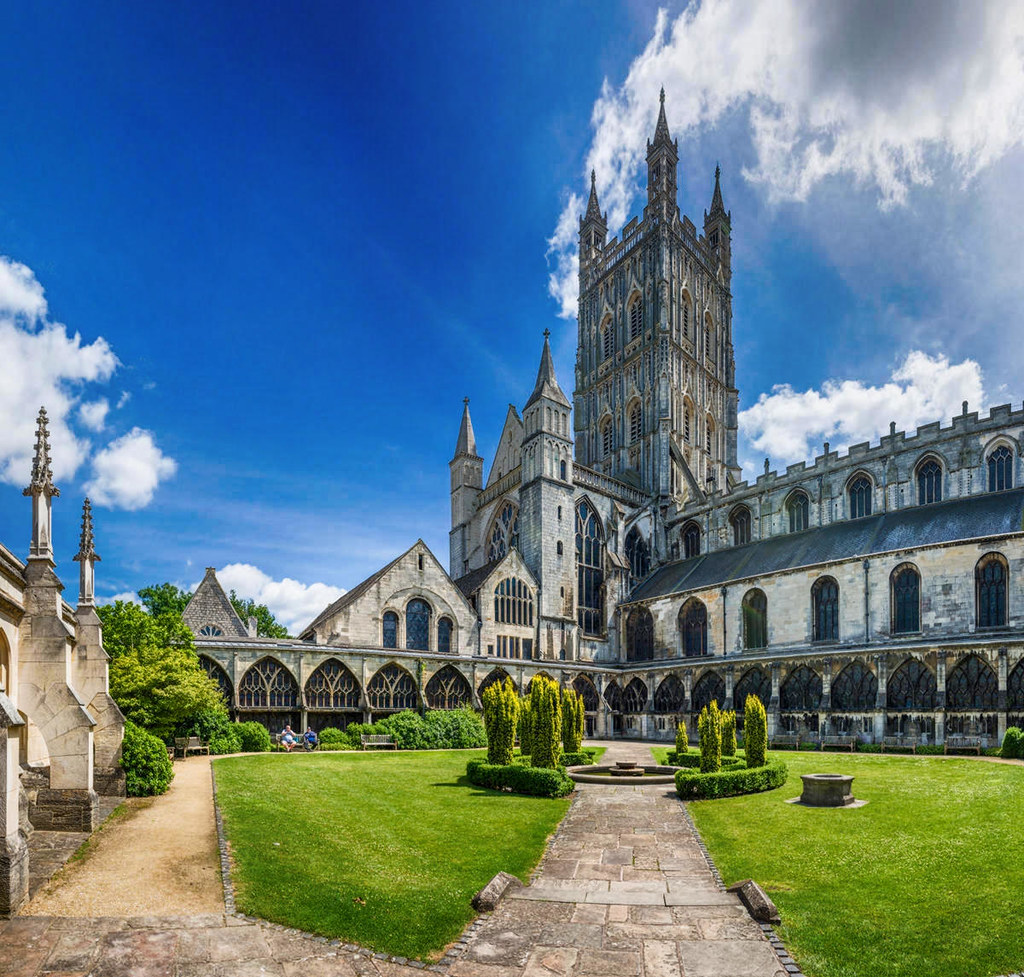
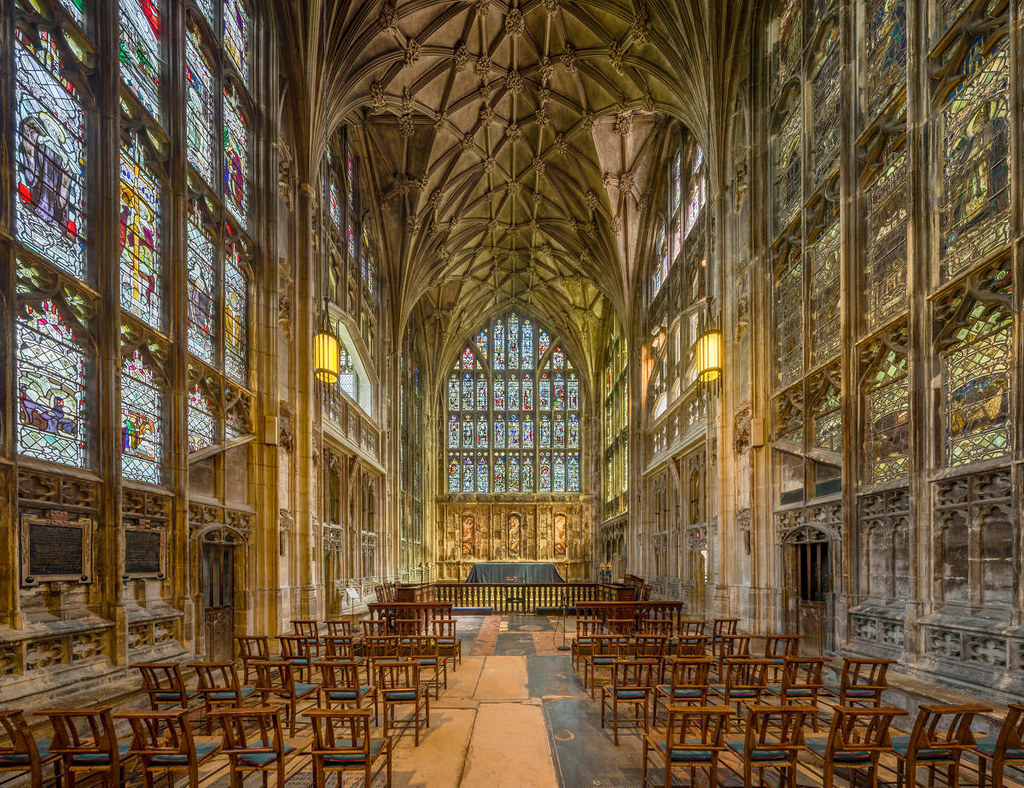


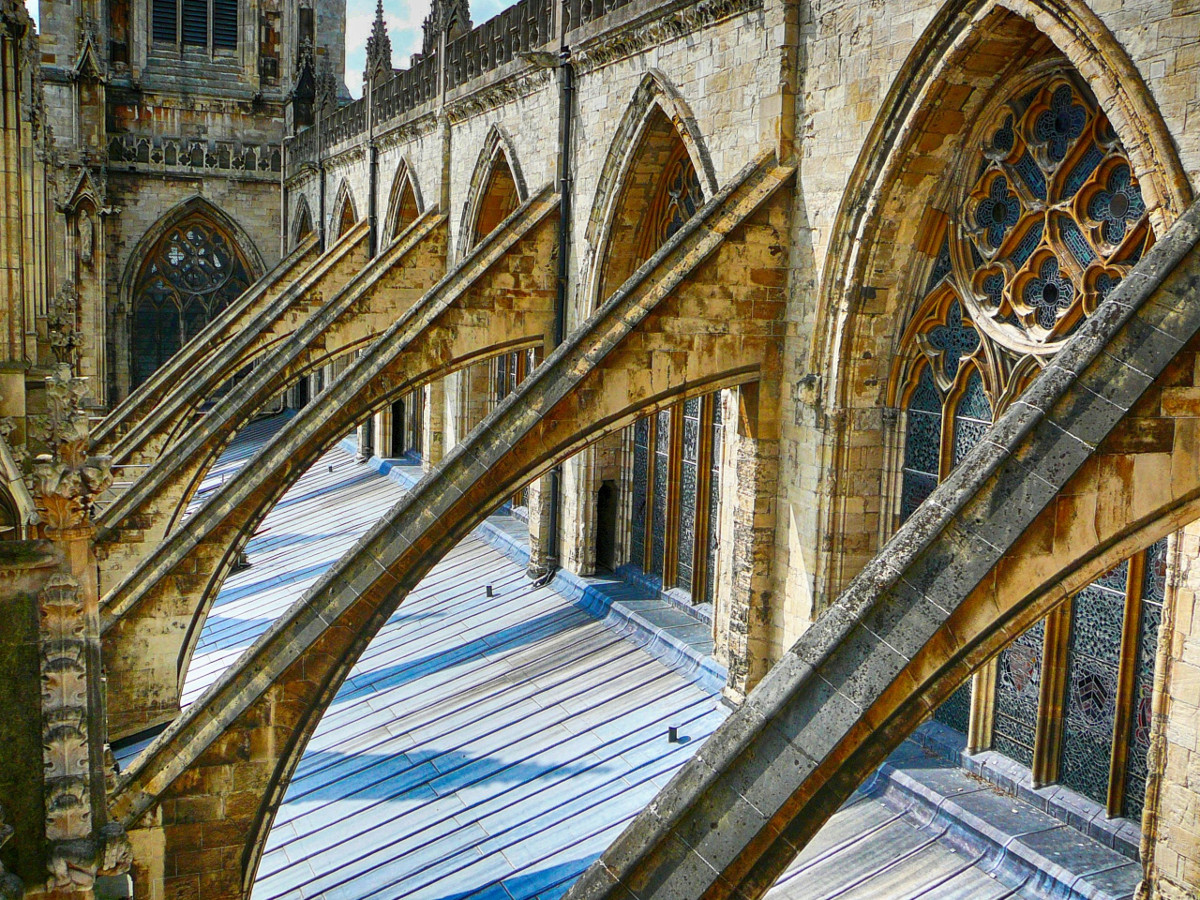
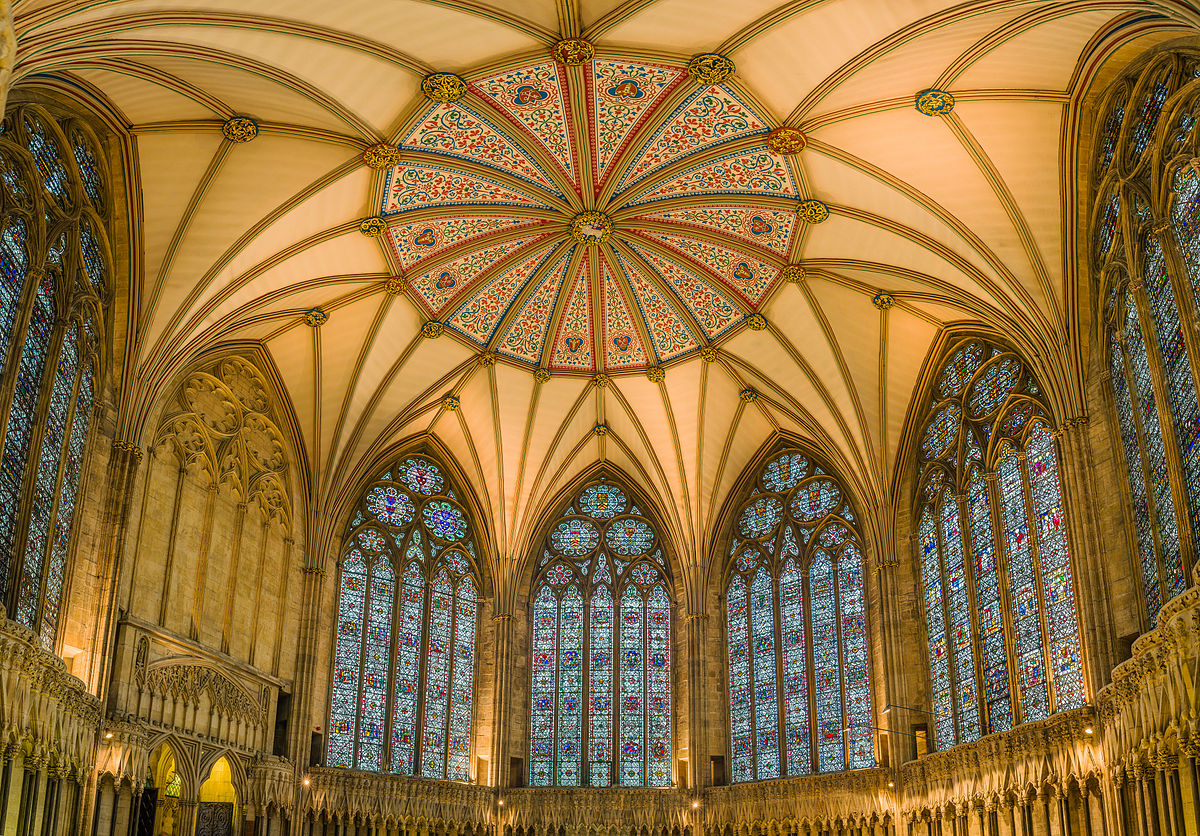
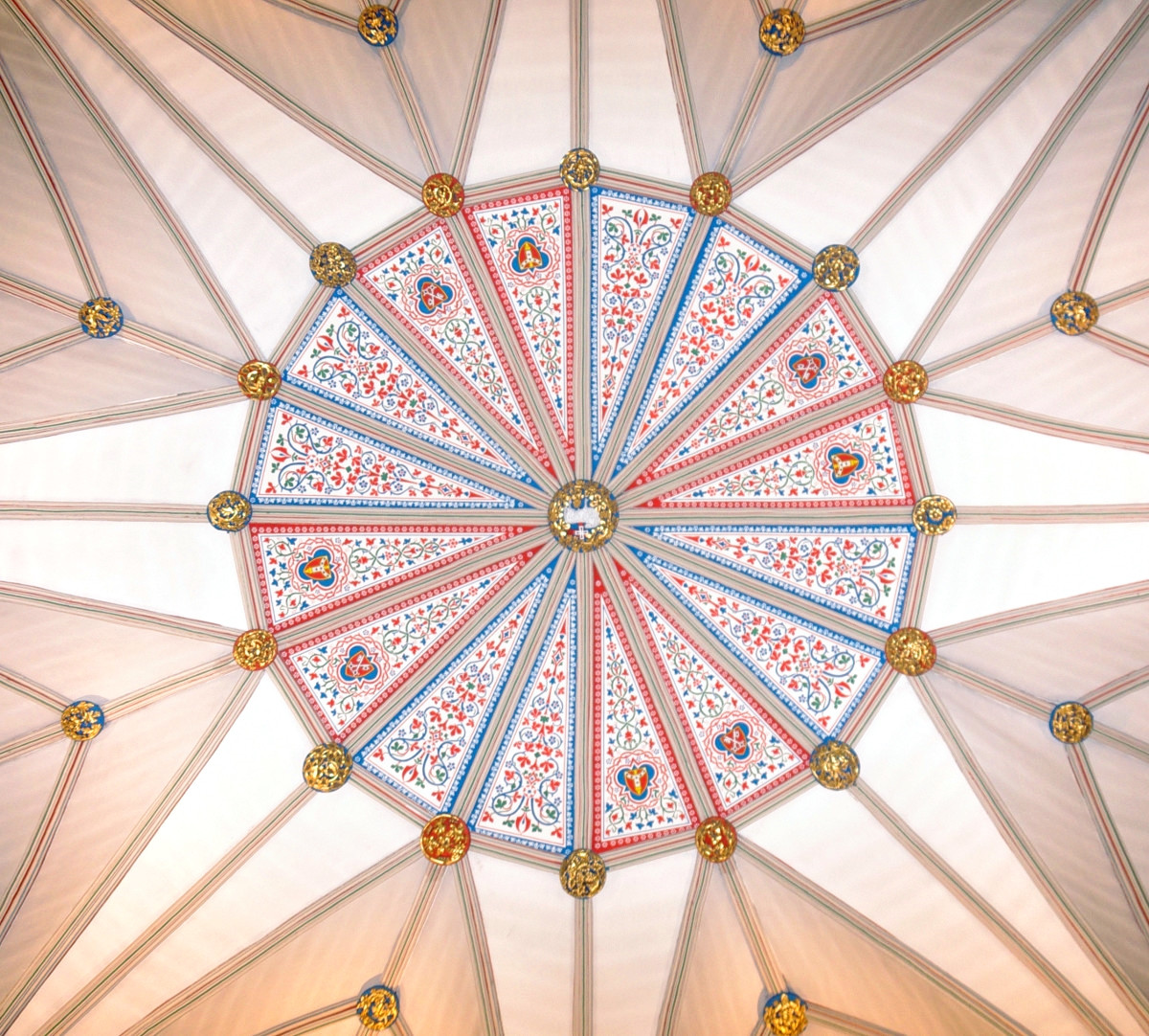
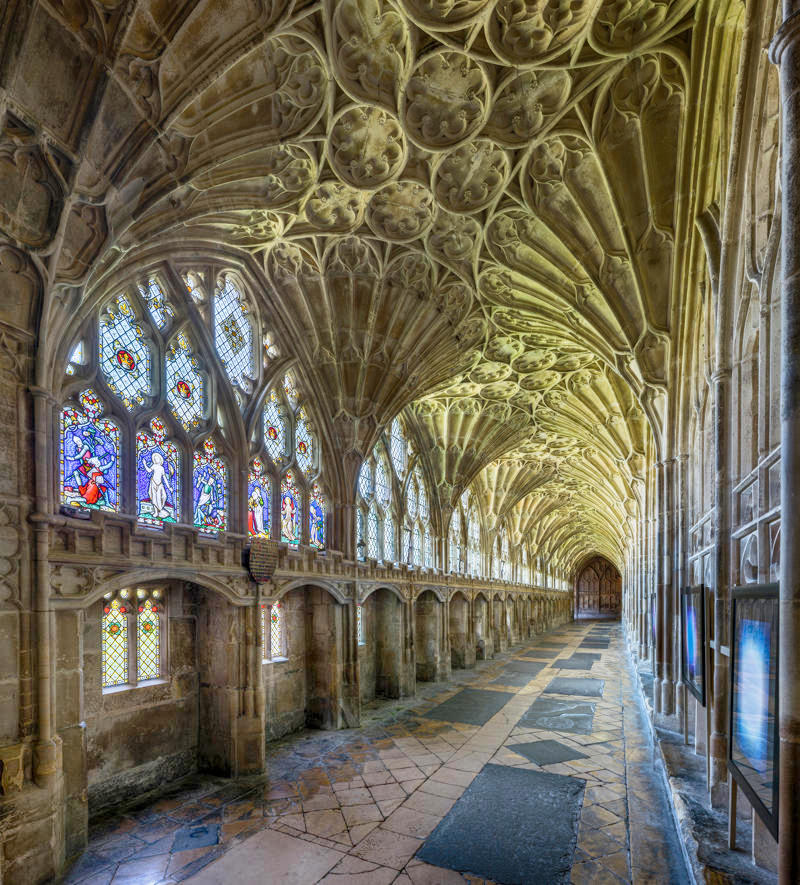
Designed between 1351 and 1377 by Thomas de Canterbury, the cloisters at Gloucester are the earliest surviving fan vaults.

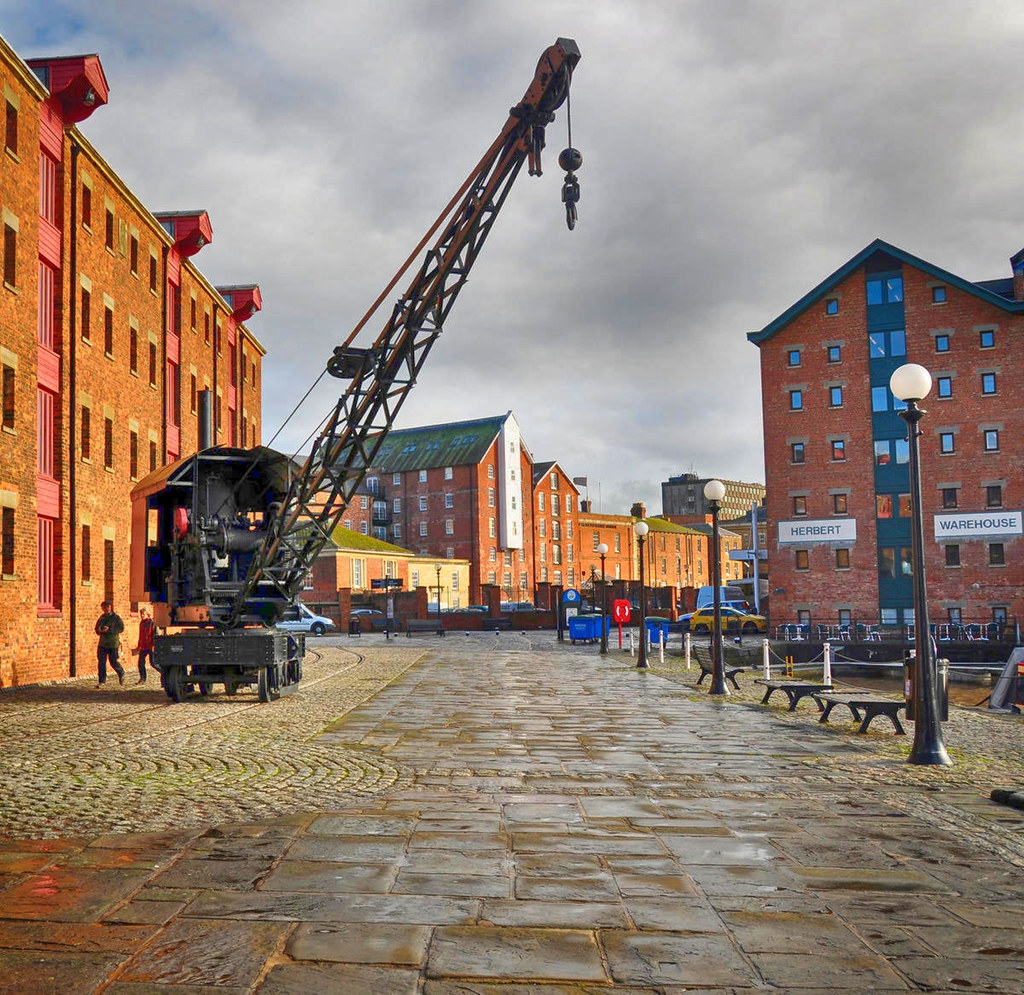
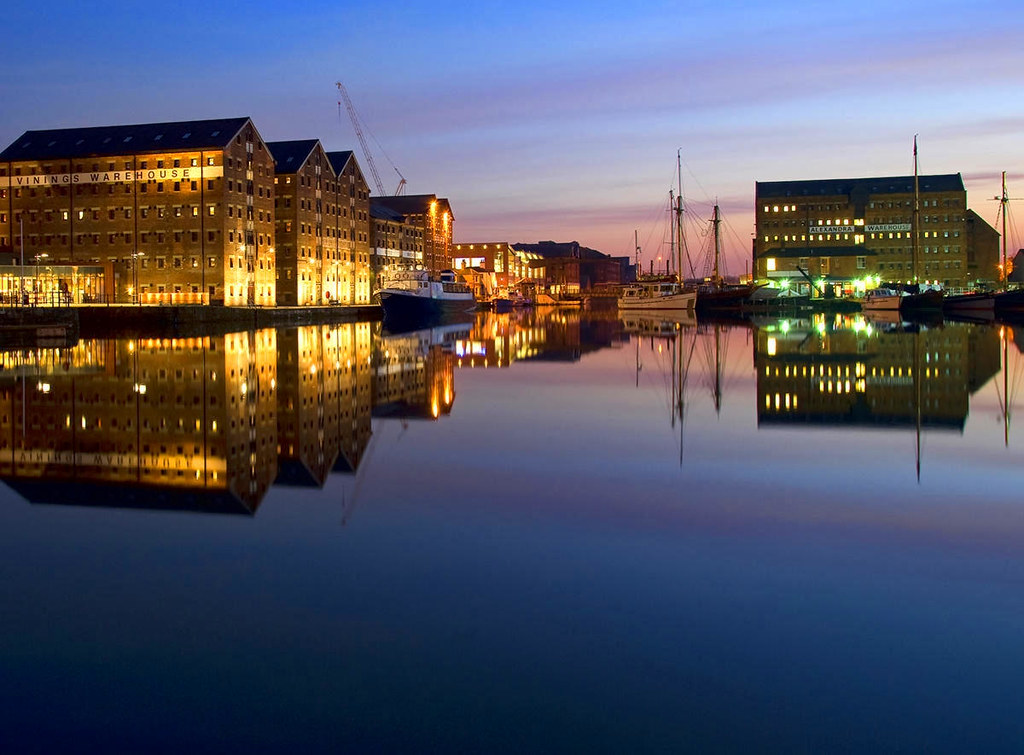
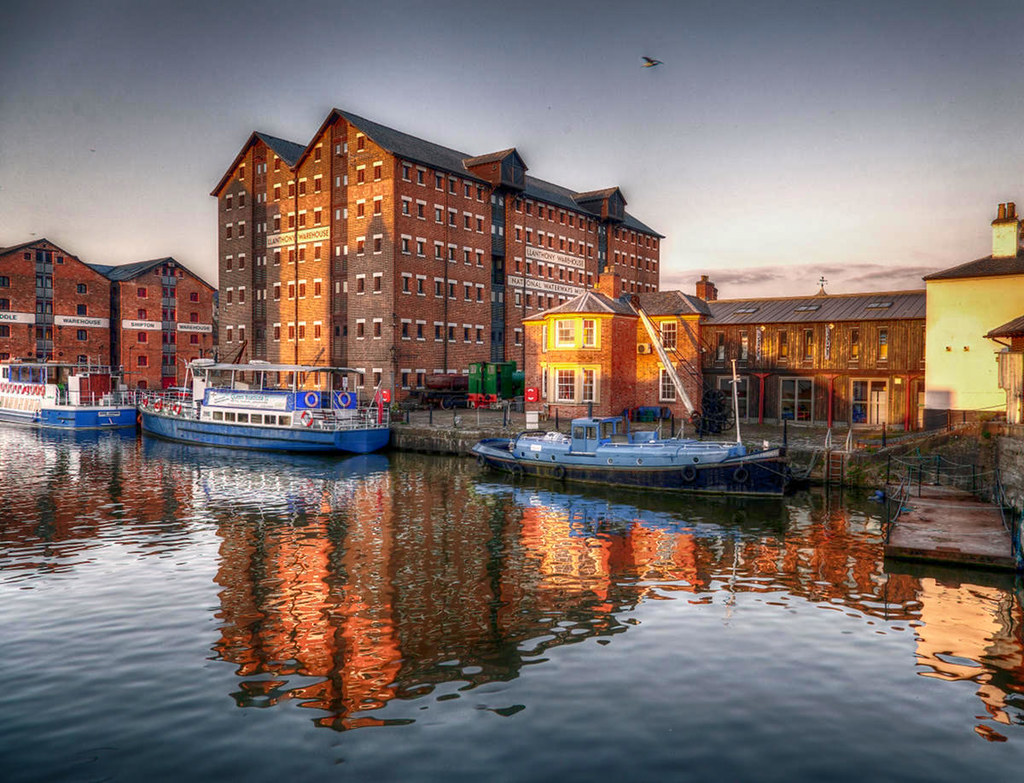
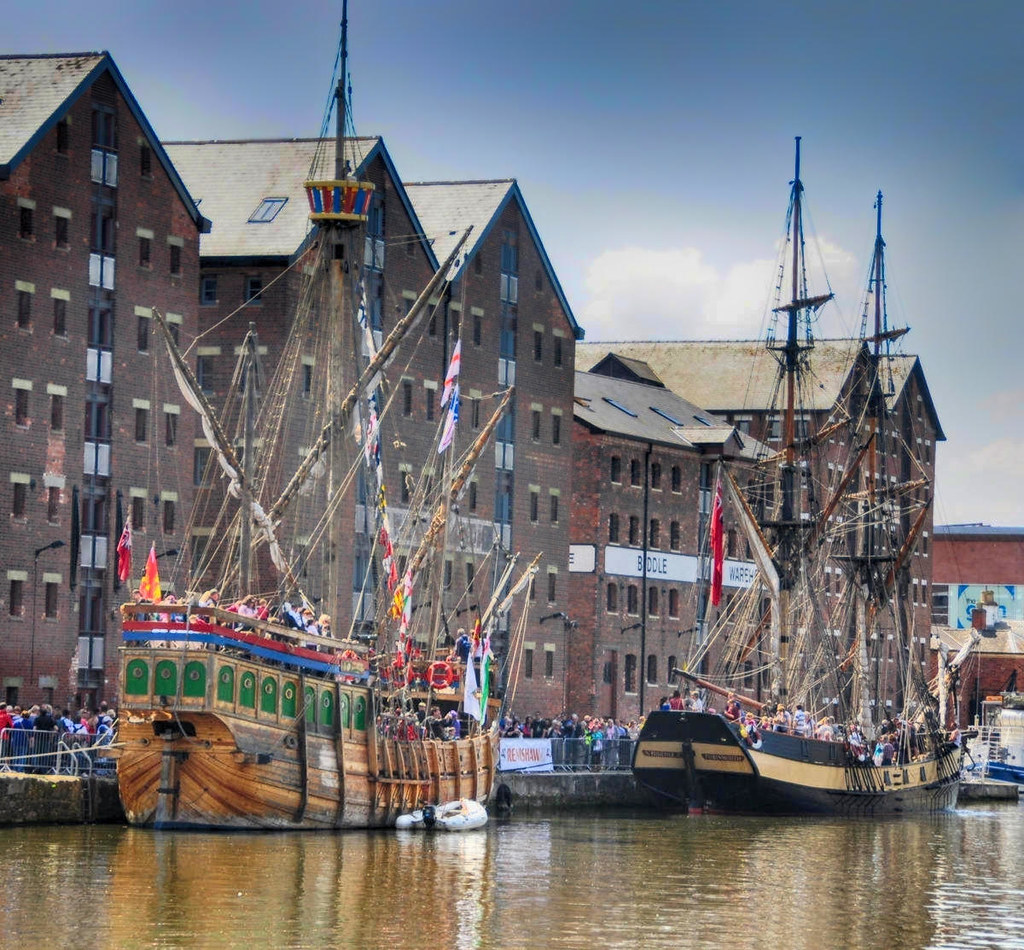
Gloucester’s Docklands
Victorian ships once discharged their cargoes of corn from Ireland and Europe, timber from the Baltic and North America, and wines and spirits from Portugal and France.
Transferred to narrow canal boats, the goods were carried up the River Severn and through the inland canal network to the growing industrial towns of the Midlands.




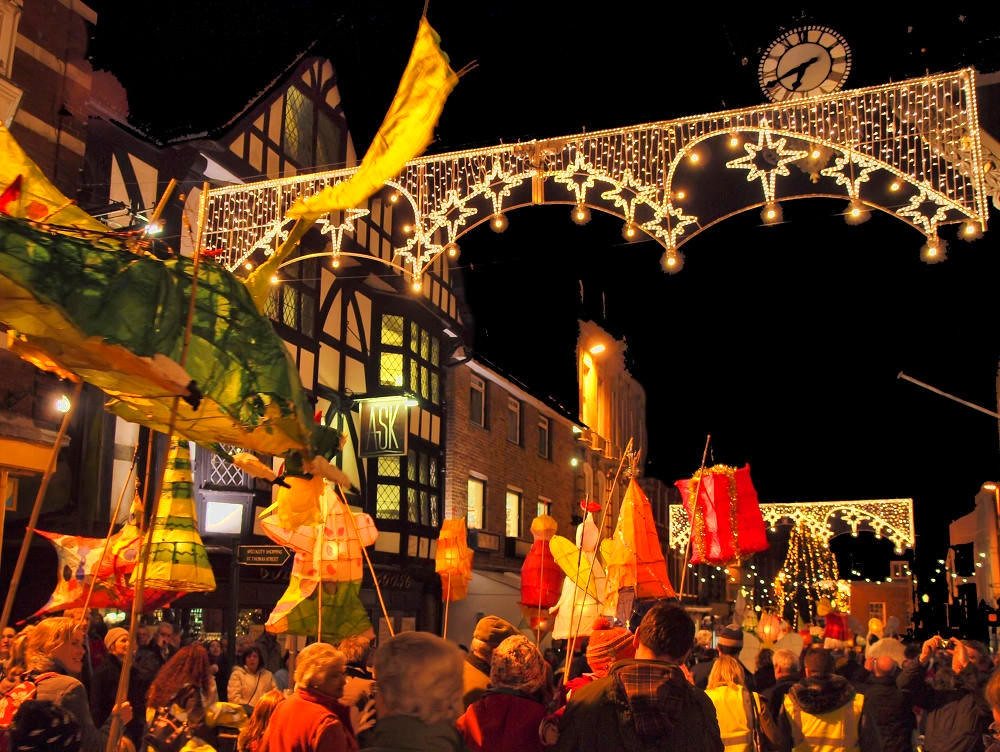
Cheltenham Spa
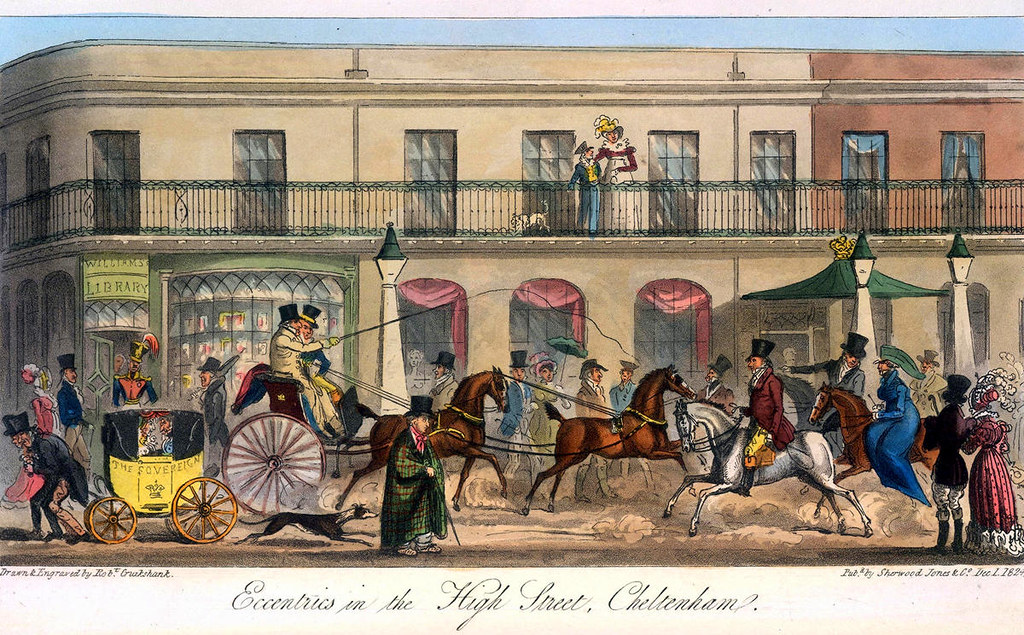
Meaning “health and education”, Cheltenham’s motto “Salubritas et Eruditio” helped establish the town as a health and holiday spa resort since mineral springs were discovered in 1716.
Recognizing the commercial potential of its mineral springs, Captian Henry Skillicorne was regarded as “the founder of Cheltenham as a watering place”.
Building a pump room to regulate the water flow and an elaborate well-house with ballrooms and billiard room, well-to-do Georgian society flocked to Cheltenham.

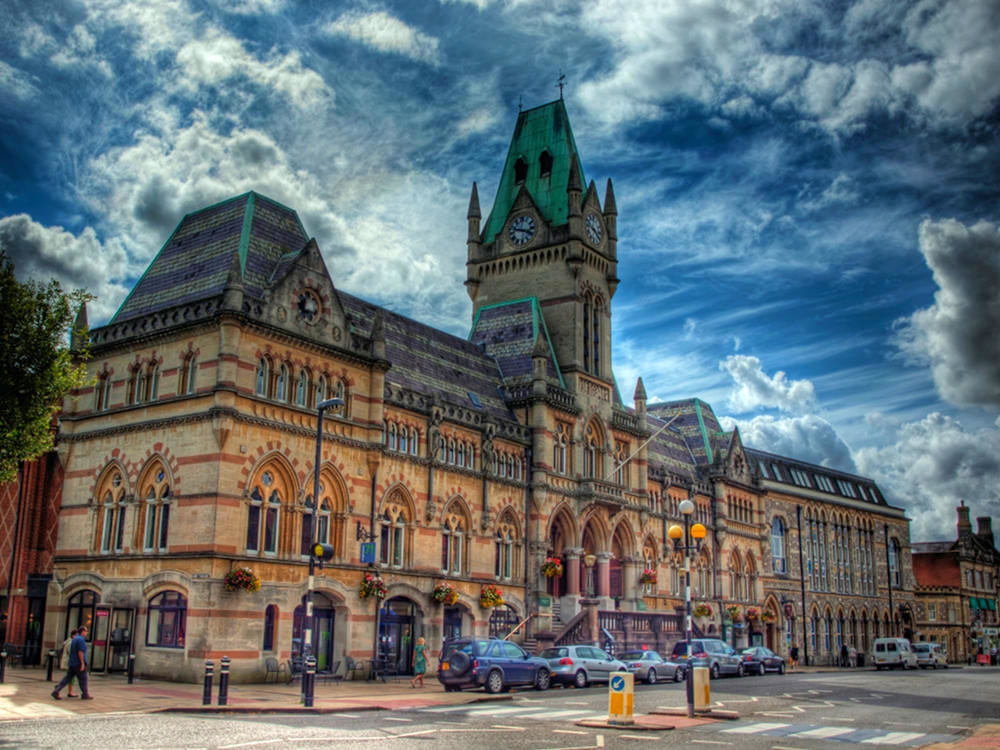
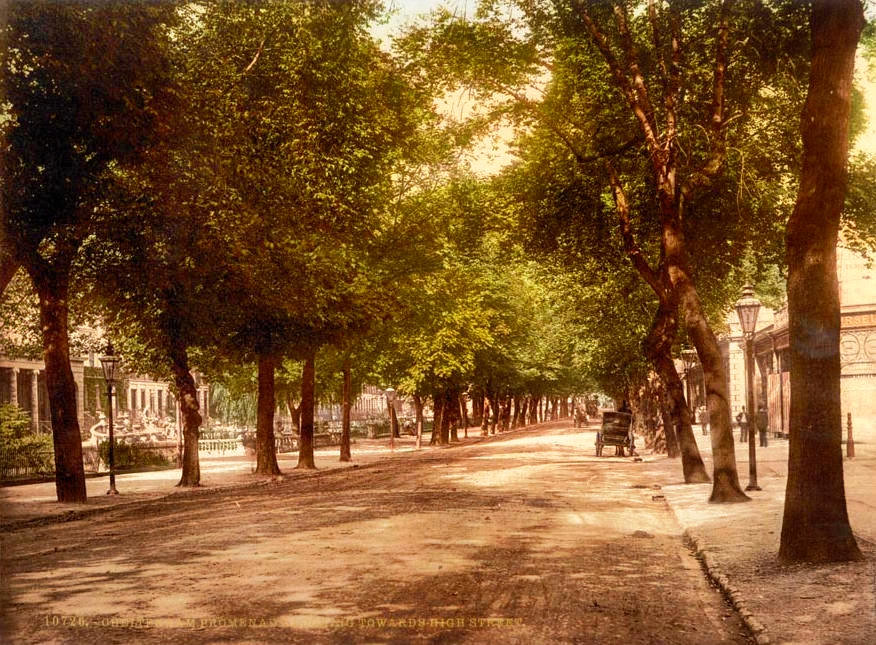
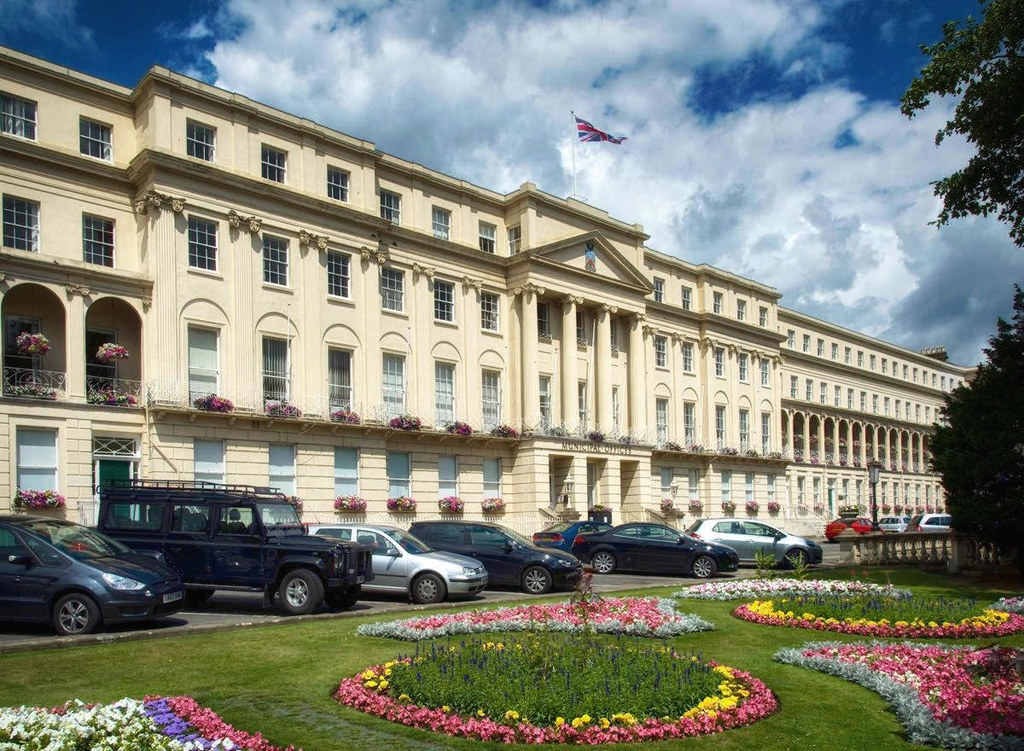
Known for its elegant Regency buildings, tree-lined promenades and gardens, Cheltenham has remained a popular upscale shopping and entertainment destination through the Victorian era and up to the present day.

Regarded by many as among the finest Regency buildings in Britain, Cheltenham’s municipal offices were constructed during the reign of King George IV (1820 – 1830).

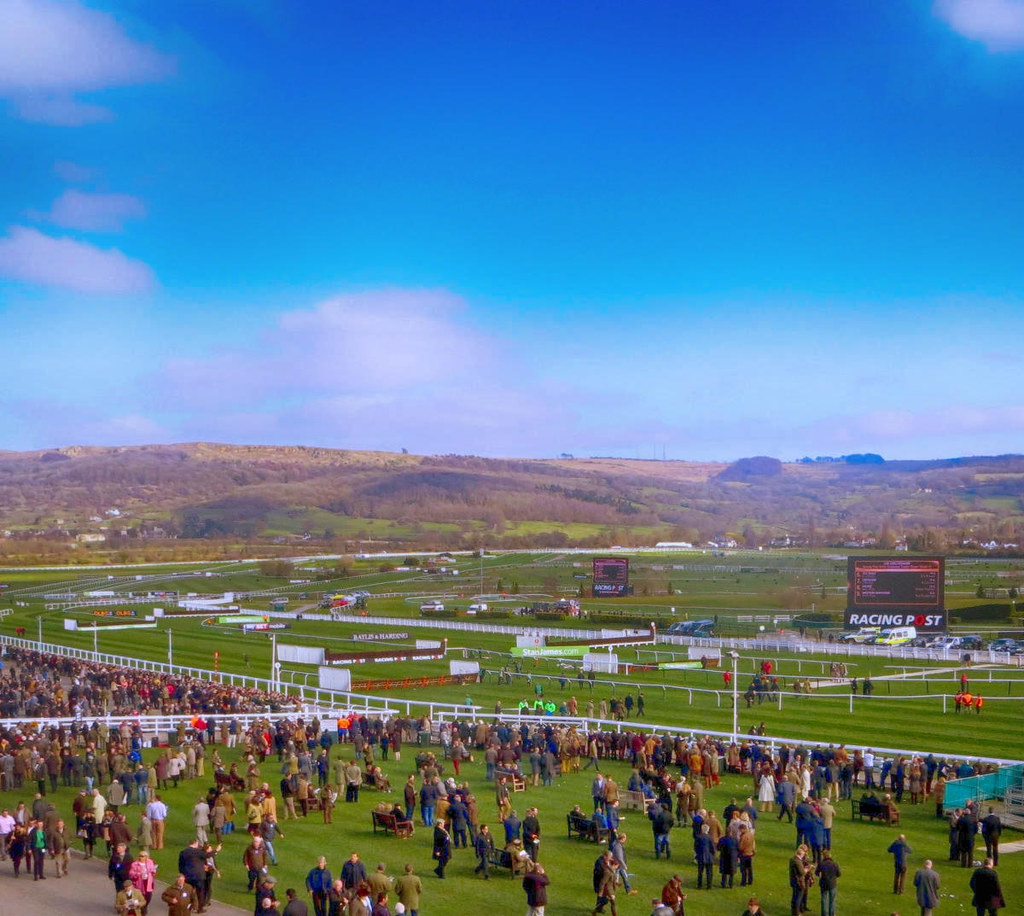
Since 1815, horse racing has been an important sport in Cheltenham, with £6m in prize money and over 700,000 visitors each year.

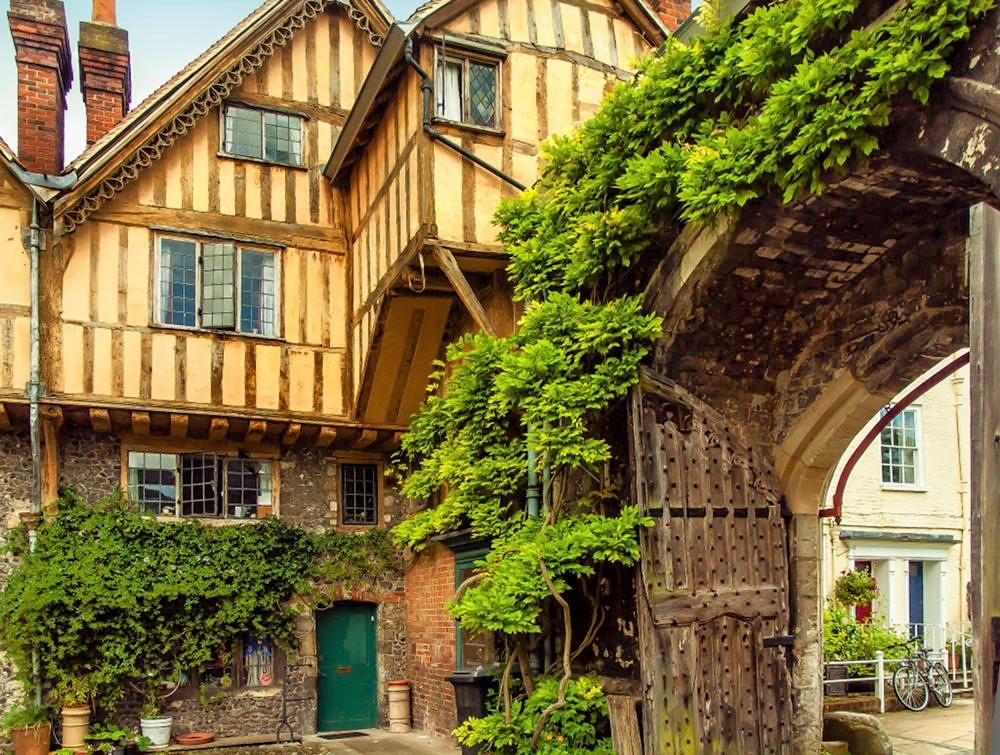
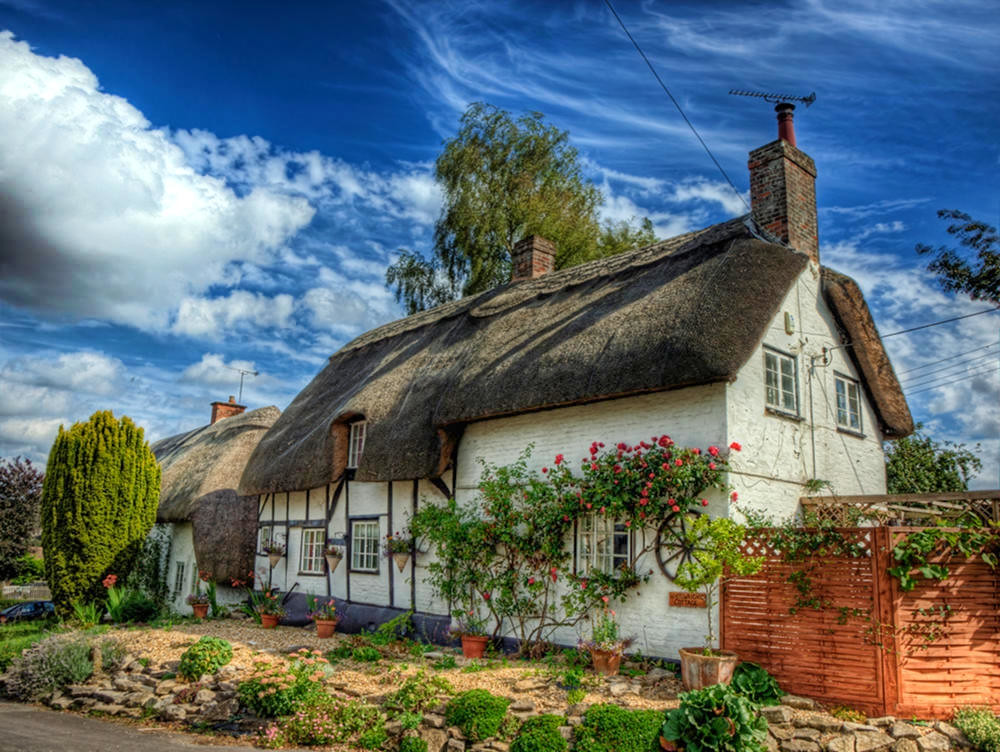
Cotswold Towns and Villages
Dozens of pretty villages and towns dot the Gloucestershire landscape.
Rising from the meadows of the upper River Thames is a range of rolling hills with a grassland habitat and a beautiful honey-coloured stone used to build villages, towns, and country houses.
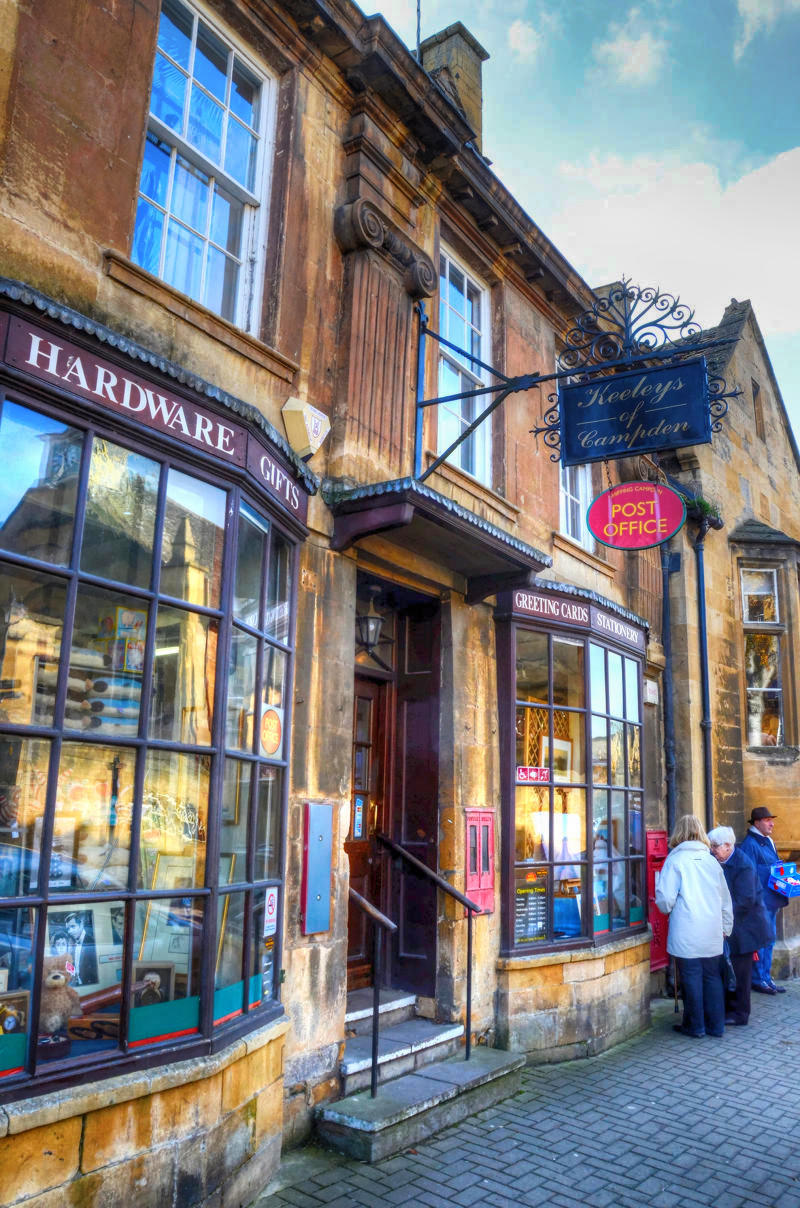

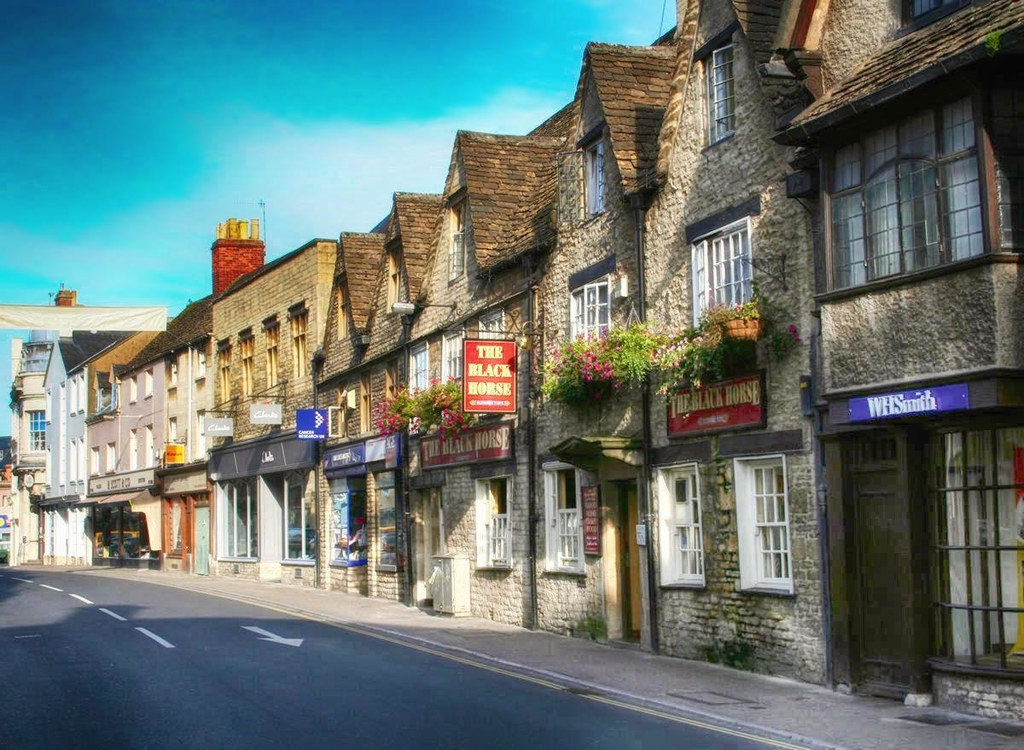
Notable for its elegant terraced High Street, dating from the 14th century to the 17th century, Chipping Campden was a rich wool centre of the Middle Ages.
“Chipping” derives from the Old English “cēping”, meaning marketplace.
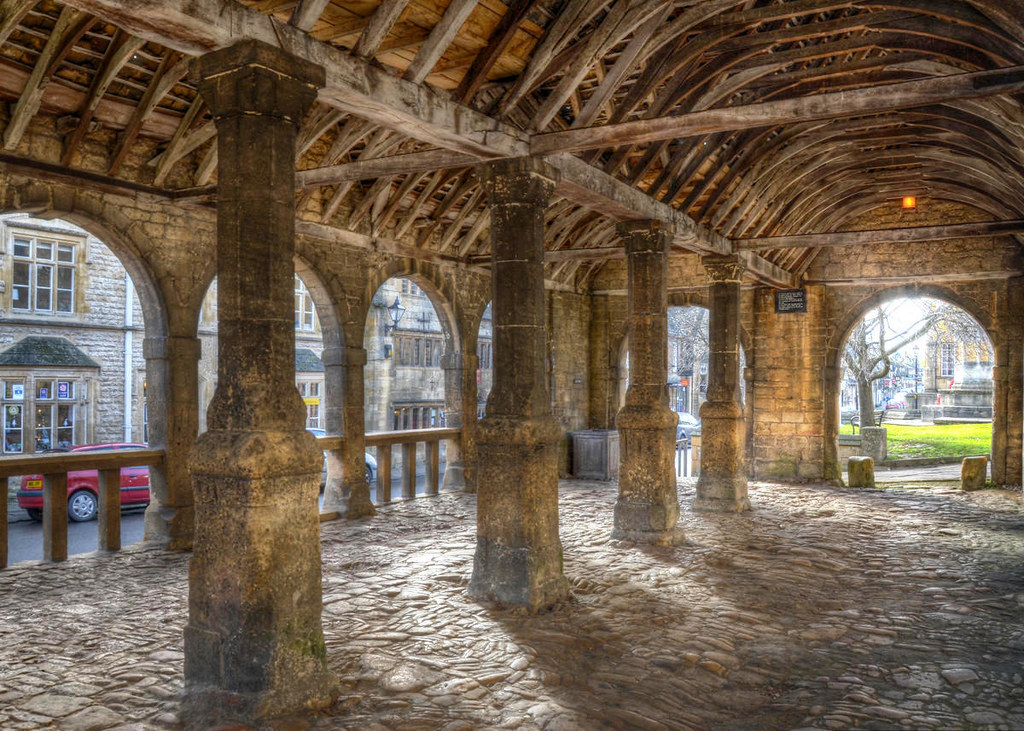
Built in 1627, the arched Market Hall stands proudly at the centre of town.
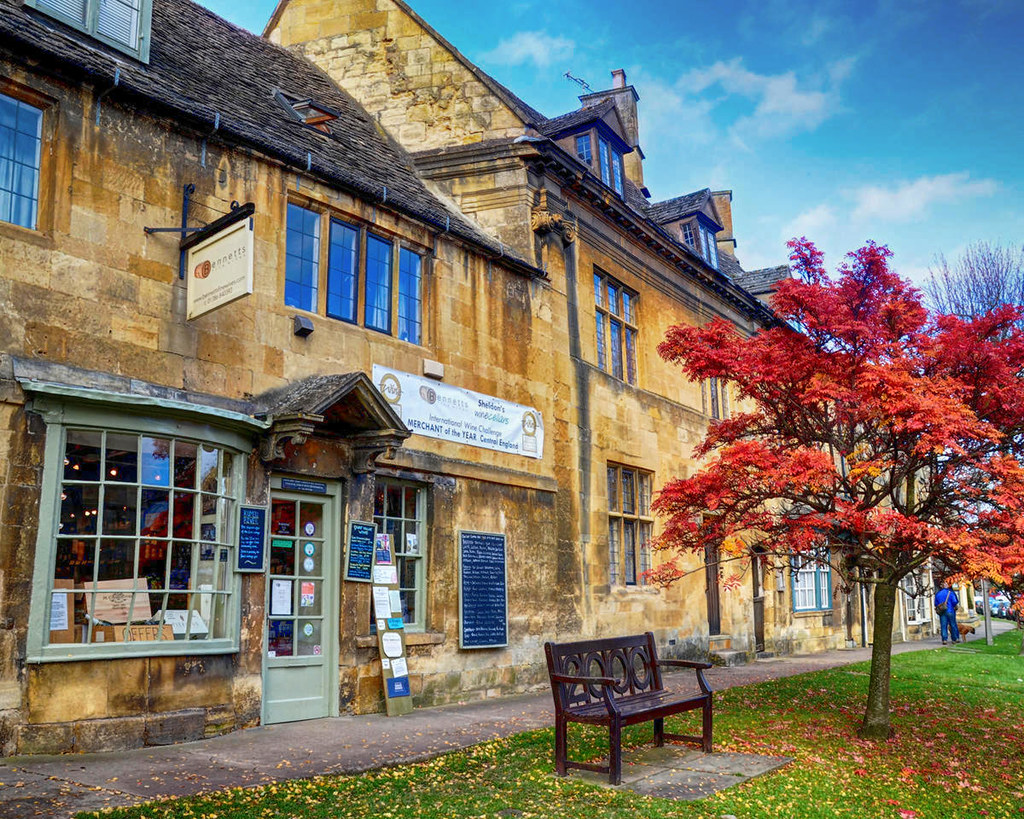
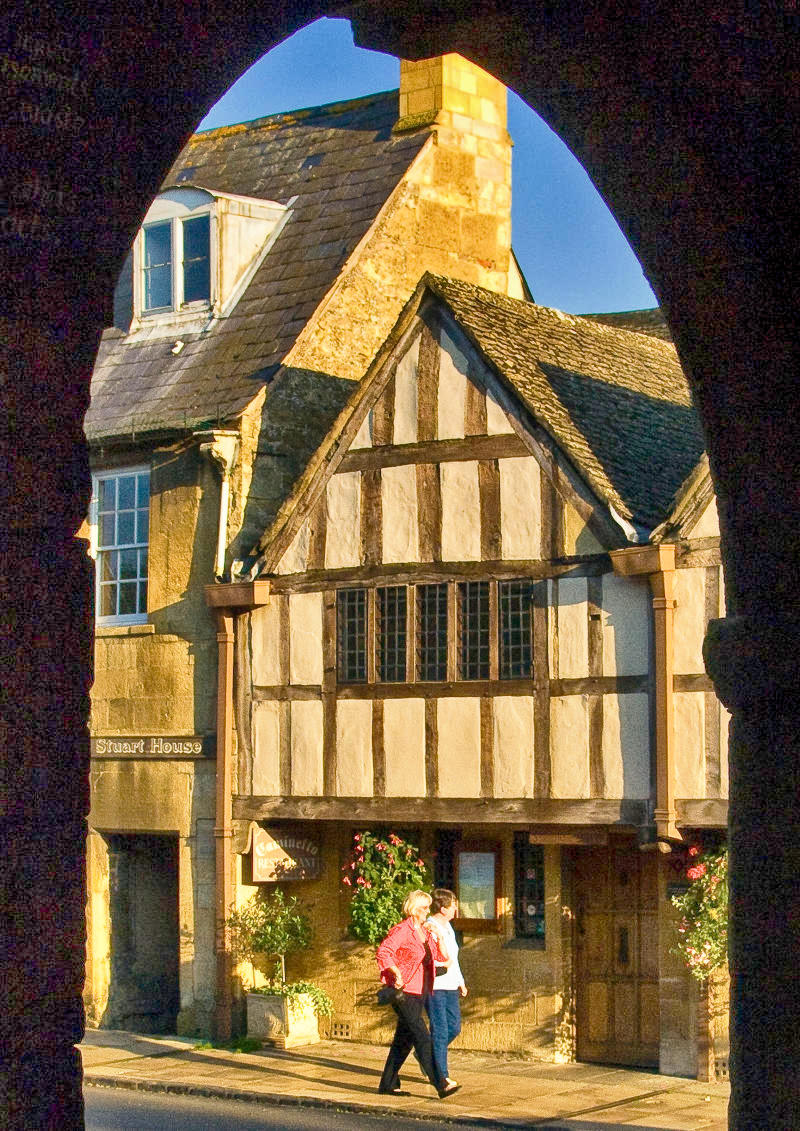



Meaning “Farmstead on the Moor”, the delightful town of Moreton-in-Marsh has many buildings made from the local honey-colored Cotswold Stone, including several antique shops, art galleries, and hotels.
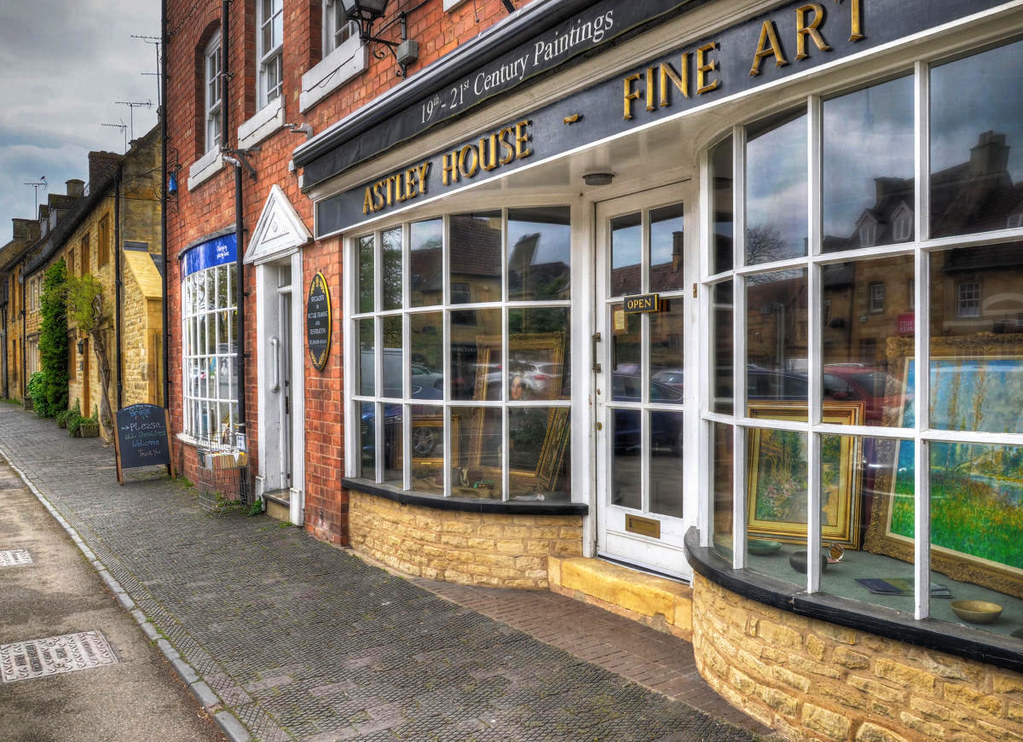
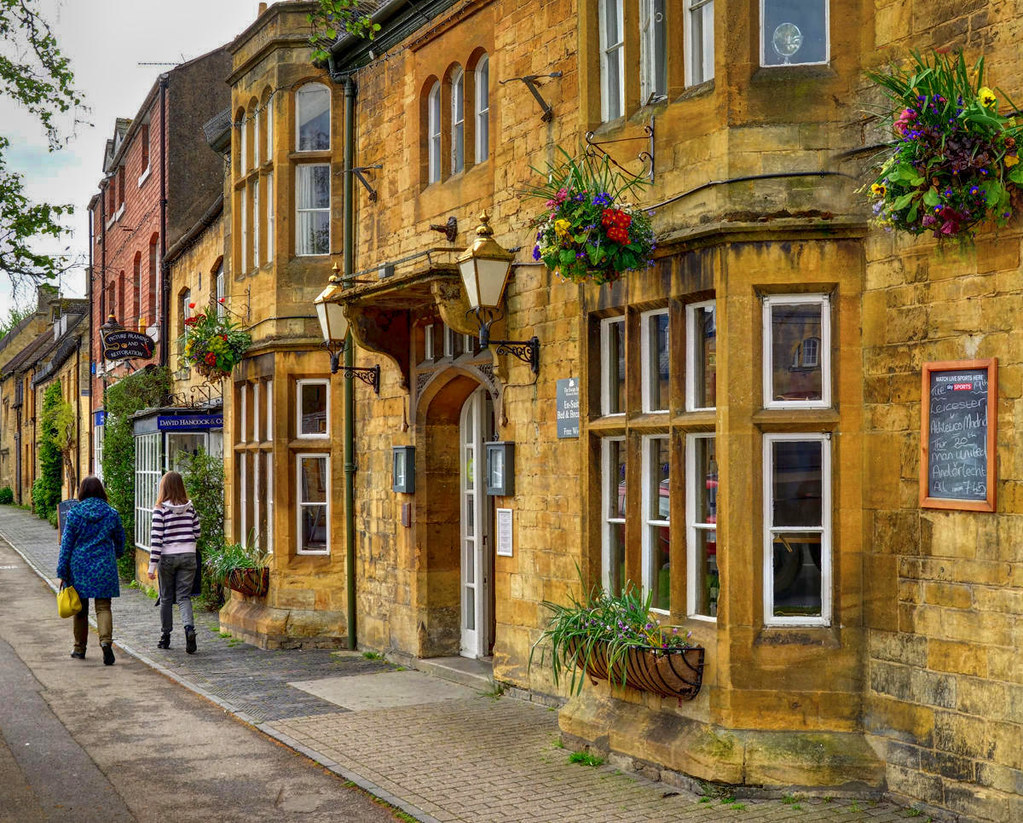



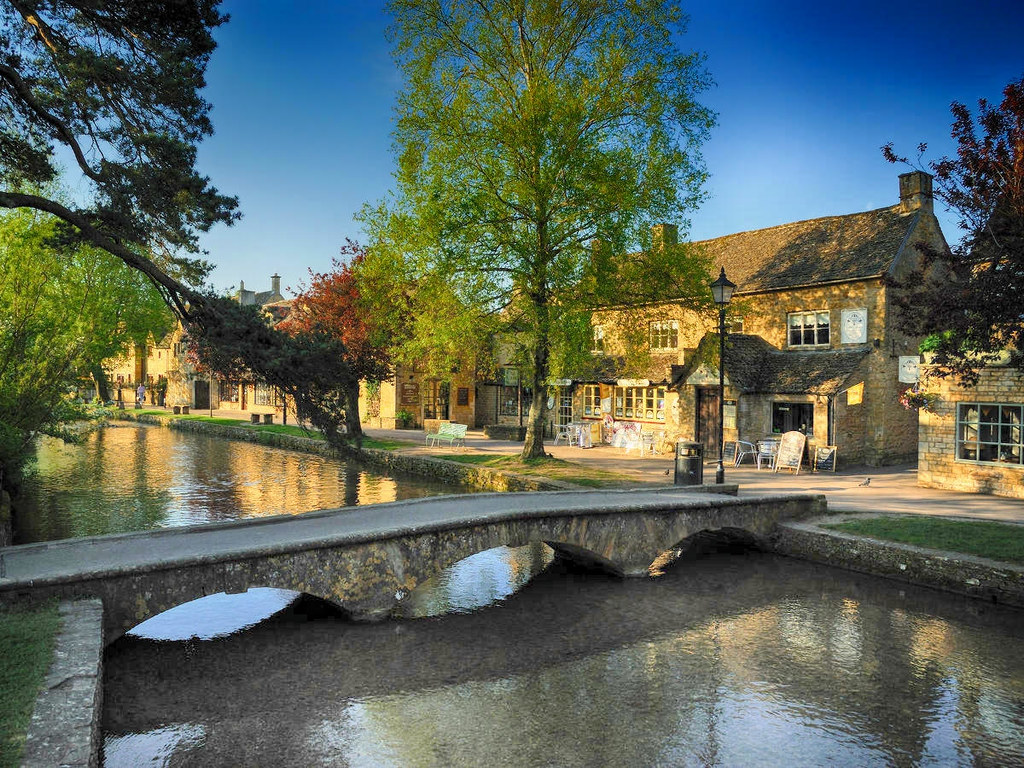
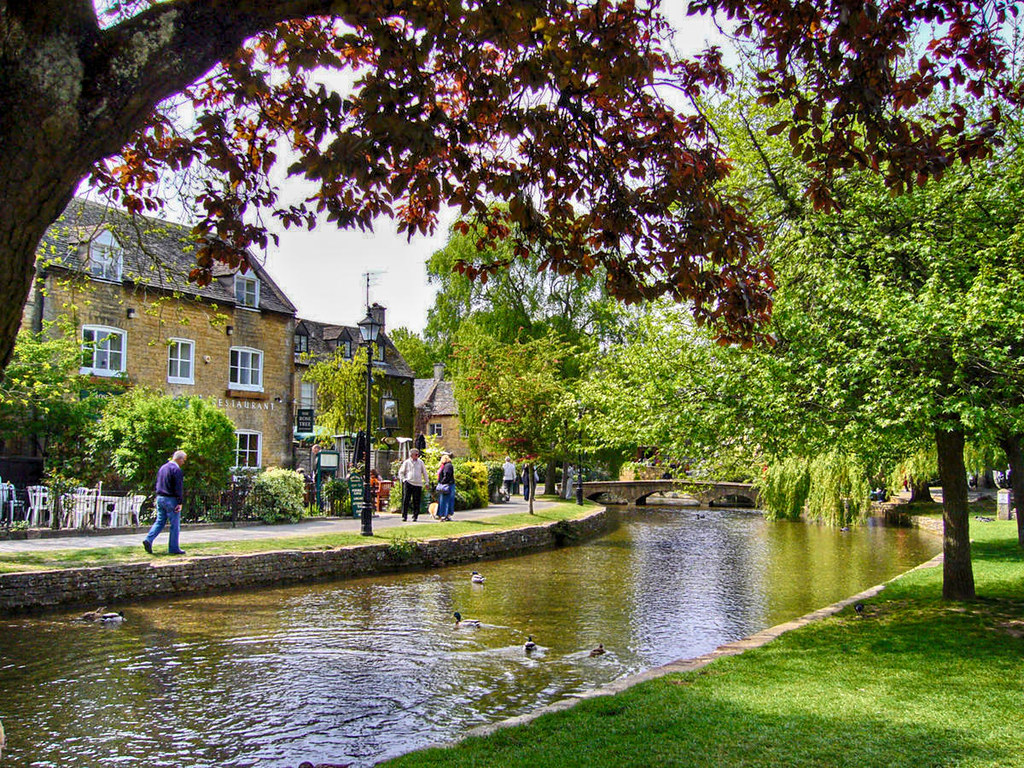
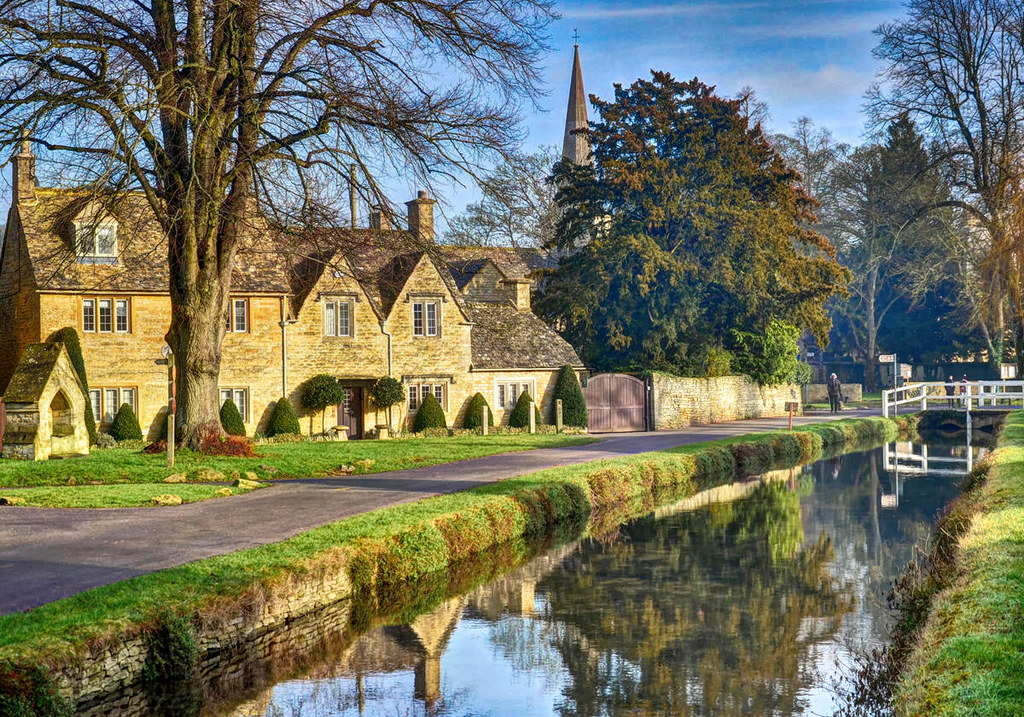
Known for its picturesque High Street, flanked by long, wide greens with the River Windrush running through it, Bourton-on-the-Water is known locally as the “Venice of the Cotswolds”.
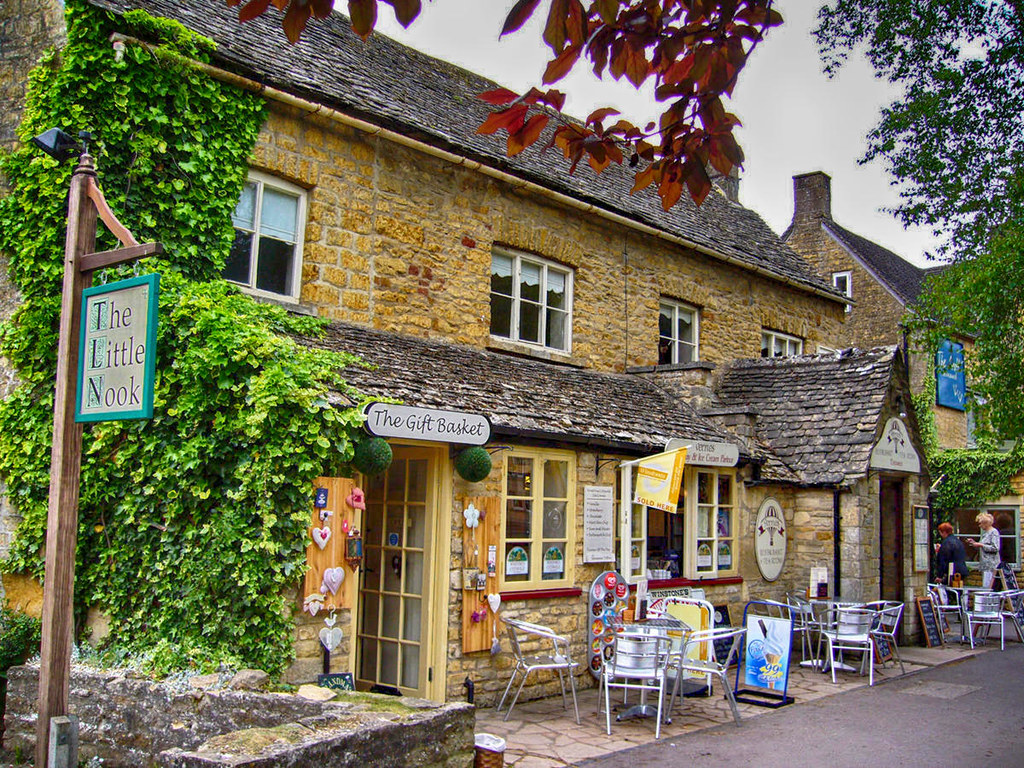




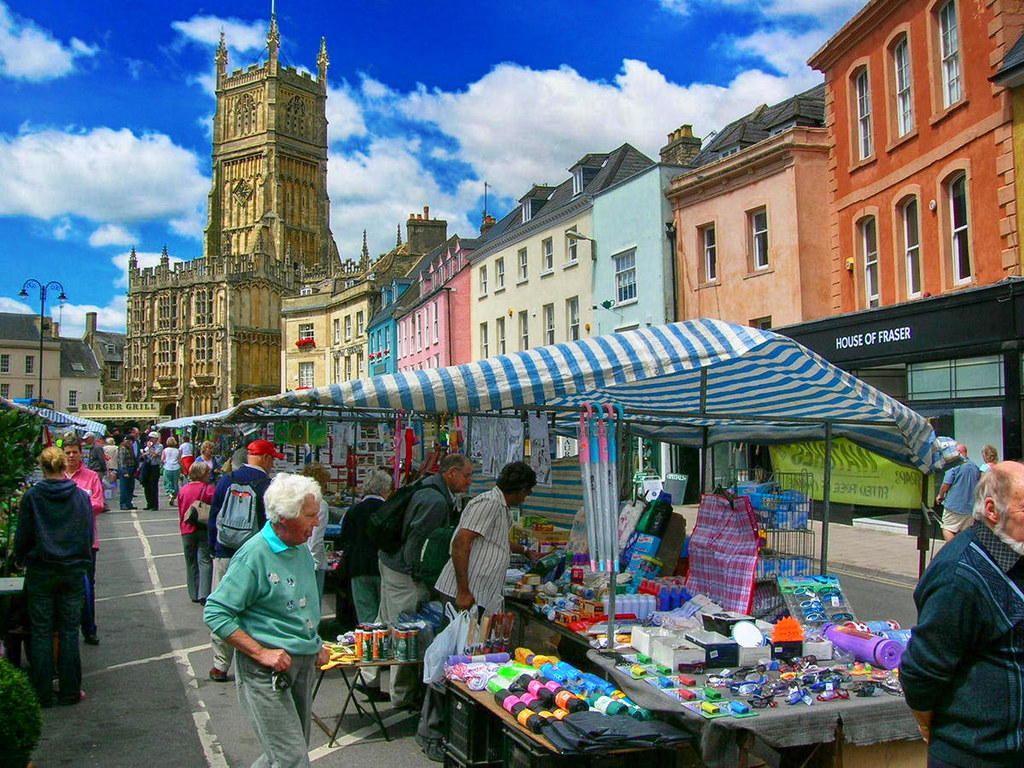
Once part of the second-largest area of a city in Roman Britain, Cirencester grew into a thriving market town in the Middle Ages, trading in wool and cloth.


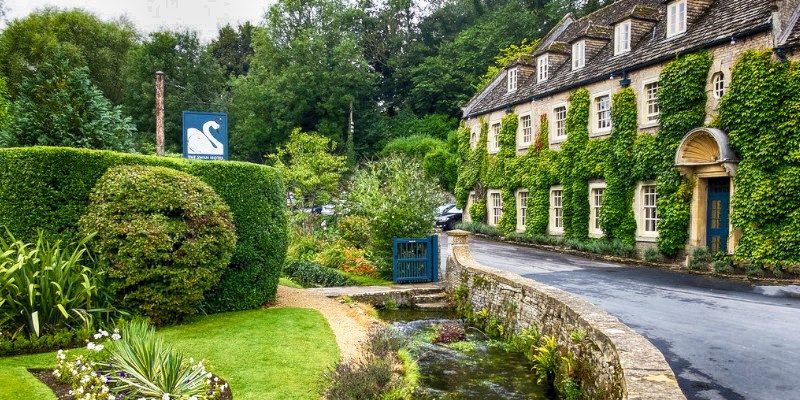
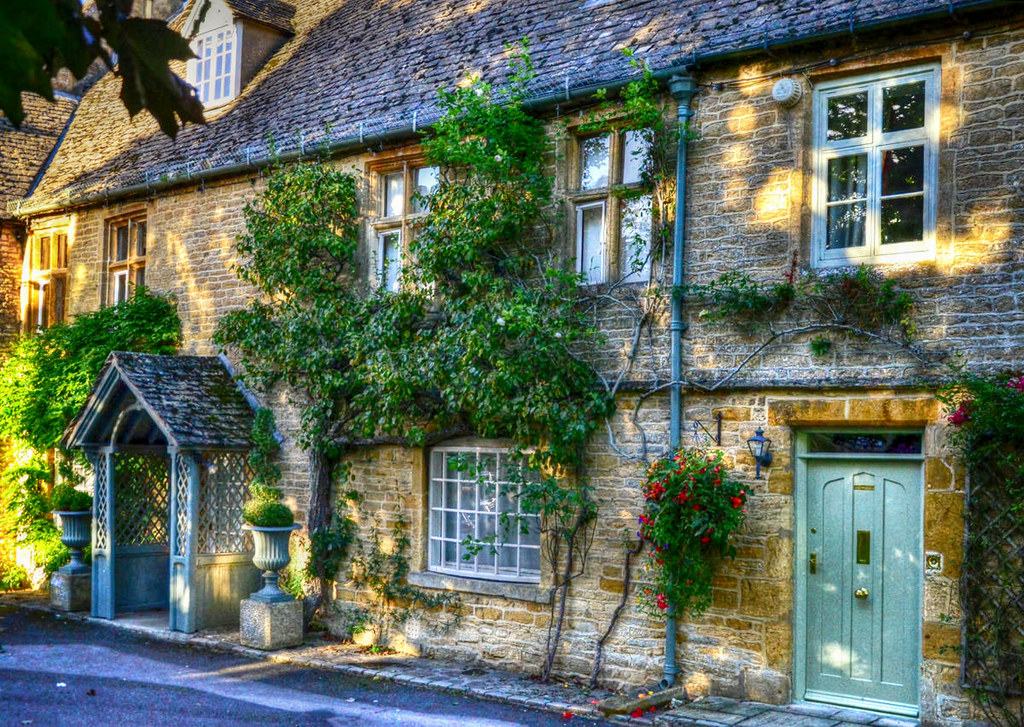
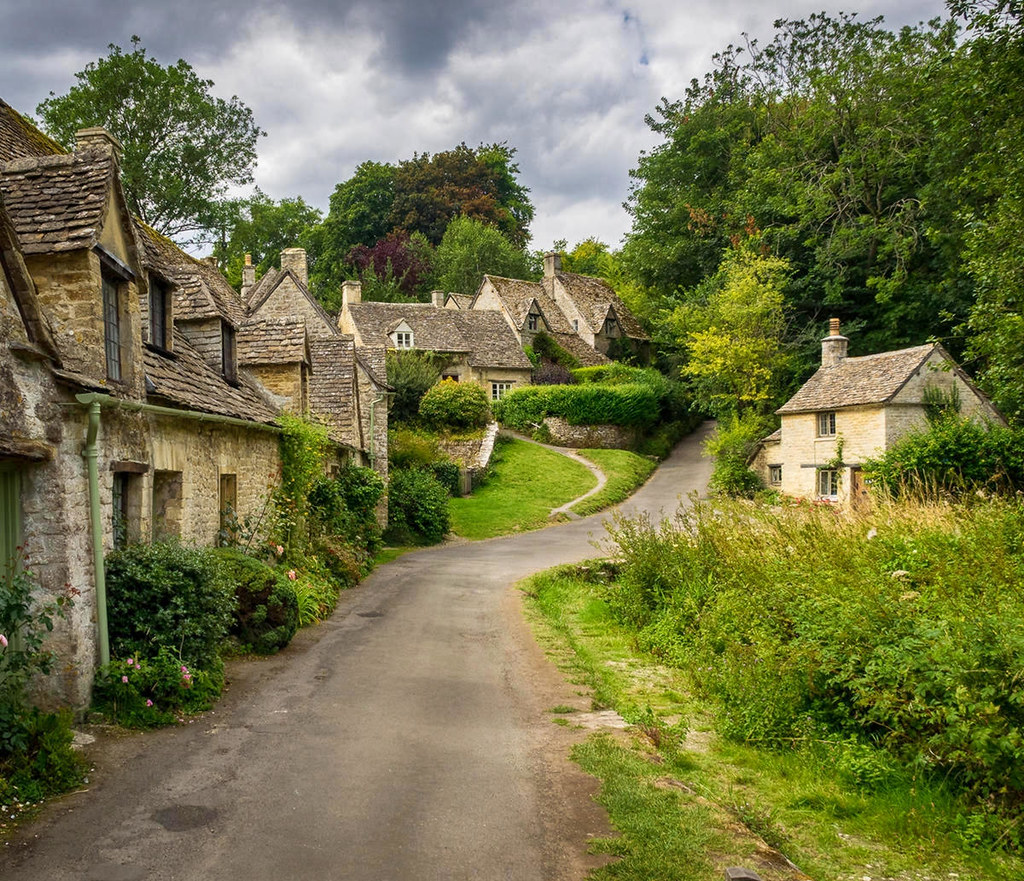
Built in 1380 as a monastic wool store, the picturesque Arlington Row cottages were converted into weavers cottages in the 17th century and are a very popular tourist hotspot and photographers’ favorite.

Castles, Country Houses, and Gardens
Castle-building in Gloucestershire began after the 1066 Norman invasion, with fortified manor houses becoming more popular in the 13th and 14th centuries.
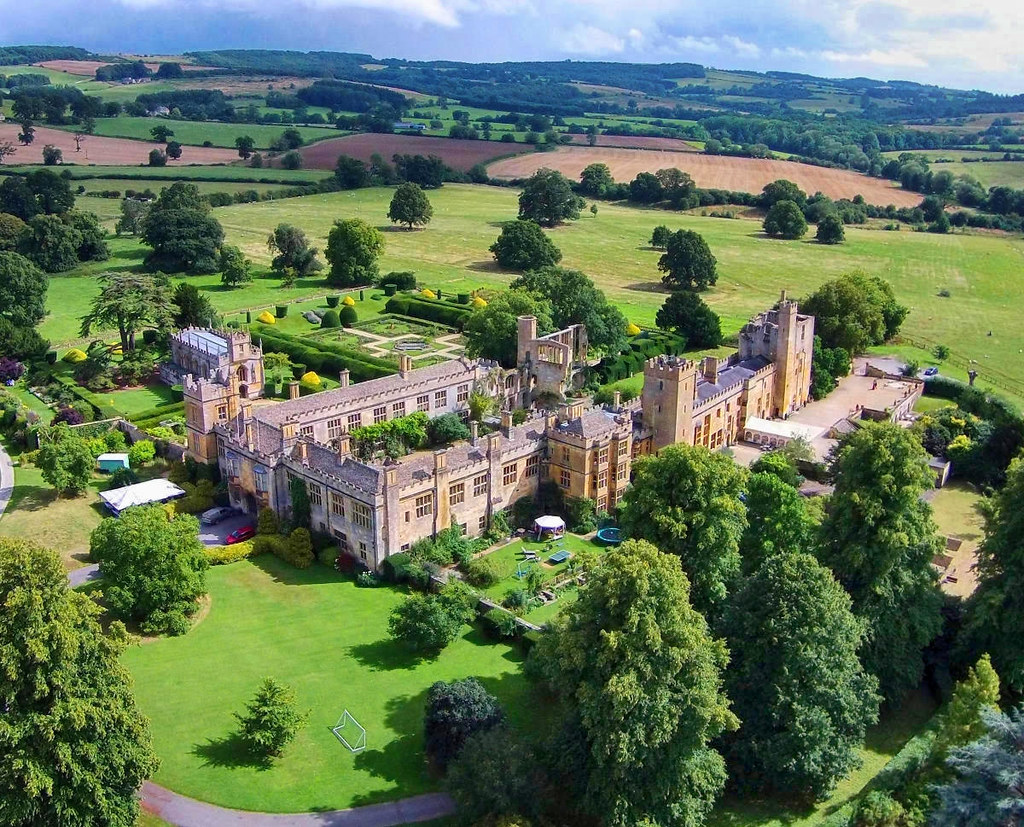

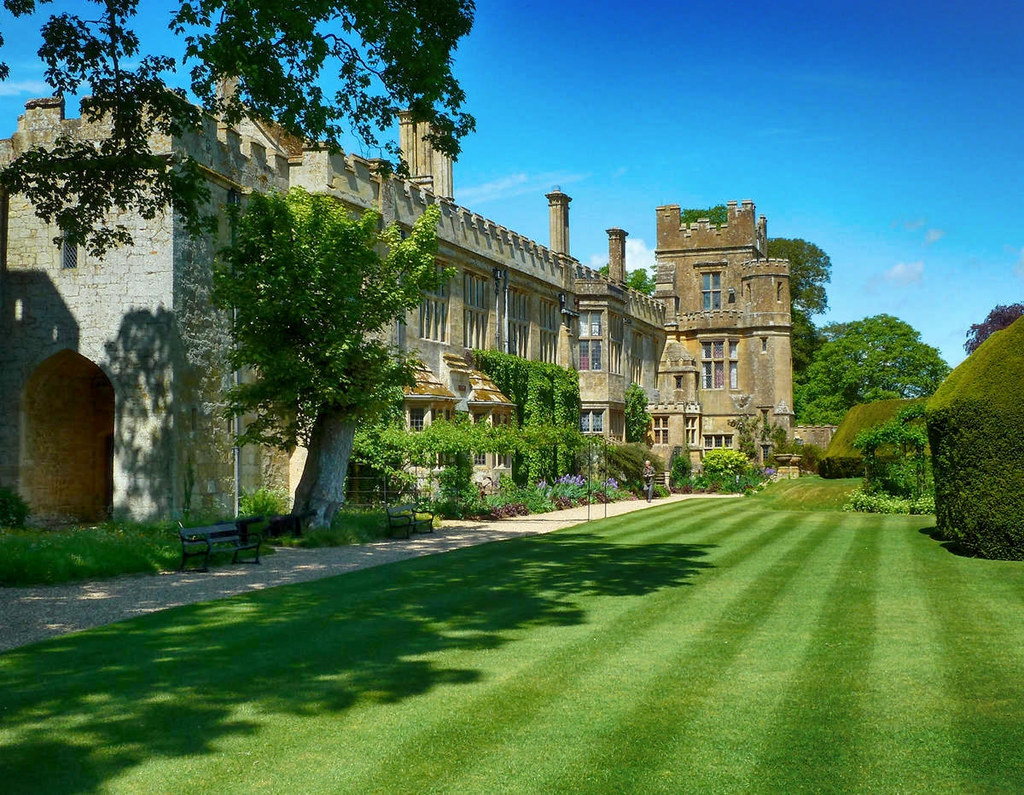
Built in the 15th century, Sudeley Castle replaced a much earlier 12th-century castle that was destroyed by King Stephen during the “Anarchy”—a civil war against his cousin Empress Matilda.
Severely damaged during the English Civil War, the current castle is the result of extensive Victorian restoration.

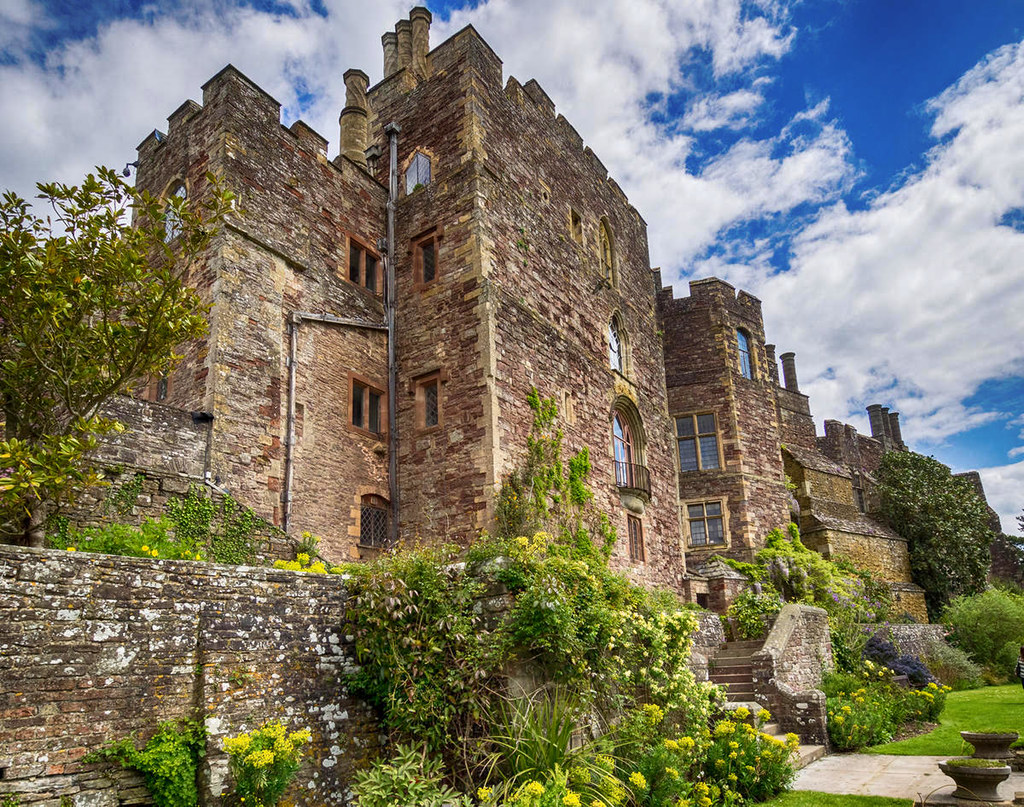
Dating back to the 11th century, Berkeley Castle is believed to be the scene of King Edward II’s murder.
His body is interred in a canopied shrine in Gloucester Cathedral
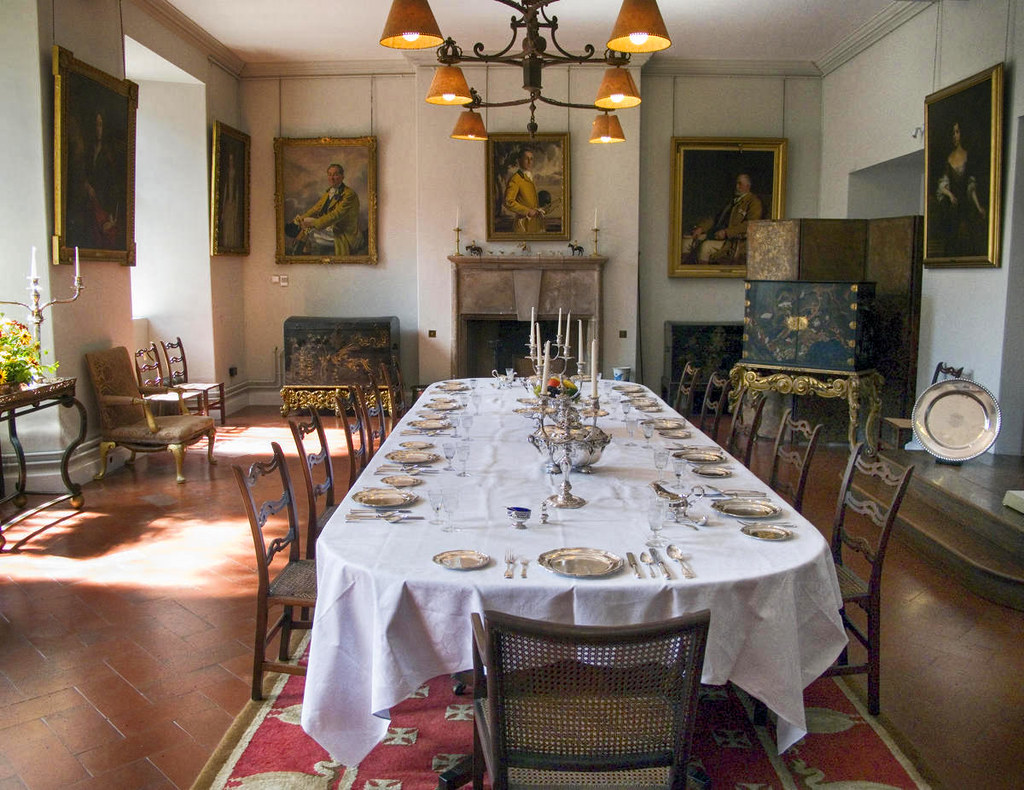


Built by Walter and Miles de Gloucester for the crown in the 11th century, St Briavels Castle was used to govern the Welsh Marches on the border of England and Wales.
Empress Matilda held the castle during the Anarchy and it later became a hunting lodge for King John and then a center for making crossbow arrows.
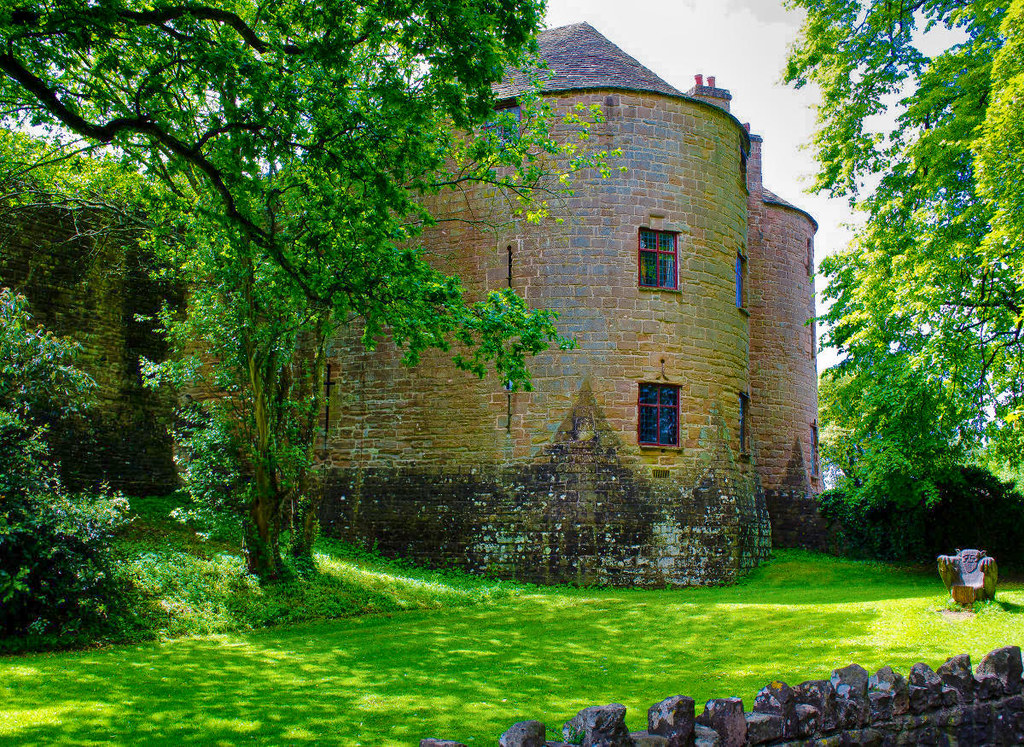

Hidcote Manor Garden is one of the best-known Arts and Crafts gardens in Britain.
Flourishing in Europe and North America between 1880 and 1920, Arts and Crafts was a movement of decorative and fine arts that began in Britain and advocated traditional craftsmanship of simple forms, with medieval, folk, and romantic influences.
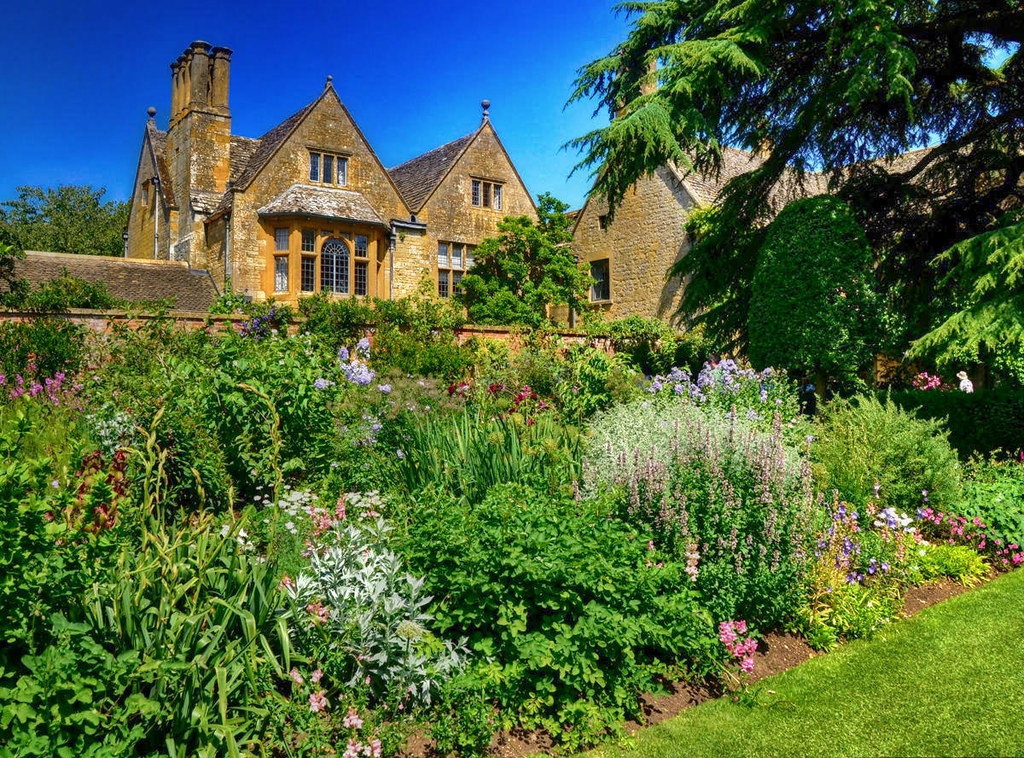
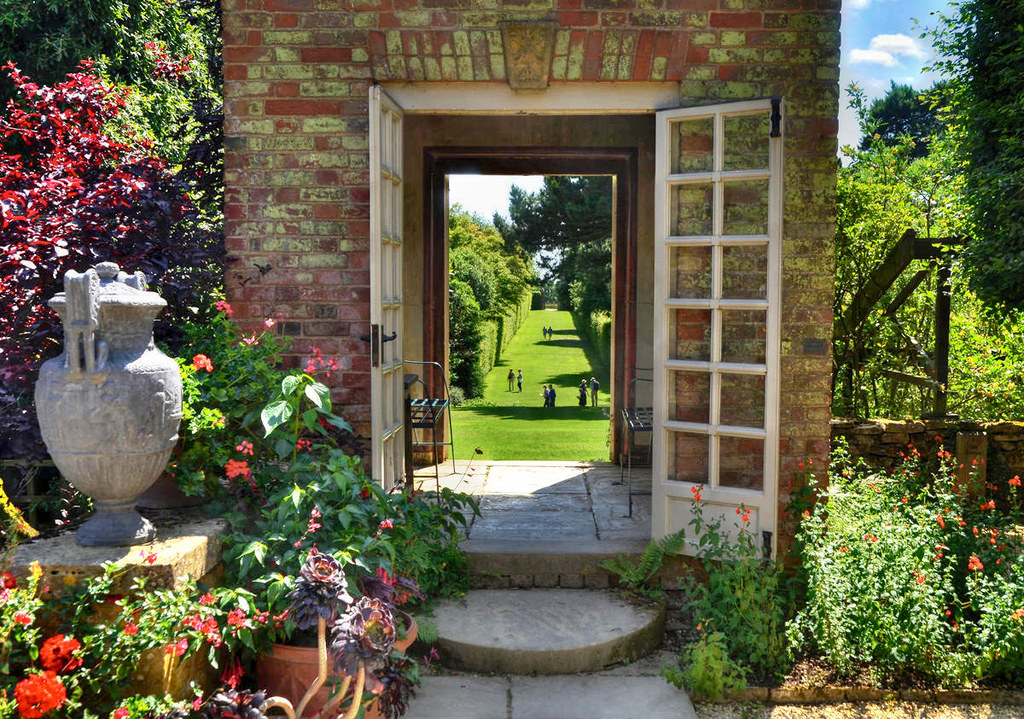
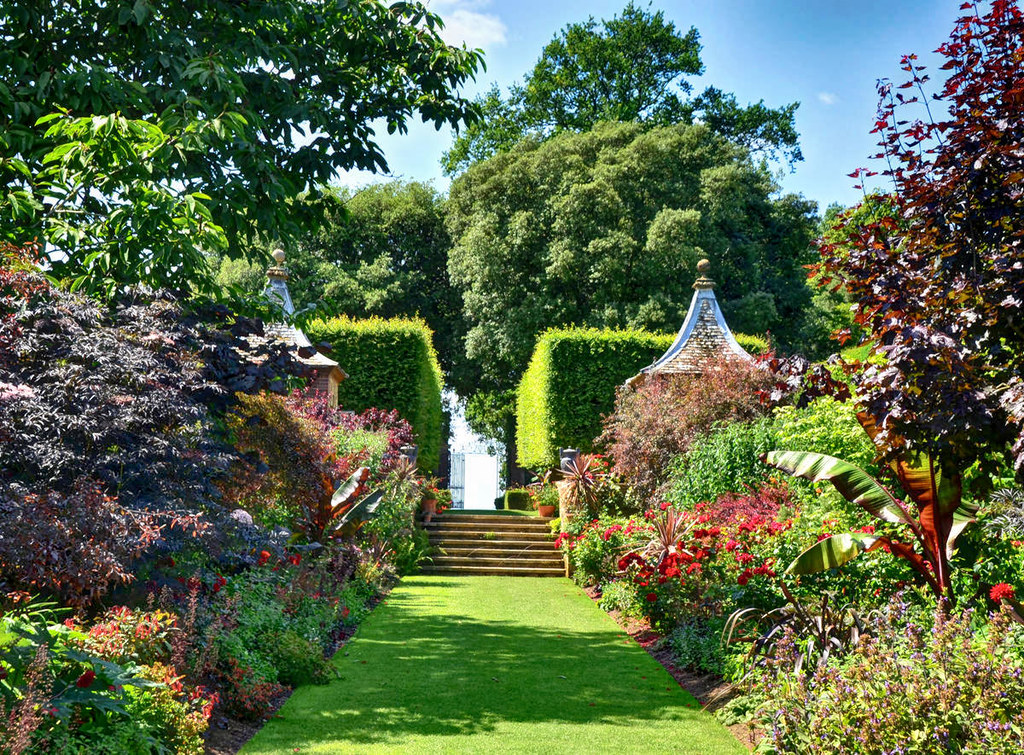



Built in the 1860s in an Elizabethan style, the Victorian mansion of Westonbirt House replaced earlier buildings in the Georgian and Tudor eras.
Occupied by Westonbirt School—a girls’ boarding school—since 1928, the house and 210-acre grounds are open to the public on certain days.
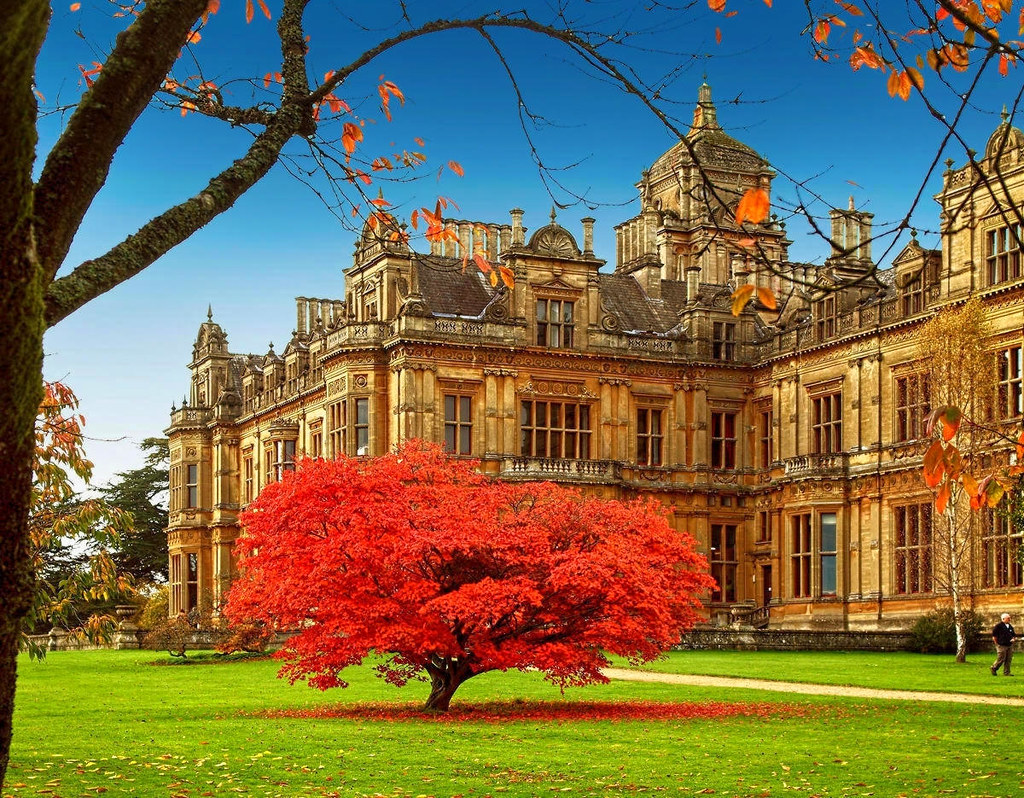

Surrounded by 274 acres of formal gardens, the baroque Dyrham Park country house was built during the 17th and early 18th centuries.
Sumptuously decorated with wood paneling and tiles of Dutch Delftware, the artwork and artifacts include a collection of Dutch Masters.
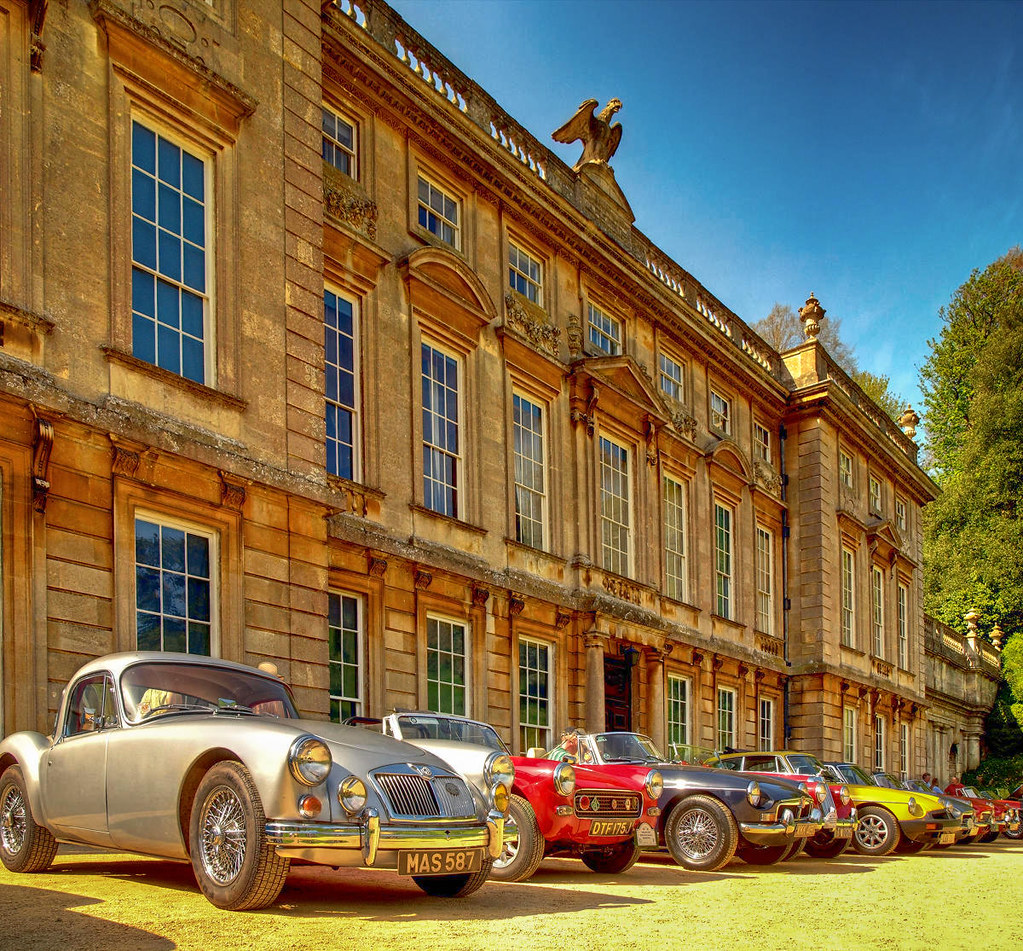
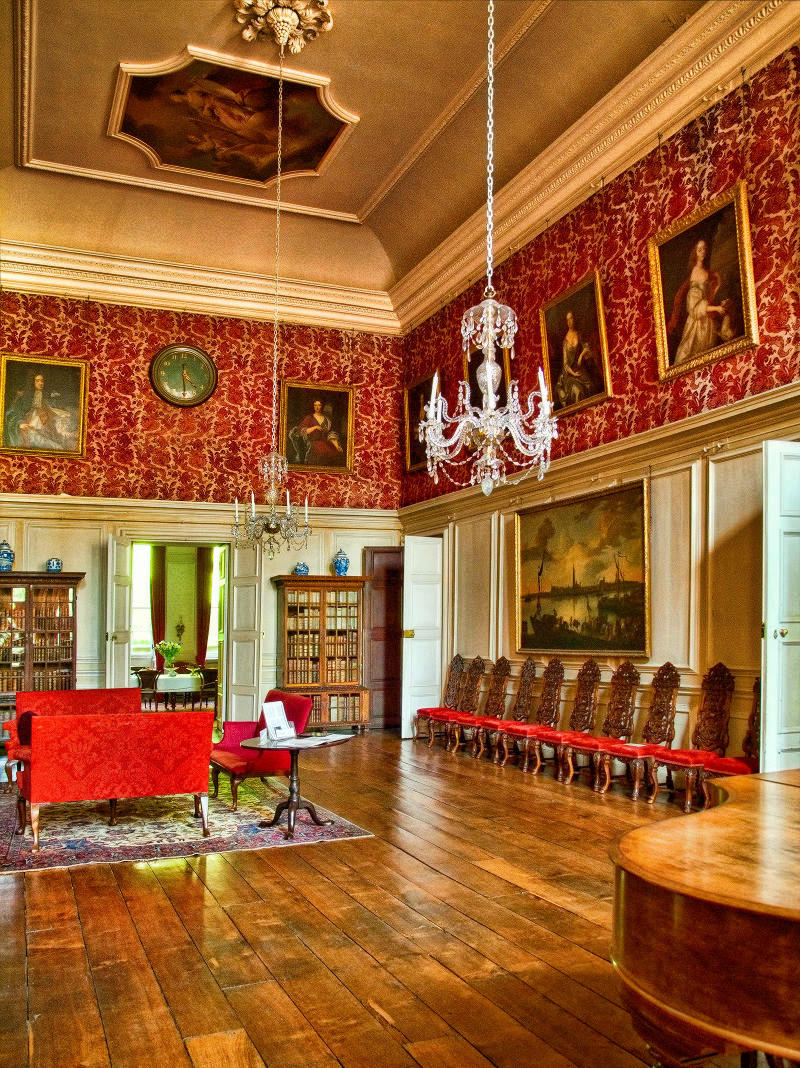
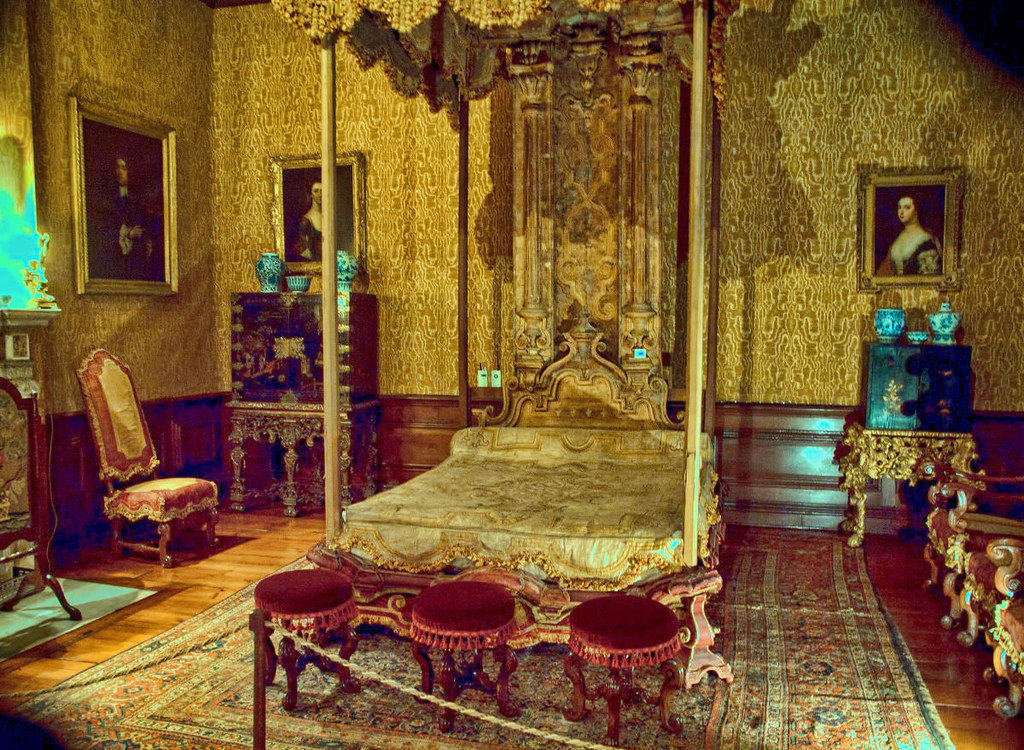
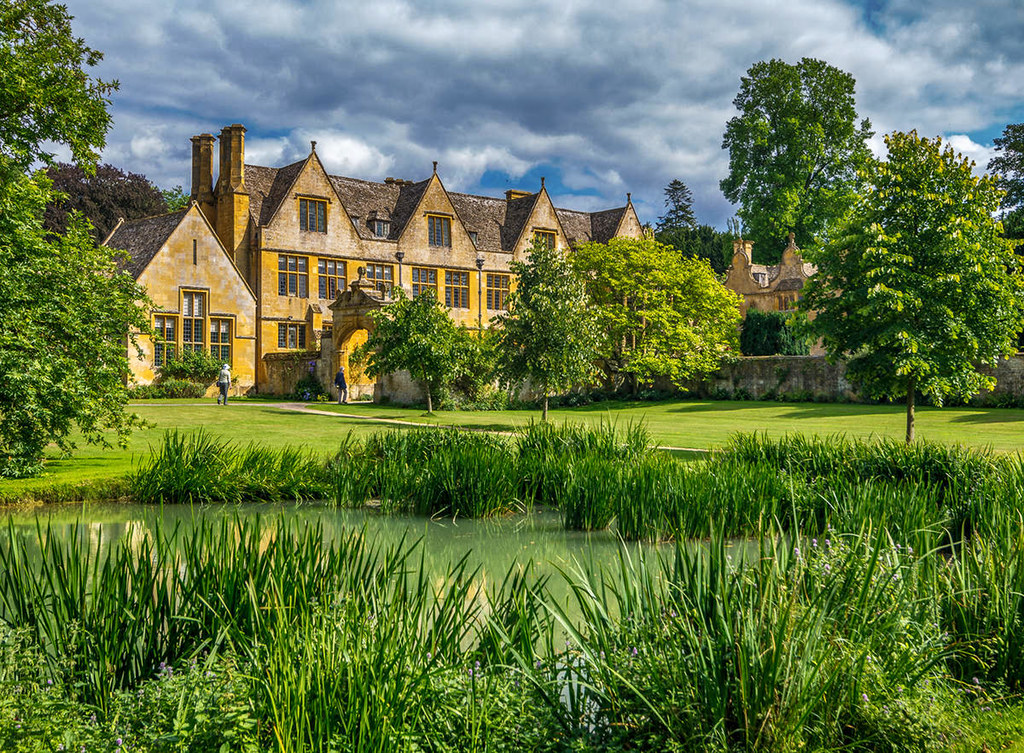




Stanway House is a Jacobean manor house set in historic parkland with a recently installed fountain rising 300ft, making it the tallest gravity fountain in the world.
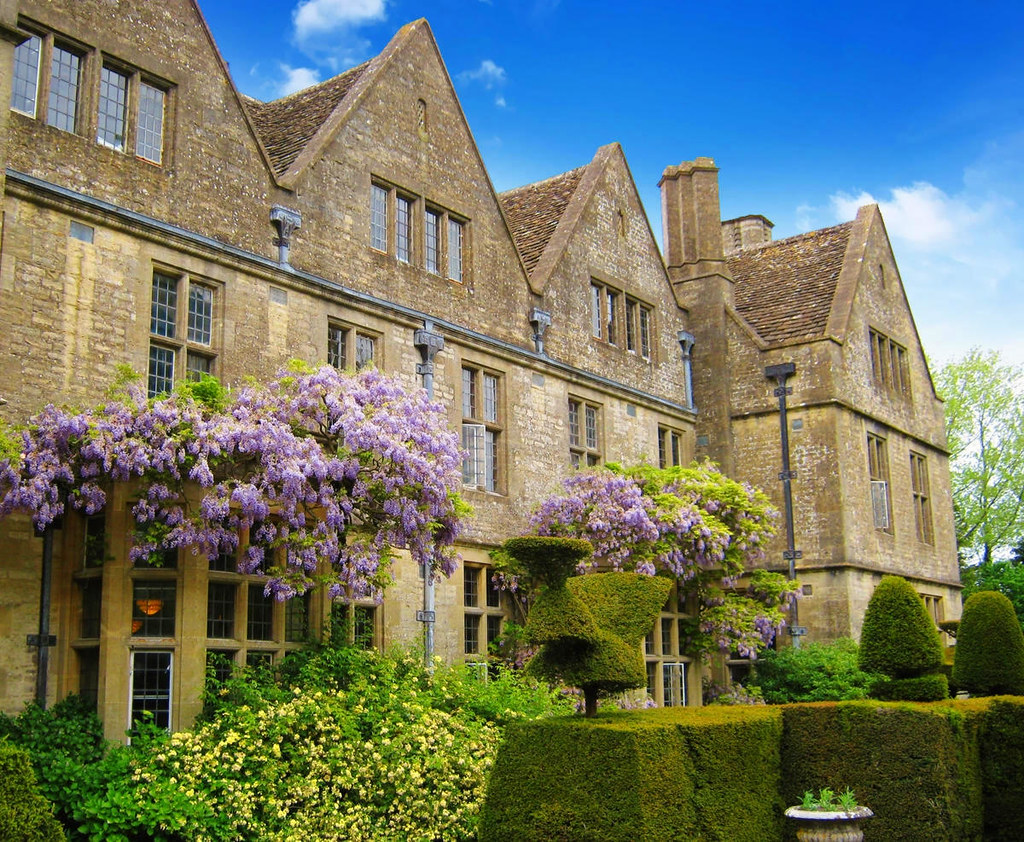

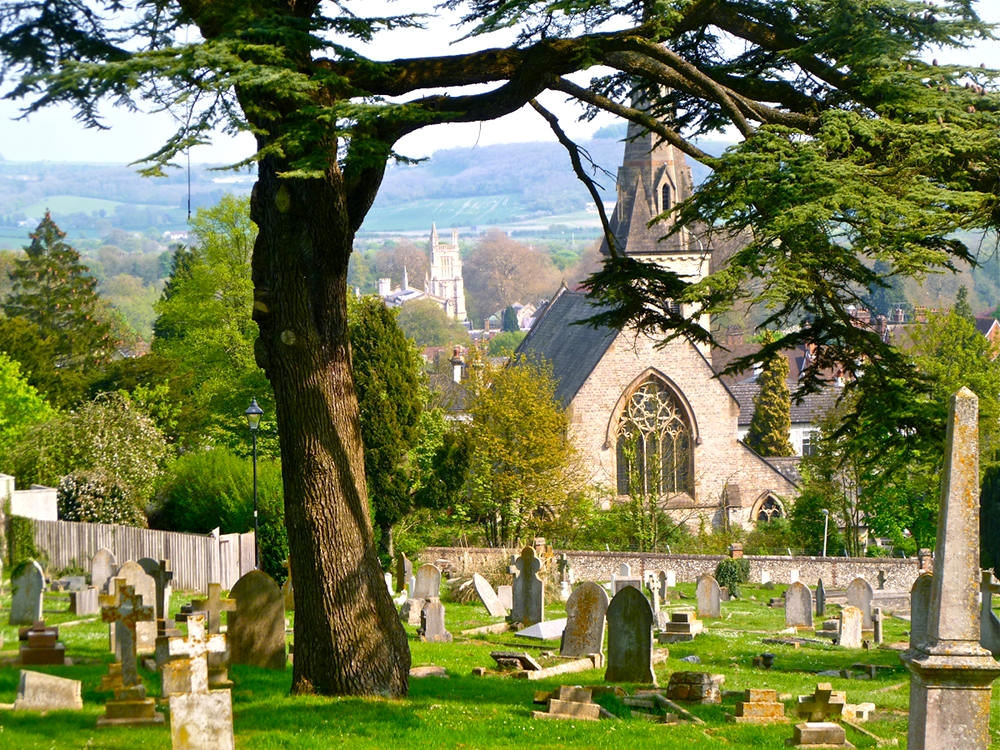
Churches and Abbeys
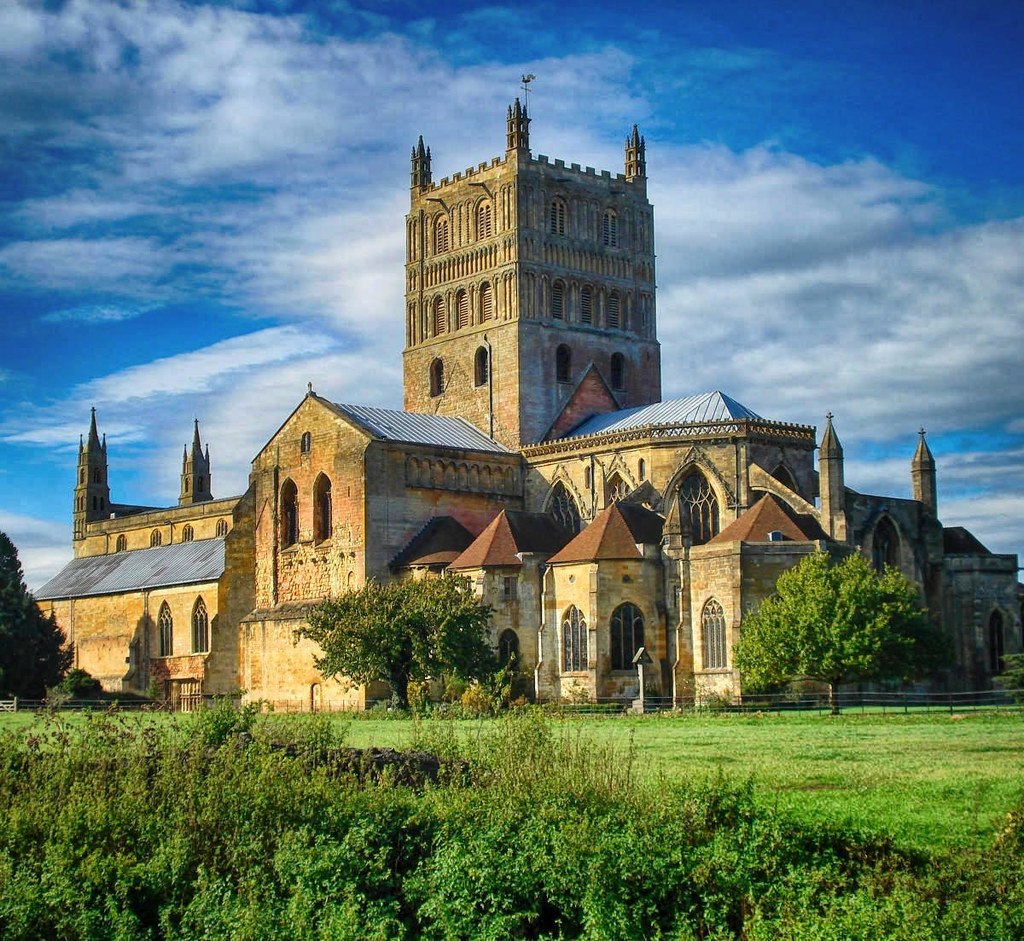
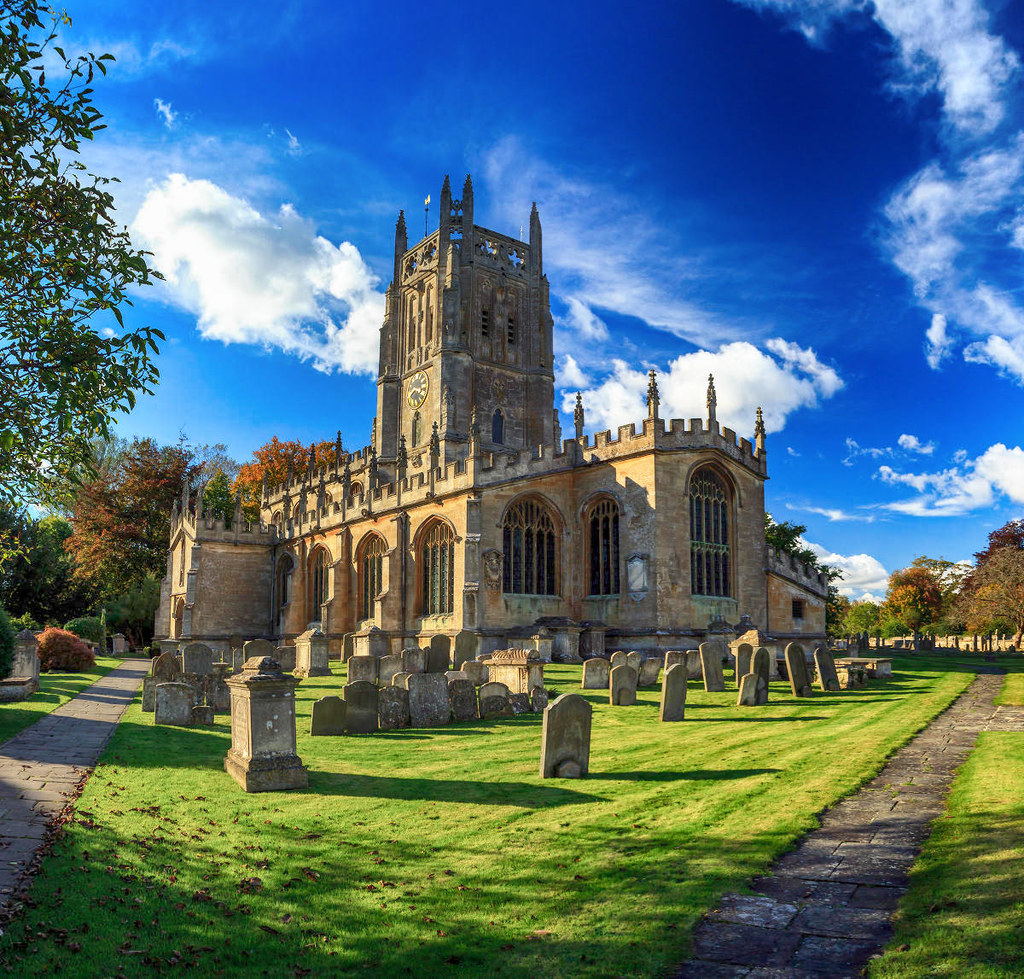
One of the finest examples of Norman architecture in Britain, Tewkesbury Abbey is also the second largest parish church in the country.
Formerly a Benedictine Monastery, it became one of the wealthiest abbeys of medieval England.
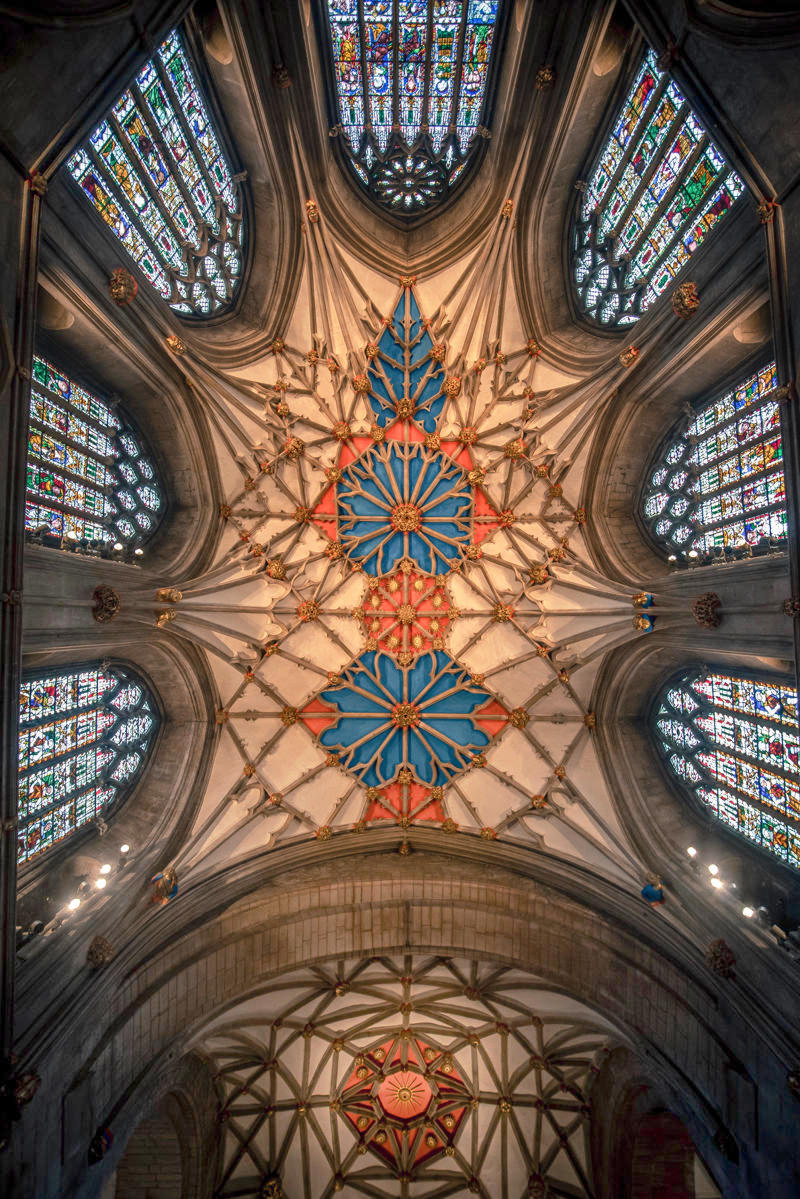


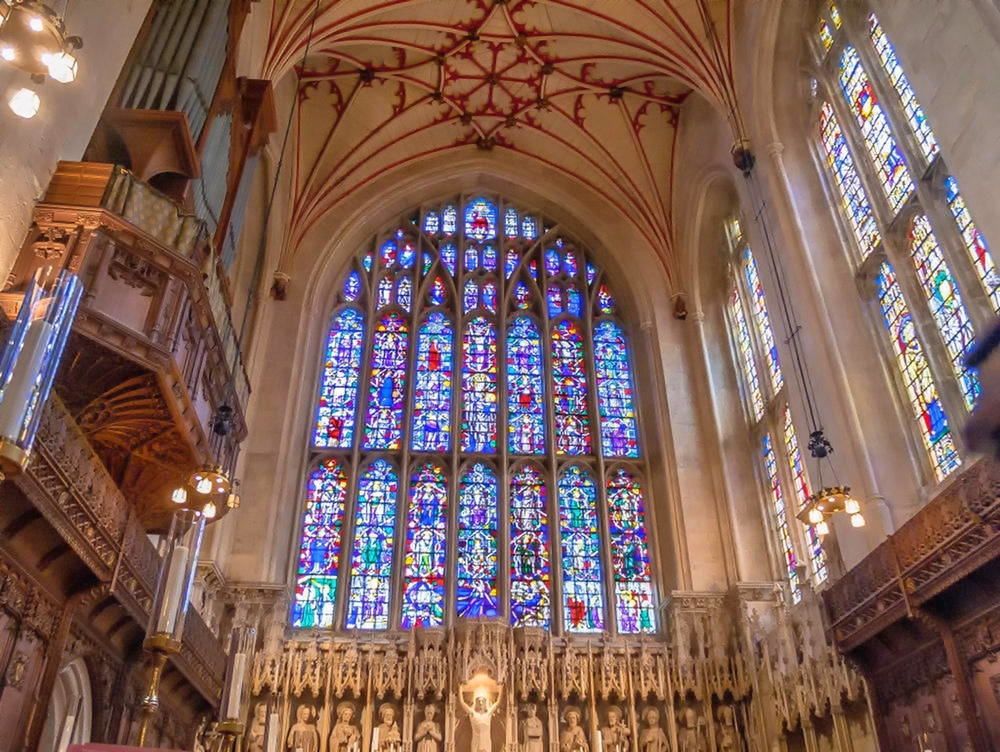
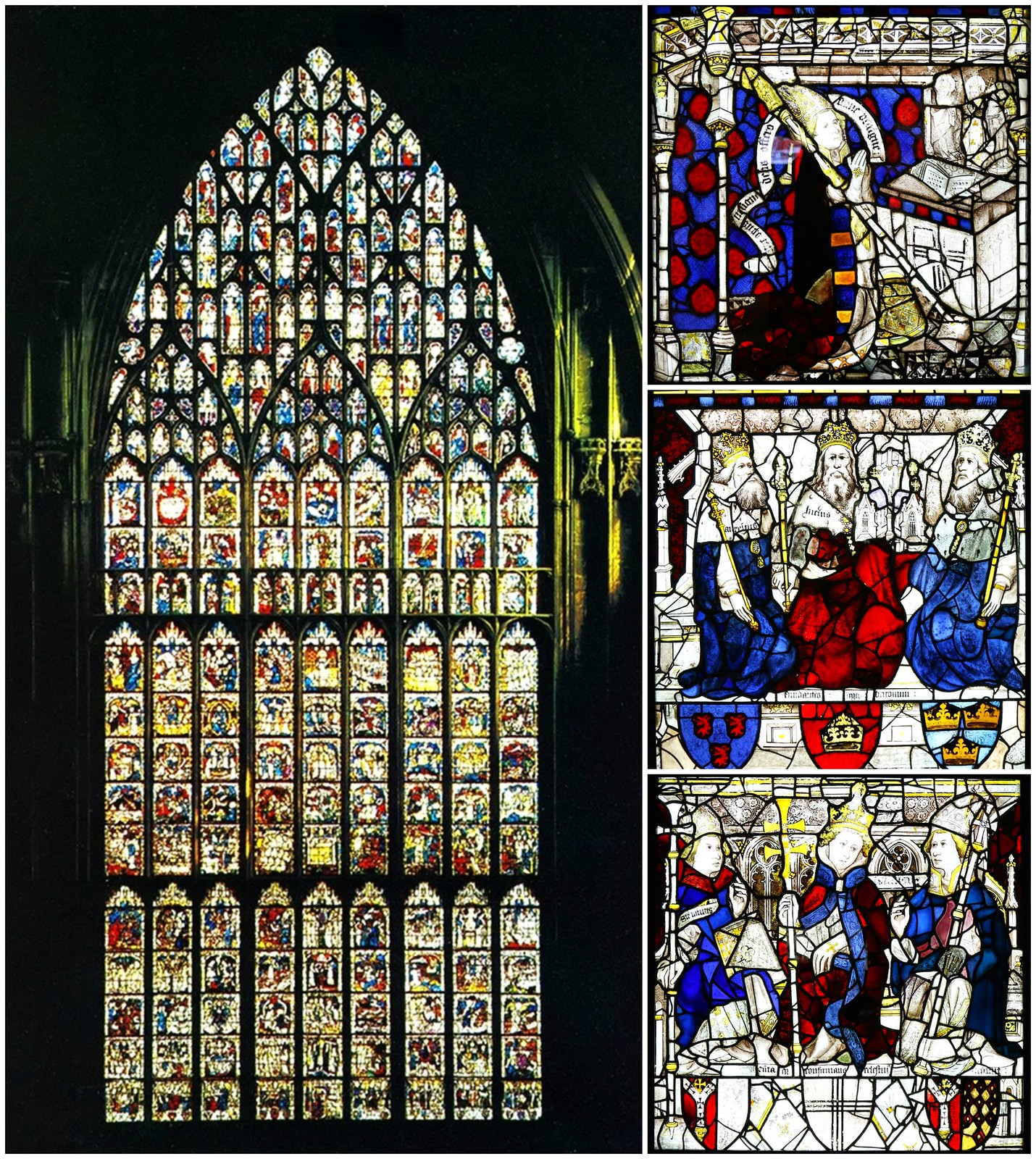
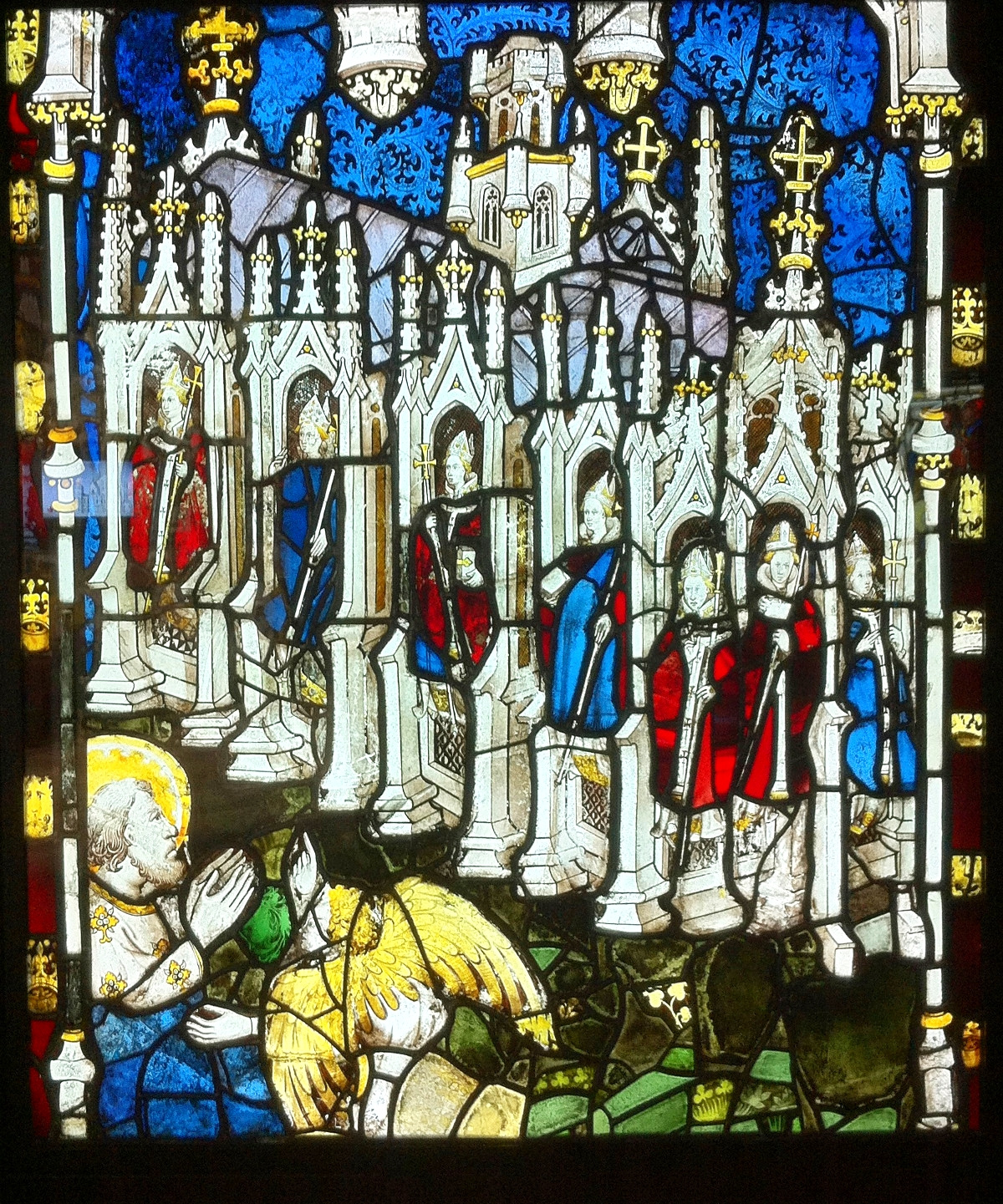
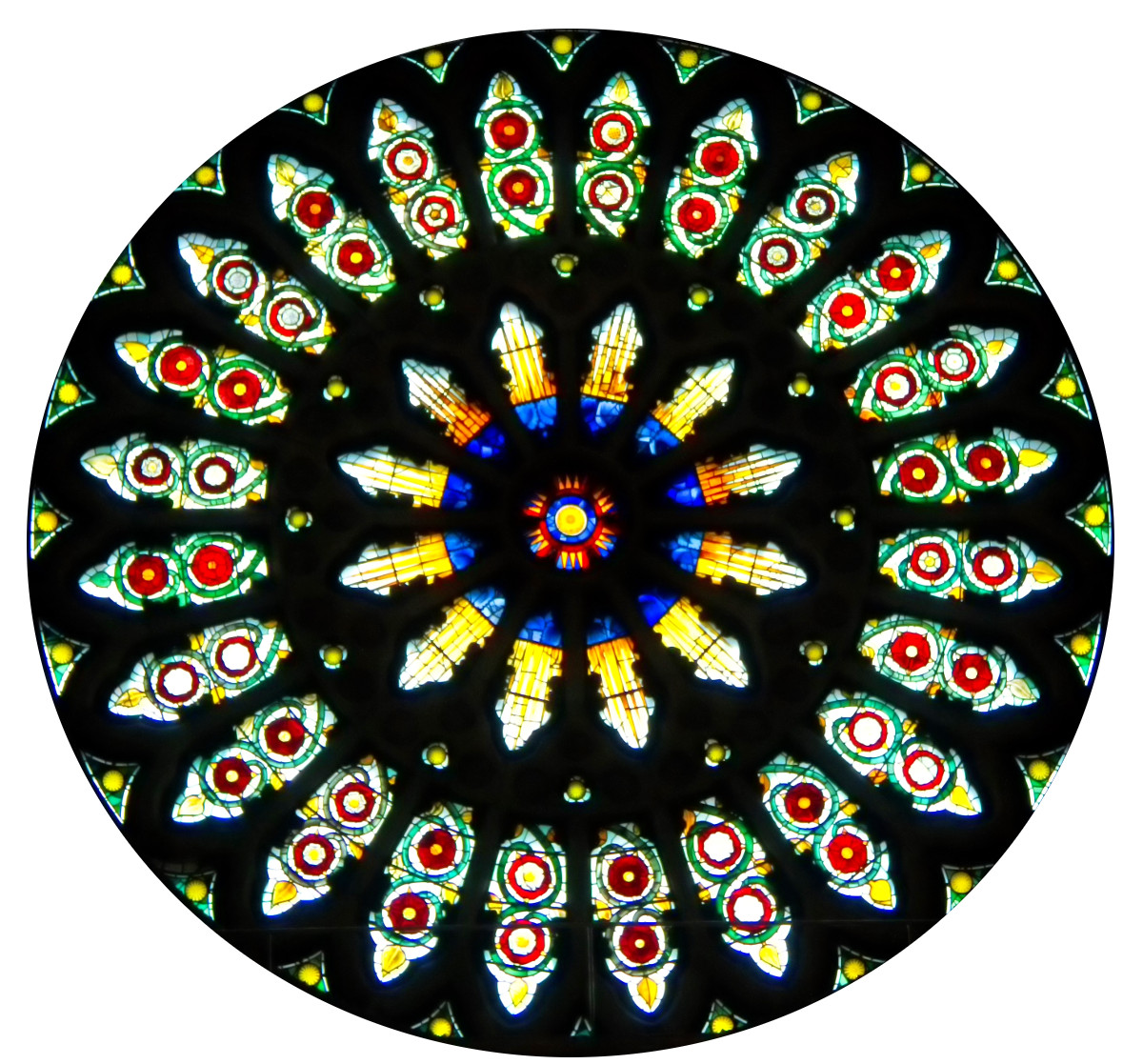
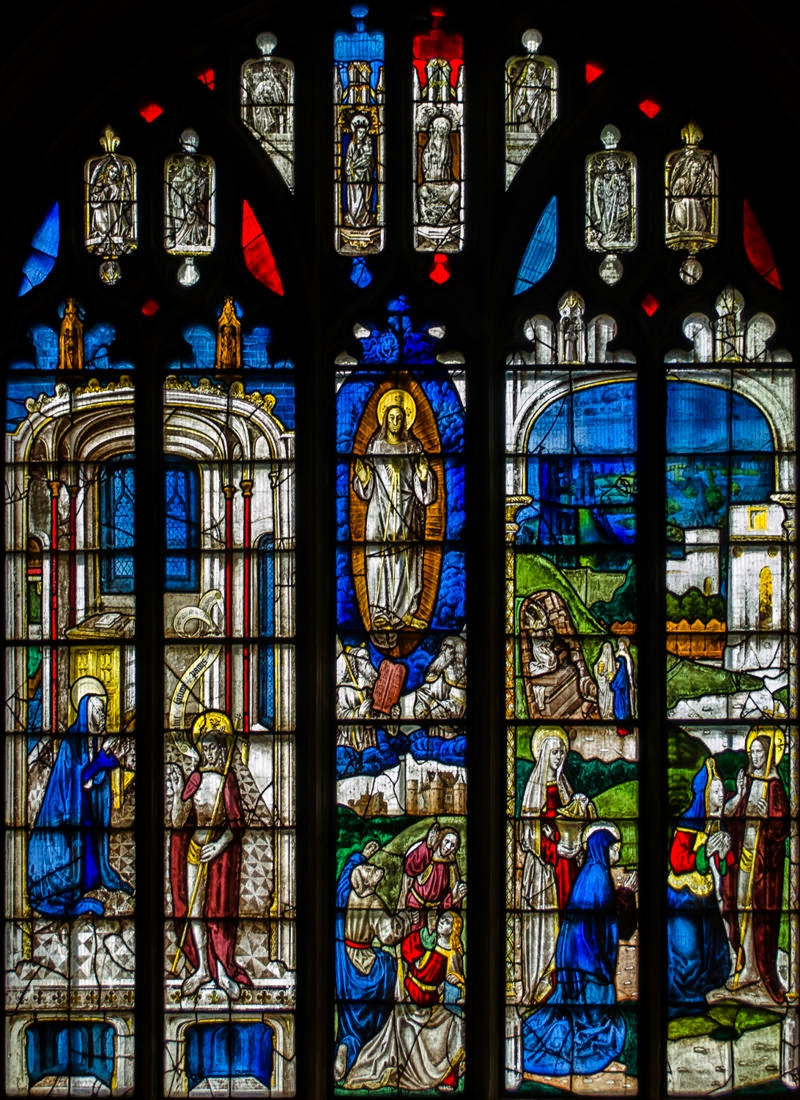
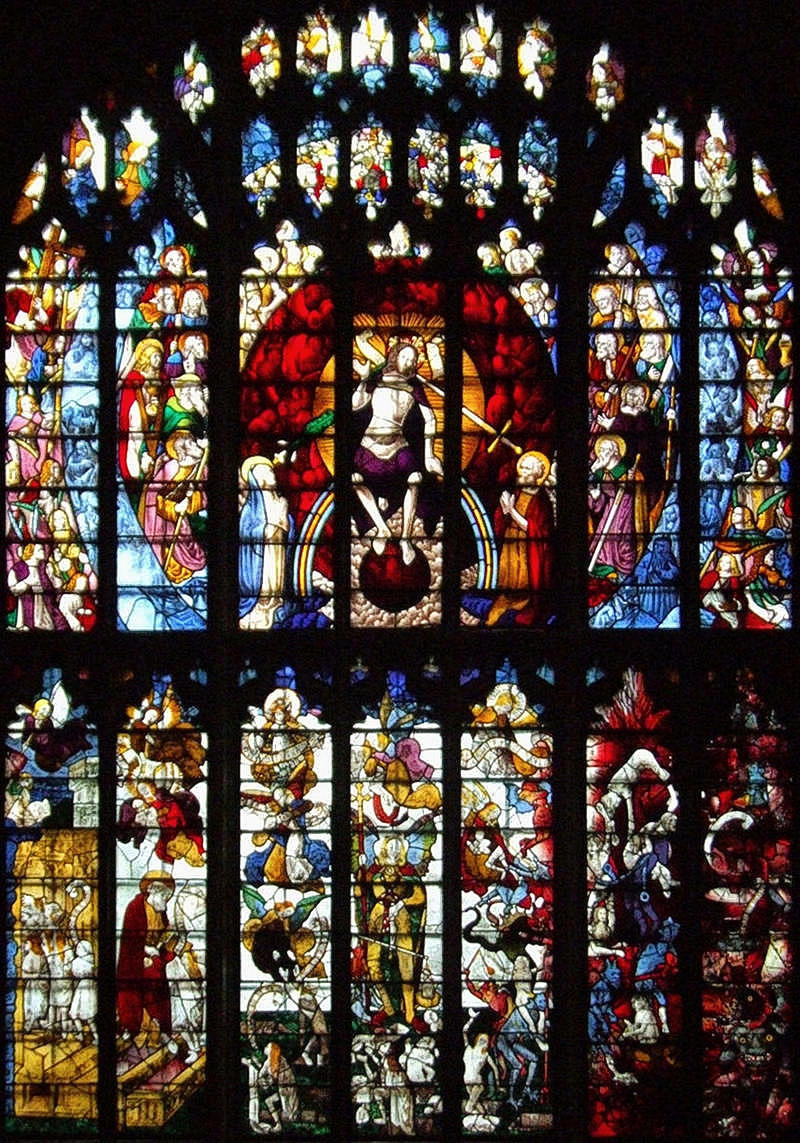
Housing the most complete set of medieval stained glass in Britain, the parish church of Saint Mary at Fairford is an example of late Perpendicular Gothic architecture characterised by slim stone window mullions and light but strong buttresses.

The style enabled larger windows than previously, allowing much more light into the building.


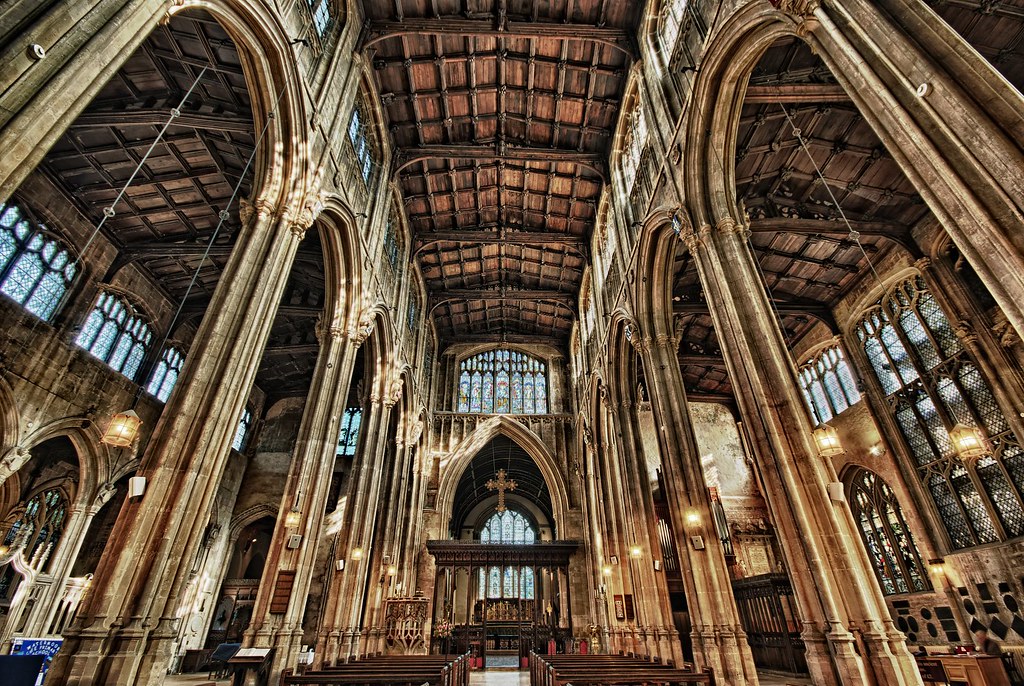
Known as the “Cathedral of the Cotswolds”, St John the Baptist parish church in Cirencester was financed by wealthy wool merchants.


Whether you visit for a day trip or a longer stay, you’re sure to fall in love with Gloucestershire again and again.